Abstract
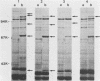
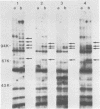
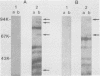
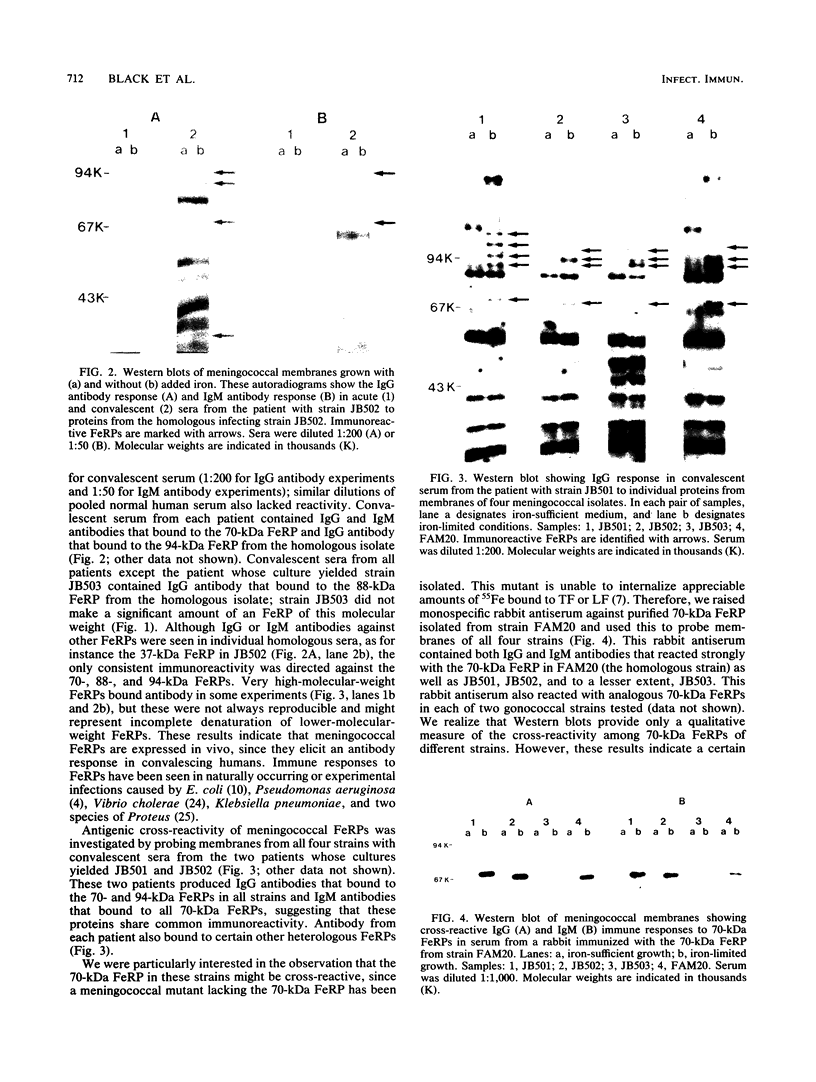
Neisseria meningitidis grown under iron-limiting conditions in vitro expresses additional iron-repressible outer membrane proteins (FeRPs). To see which FeRPs were expressed and immunogenic in human infection, we examined purified membranes from four meningococcal disease isolates with Western blotting of patient sera. Convalescent serum from each patient contained immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM antibodies against the homologous 70-kilodalton (kDa) FeRP and IgG antibody to the homologous 94-kDa FeRPs. Three other immunoreactive FeRPs were identified in two or more strains. Neither acute-phase sera nor pooled normal human sera contained appreciable levels of these antibodies. Antigenic cross-reactivity among FeRPs was suggested by the observation that the convalescent sera of two patients contained IgG antibodies reactive with the 70- and 94-kDa FeRPs and IgM antibodies reactive with the 70-kDa FeRPs from all four strains. Additionally, rabbit antiserum against the 70-kDa FeRP from one of these disease isolates contained IgG and IgM antibodies that reacted in Western blots with the 70-kDa FeRPs in all four strains. These results demonstrate that meningococcal FeRPs are expressed and immunogenic in vivo and that certain of these proteins are immunologically cross-reactive.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald F. S., DeVoe I. W. Iron acquisition by Neisseria meningitidis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):322–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.322-334.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brener D., DeVoe I. W., Holbein B. E. Increased virulence of Neisseria meningitidis after in vitro iron-limited growth at low pH. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.59-66.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1127–1138. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W. The meningococcus and mechanisms of pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):162–190. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.162-190.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Zollinger W. D., Poolman J. T. Serotype antigens of Neisseria meningitidis and a proposed scheme for designation of serotypes. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):504–510. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Brandt B. L., Broud D. D., Goroff D. K., Baker C. J. Immune response of infants and children to disseminated infections with Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):71–79. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Hantke K., Braun V. Iron transport of Escherichia coli K-12: involvement of the colicin B receptor and of a citrate-inducible protein. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1370–1375. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1370-1375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K. Regulation of ferric iron transport in Escherichia coli K12: isolation of a constitutive mutant. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):288–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00269672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E. Enhancement of Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice by addition of iron bound to transferrin. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):120–125. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.120-125.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh M. A., Earhart C. F. Coordinate regulation by iron of the synthesis of phenolate compounds and three outer membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):331–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.331-339.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from lactoferrin. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):915–920. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.915-920.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.555-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietzner T. A., Luginbuhl G. H., Sandstrom E., Morse S. A. Identification of an iron-regulated 37,000-dalton protein in the cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):410–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.410-416.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciortino C. V., Finkelstein R. A. Vibrio cholerae expresses iron-regulated outer membrane proteins in vivo. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):990–996. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.990-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand G. H., Anwar H., Kadurugamuwa J., Brown M. R., Silverman S. H., Melling J. In vivo evidence that bacteria in urinary tract infection grow under iron-restricted conditions. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):35–39. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.35-39.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Brener D., DeVoe I. W. Expression of a high-affinity mechanism for acquisition of transferrin iron by Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.107-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Role of iron in host-parasite interactions. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):401–410. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Response of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to iron limitation: alterations in expression of membrane proteins without apparent siderophore production. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):388–394. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.388-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H., Warner P. J. ColV plasmid-mediated, colicin V-independent iron uptake system of invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):411–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.411-416.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Finkelstein R. A. Siderophore production by pathogenic Neisseria spp. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):600–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.600-608.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]