Abstract
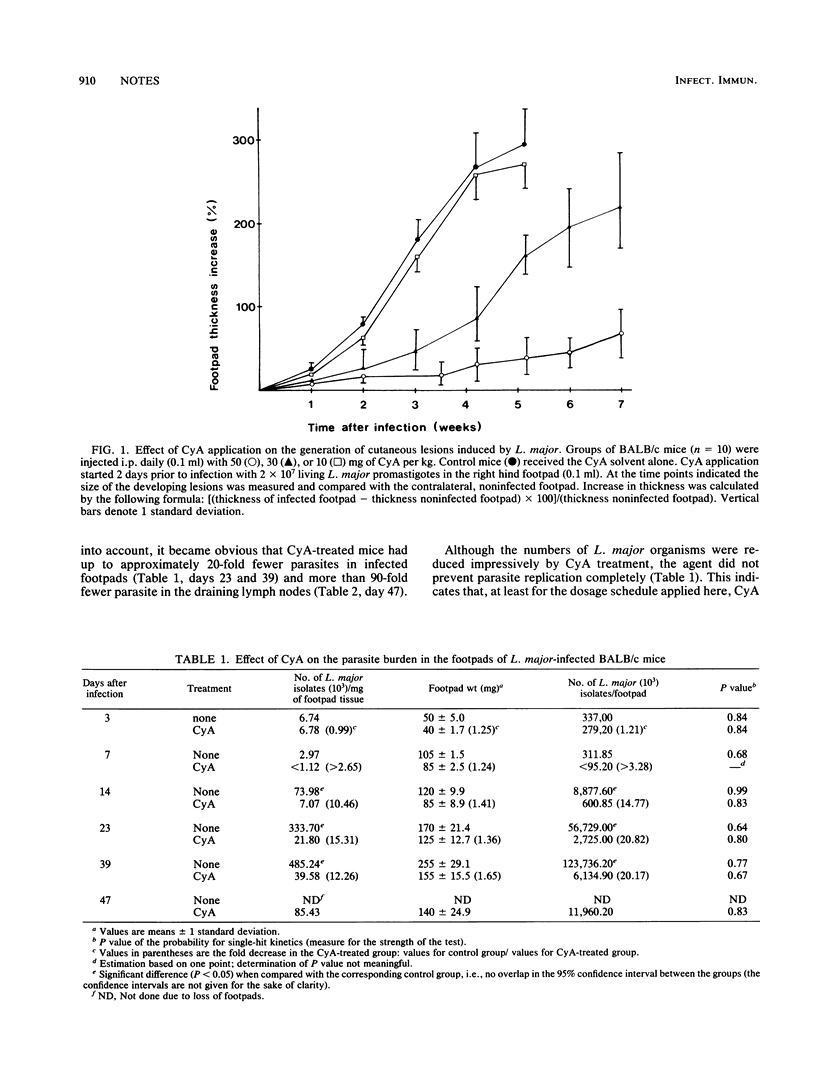
Treatment of Leishmania major-infected, genetically susceptible BALB/c mice with the T-lymphocyte-immunosuppressive drug cyclosporin A (CyA) resulted in a significantly reduced parasite burden in the local site of infection and in the draining lymph nodes. These data indicate that T cells are pivotal for the propagation of L. major in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryceson A. D., Bray R. S., Wolstencroft R. A., Dumonde D. C. Immunity in cutaneous leishmaniasis of the guinea-pig. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Sep;7(3):301–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunjes D., Hardt C., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Cyclosporin A mediates immunosuppression of primary cytotoxic T cell responses by impairing the release of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Aug;11(8):657–661. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Andrus L., Steinman R. M. Lymphokine and nonlymphokine mRNA levels in stimulated human T cells. Kinetics, mitogen requirements, and effects of cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):922–937. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Ceredig R., Mitchell G. F. Murine cutaneous leishmaniasis: disease patterns in intact and nude mice of various genotypes and examination of some differences between normal and infected macrophages. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1979 Feb;57(1):9–29. doi: 10.1038/icb.1979.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. III. Nature and significance of specific suppression of cell-mediated immunity in mice highly susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):594–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Nicklin S., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Prophylactic immunization against experimental leishmaniasis: I. Protection induced in mice genetically vulnerable to fatal Leishmania tropica infection. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2206–2212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. E., Remington J. S., Araujo F. G. In vivo and in vitro effects of cyclosporin A on Trypanosoma cruzi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Sep;34(5):861–865. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milon G., Lebastard M., Marchal G. T-dependent production and activation of mononuclear phagocytes during murine BCG infection. Immunol Lett. 1985;11(3-4):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Rothermel C. D. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by lymphokine-stimulated human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence that interferon-gamma is the activating lymphokine. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI111107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Fortier A. H., Meltzer M. S., Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Macrophage activation to kill Leishmania major: activation of macrophages for intracellular destruction of amastigotes can be induced by both recombinant interferon-gamma and non-interferon lymphokines. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3505–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickell S. P., Scheibel L. W., Cole G. A. Inhibition by cyclosporin A of rodent malaria in vivo and human malaria in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1093–1100. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1093-1100.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadick M. D., Locksley R. M., Tubbs C., Raff H. V. Murine cutaneous leishmaniasis: resistance correlates with the capacity to generate interferon-gamma in response to Leishmania antigens in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):655–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shidani B., Milon G., Marchal G., Truffa-Bachi P. Cyclosporin A inhibits the delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction: impaired production of early pro-inflammatory mediator(s). Eur J Immunol. 1984 Apr;14(4):314–318. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solbach W., Forberg K., Kammerer E., Bogdan C., Röllinghoff M. Suppressive effect of cyclosporin A on the development of Leishmania tropica-induced lesions in genetically susceptible BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss R., Heymer B., Hof H. Effects of cyclosporin A on experimental infection with Listeria monocytogenes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):491–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. W., Moon D. K., Geczy C. L., Nelson D. S. Cyclosporin A inhibits lymphokine production but not the responses of macrophages to lymphokines. Immunology. 1983 Feb;48(2):291–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Lima G. C., Engers H. D., Louis J. A. Exacerbation of murine cutaneous leishmaniasis by adoptive transfer of parasite-specific helper T cell populations capable of mediating Leishmania major-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1594–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Marchand M., Boon T., Louis J. A. A limiting dilution assay for quantifying Leishmania major in tissues of infected mice. Parasite Immunol. 1985 Sep;7(5):545–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1985.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



