Abstract
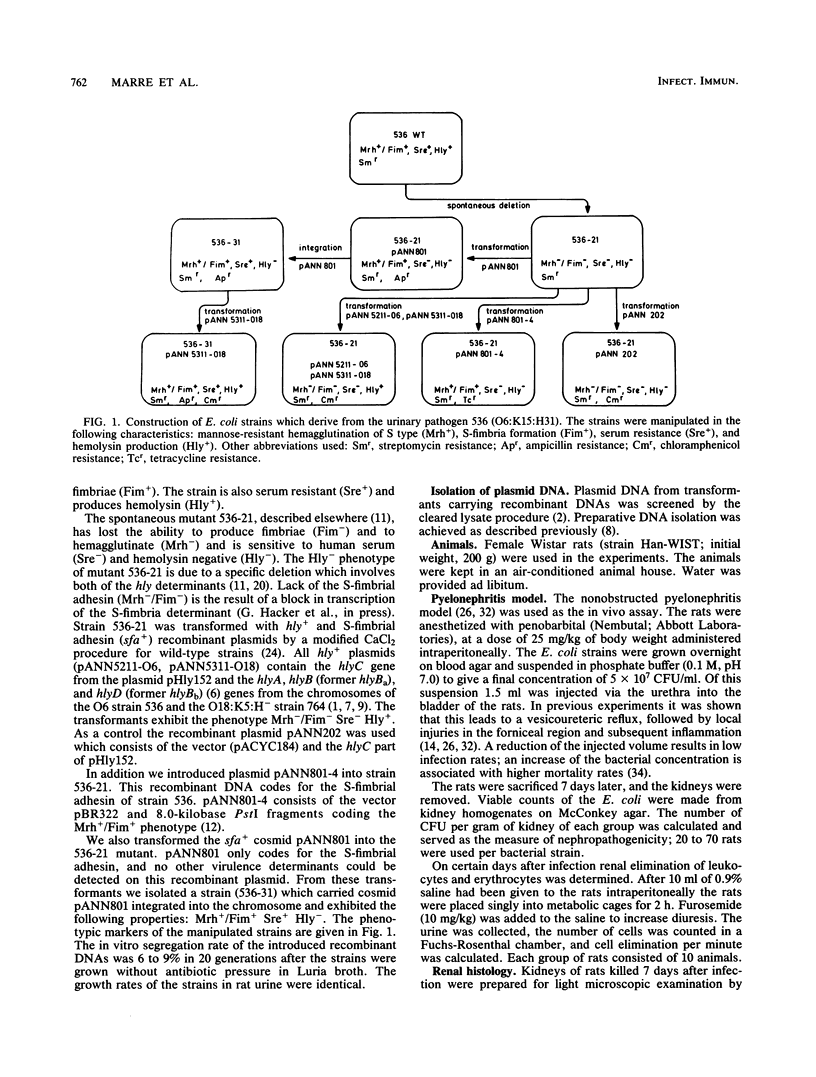
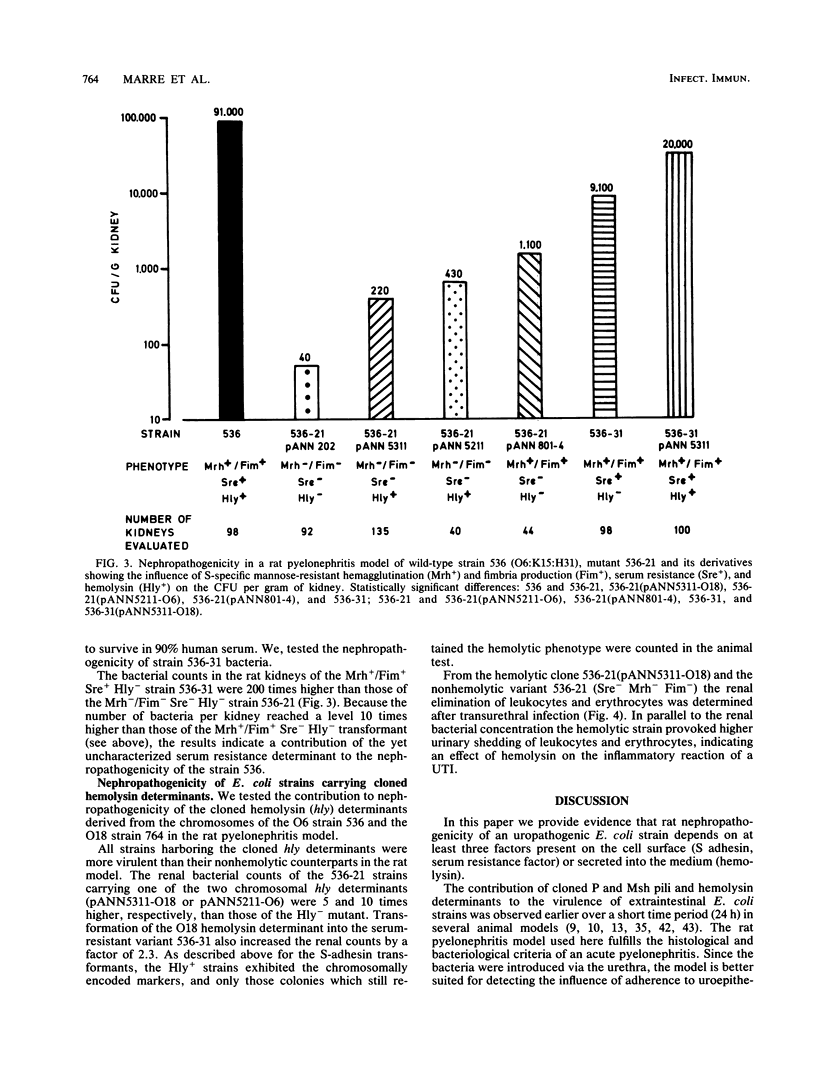
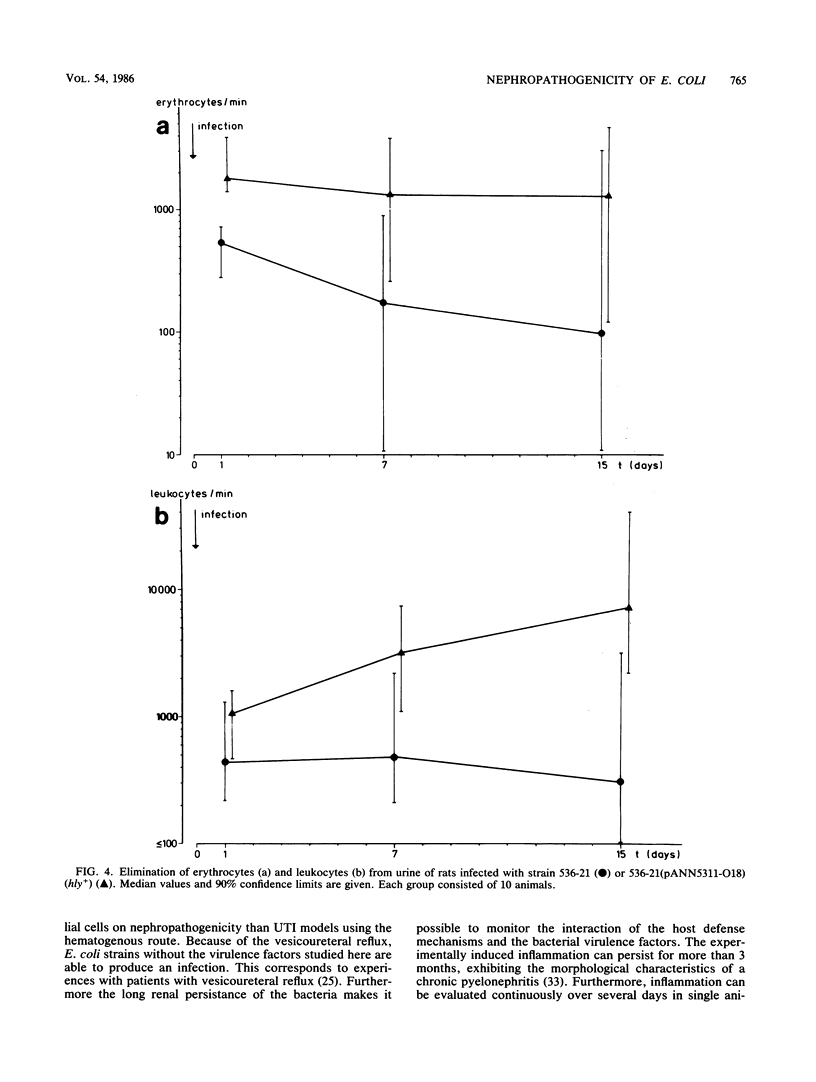
Escherichia coli 536 (O6:K15:H31), which was isolated from a case of urinary tract infection, determines high nephropathogenicity in a rat pyelonephritis system as measured by renal bacterial counts 7 days after infection. The loss of S fimbrial adhesin formation (Sfa-) (mannose-resistant hemagglutination [Mrh-] and fimbria production [Fim-]), serum resistance (Sre-), and hemolysin production (Hly-) in the mutant 536-21 led to a dramatic reduction of bacterial counts from almost 10(5) to only 40 cells per g of kidney. The reintroduction of the cloned S fimbrial adhesin determinant (sfa) increases the virulence of the avirulent mutant strain by a factor of 20; almost the same effect was observed after restoration of serum resistance by integration of an sfa+ recombinant cosmid into the chromosome. Additional reintroduction of the Hly+ phenotype by transformation of two hly determinants increased the virulence of the strains. Hemolysin production determined increased renal elimination of leukocytes and erythrocytes. Thus all three determinants investigated, S fimbriae, serum resistance, and hemolysin, contribute to the multifactorial phenomenon of E. coli nephropathogenicity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger H., Hacker J., Juarez A., Hughes C., Goebel W. Cloning of the chromosomal determinants encoding hemolysin production and mannose-resistant hemagglutination in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1241–1247. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1241-1247.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri S. J., Snyder I. S. Effect of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin on human peripheral leukocyte viability in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):455–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.455-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden C. S., Eriksson B., Hanson L. A. Adhesion of Escherichia coli to human uroepithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):767–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.767-774.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Classification of pathogenic Escherichia coli according to serotype and the production of virulence factors, with special reference to colonization-factor antigens. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S692–S701. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel W., Hedgpeth J. Cloning and functional characterization of the plasmid-encoded hemolysin determinant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1290-1298.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Bennett P. M., Higginson S., Richmond M. H. Regional preference of insertion of Tn501 and Tn802 into RP1 and its derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):313–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00267624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPTINSTALL R. H. EXPERIMENTAL PYELONEPHRITIS. BACTERIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE ASCENDING ROUTE OF INFECTION IN THE RAT. Nephron. 1964;1:73–92. doi: 10.1159/000179321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Hughes C. Genetics of Escherichia coli hemolysin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:139–162. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Hughes C., Hof H., Goebel W. Cloned hemolysin genes from Escherichia coli that cause urinary tract infection determine different levels of toxicity in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.57-63.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Knapp S., Goebel W. Spontaneous deletions and flanking regions of the chromosomally inherited hemolysin determinant of an Escherichia coli O6 strain. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1145–1152. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1145-1152.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Schmidt G., Hughes C., Knapp S., Marget M., Goebel W. Cloning and characterization of genes involved in production of mannose-resistant, neuraminidase-susceptible (X) fimbriae from a uropathogenic O6:K15:H31 Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):434–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.434-440.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Falkow S., Freter R., Svanborg Edén C. Contribution of adhesion to bacterial persistence in the mouse urinary tract. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):265–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.265-272.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C., Hacker J., Roberts A., Goebel W. Hemolysin production as a virulence marker in symptomatic and asymptomatic urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):546–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.546-551.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Hacker J., Then I., Müller D., Goebel W. Multiple copies of hemolysin genes and associated sequences in the chromosomes of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1027-1033.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Valtonen M. V., Parkkinen J., Väisänen-Rhen V., Finne J., Orskov F., Orskov I., Svenson S. B., Mäkelä P. H. Serotypes, hemolysin production, and receptor recognition of Escherichia coli strains associated with neonatal sepsis and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):486–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.486-491.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Väisänen-Rhen V., Rhen M., Pere A., Parkkinen J., Finne J. Escherichia coli fimbriae recognizing sialyl galactosides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):762–766. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.762-766.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Scheffer J., Bremm K. D., Hacker J., Goebel W. Role of bacterial adherence and toxin production from Escherichia coli on leukotriene generation from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;77(1-2):118–120. doi: 10.1159/000233764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg E. M., Cohen S. N. Transformation of Salmonella typhimurium by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1072–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1072-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomberg H., Hellström M., Jodal U., Leffler H., Lincoln K., Svanborg Edén C. Virulence-associated traits in Escherichia coli causing first and recurrent episodes of urinary tract infection in children with or without vesicoureteral reflux. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):561–569. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marre R., Schulz E., Freiesleben H. Influence of R-plasmid mediated beta-lactamase production on the therapeutic efficacy of cefoxitin and cefamandole in experimental chemotherapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6(5):633–638. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.5.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshew B. H., Jorgensen J., Counts G. W., Falkow S. Association of hemolysin production, hemagglutination of human erythrocytes, and virulence for chicken embryos of extraintestinal Escherichia coli isolates. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.50-54.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Lark D., Hull R., Norgren M., Båga M., O'Hanley P., Schoolnik G., Falkow S. Genetics of digalactoside-binding adhesin from a uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):942–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.942-949.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Finne J., Achtman M., Väisänen V., Korhonen T. K. Escherichia coli strains binding neuraminyl alpha 2-3 galactosides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):456–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. P., Phillips R. Bacteria causing symptomatic urinary tract infection or asymptomatic bacteriuria. J Clin Pathol. 1979 May;32(5):492–496. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.5.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. A., Kaack B., Källenius G., Möllby R., Winberg J., Svenson S. B. Receptors for pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli in primates. J Urol. 1984 Jan;131(1):163–168. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)50251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack K., Freiesleben H., Wöhrmann W., Henkel W., Commichau R. Experimenteller Beitrag zum Infektionsweg der coli-Pyelonephritis. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1972;355(4):323–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack K., Henkel W., Commichau R. Chronische interstitielle Nephritis (Coli-Pyelonephritis) im Tierexperiment. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1971;352(3):219–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00600672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz E., Marre R., Sack K., Herhahn D. Standardization of a model of E. coli-pyelonephritis in rats. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 Apr;256(4):490–496. doi: 10.1016/s0174-3031(84)80025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Huggins M. B. The toxic role of alpha-haemolysin in the pathogenesis of experimental Escherichia coli infection in mice. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Feb;131(2):395–403. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-2-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Bactericidal and bacteriolytic activity of serum against gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):46–83. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.46-83.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Norgren M., Båga M., Normark S. Adhesion to human cells by Escherichia coli lacking the major subunit of a digalactoside-specific pilus-adhesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1800–1804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Väisänen-Rhen V., Elo J., Väisänen E., Siitonen A., Orskov I., Orskov F., Svenson S. B., Mäkelä P. H., Korhonen T. K. P-fimbriated clones among uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):149–155. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.149-155.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner W., Vogel M., Goebel W. Transport of hemolysin across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli requires two functions. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):200–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.200-210.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Dellinger E. P., Minshew B., Falkow S. Haemolysin contributes to virulence of extra-intestinal E. coli infections. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):665–667. doi: 10.1038/294665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Falkow S. Characterization of Escherichia coli hemolysins conferring quantitative differences in virulence. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.156-160.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal O., Jann K., Himmelspach K. Chemistry and immunochemistry of bacterial lipopolysaccharides as cell wall antigens and endotoxins. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:9–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M. F., Nester E. W. Molecular characterization of a host-range-determining locus from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):244–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.244-250.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



