Abstract
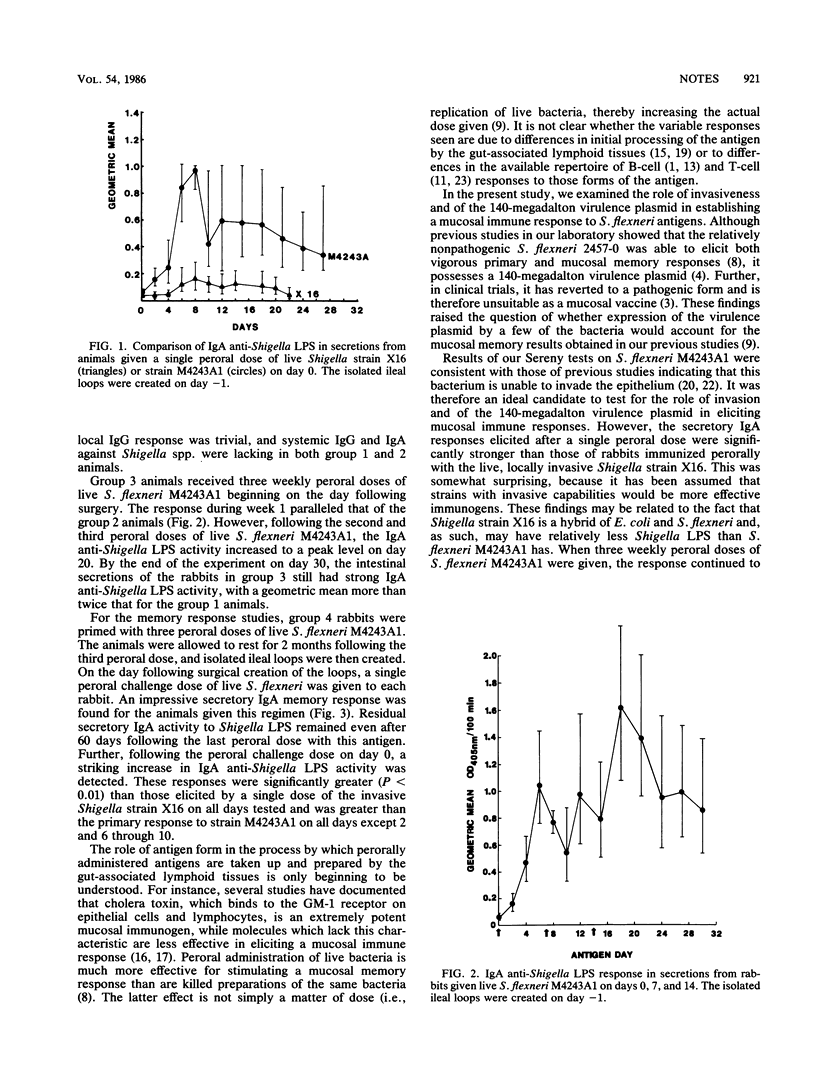
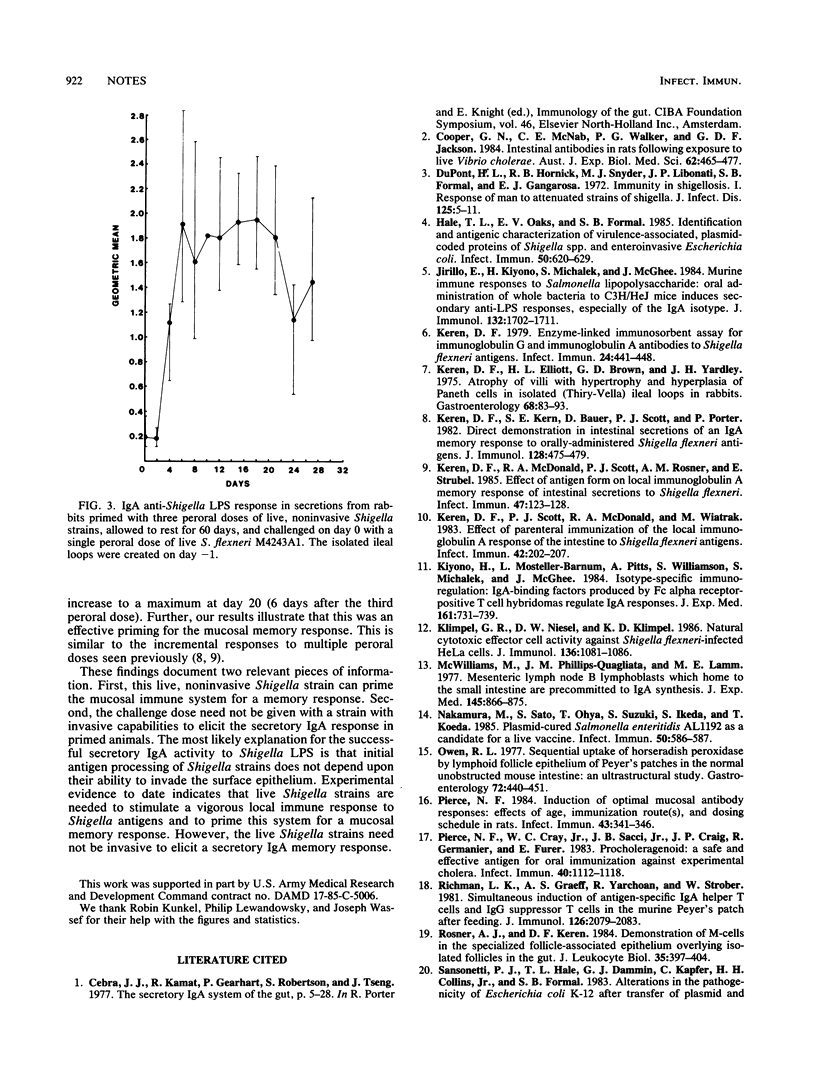
This study evaluates the ability of noninvasive Shigella spp., lacking the 140-megadalton virulence plasmid, to elicit a mucosal immunoglobulin A immune response in the intestine. For these studies, we used Shigella flexneri M4243A1 (which lacks the plasmid and is Sereny test negative) to prime and challenge three groups of rabbits perorally. Both primary and immunoglobulin A memory responses were detectable in these secretions. These findings indicate that a mucosal memory response can be primed by nonpathogenic strains of Shigella which lack the virulence plasmid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper G. N., McNab C. E., Walker P. G., Jackson G. D. Intestinal antibodies in rats following exposure to live Vibrio cholerae. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1984 Aug;62(Pt 4):465–477. doi: 10.1038/icb.1984.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Formal S. B., Gangarosa E. J. Immunity in shigellosis. I. Response of man to attenuated strains of Shigella. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jan;125(1):5–11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Oaks E. V., Formal S. B. Identification and antigenic characterization of virulence-associated, plasmid-coded proteins of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):620–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.620-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirillo E., Kiyono H., Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R. Murine immune responses to Salmonella lipopolysaccharide: oral administration of whole bacteria to C3H/HeJ mice induces secondary anti-LPS responses, especially of the IgA isotype. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1702–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Elliott H. L., Brown G. D., Yardley J. H. Atrophy of villi with hypertrophy and hyperplasia of Paneth cells in isolated (thiry-Vella) ileal loops in rabbits. Light-microscopic studies. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):83–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin A antibodies to Shigella flexneri antigens. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):441–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.441-448.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Kern S. E., Bauer D. H., Scott P. J., Porter P. Direct demonstration in intestinal secretions of an IgA memory response to orally administered Shigella flexneri antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):475–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., McDonald R. A., Scott P. J., Rosner A. M., Strubel E. Effect of antigen form on local immunoglobulin A memory response of intestinal secretions to Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):123–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.123-128.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Scott P. J., McDonald R. A., Wiatrak M. Effect of parenteral immunization on the local immunoglobulin A response of the intestine to Shigella flexneri antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):202–207. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.202-207.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., Mosteller-Barnum L. M., Pitts A. M., Williamson S. I., Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R. Isotype-specific immunoregulation. IgA-binding factors produced by Fc alpha receptor-positive T cell hybridomas regulate IgA responses. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):731–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Niesel D. W., Klimpel K. D. Natural cytotoxic effector cell activity against Shigella flexneri-infected HeLa cells. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1081–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWilliams M., Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Lamm M. E. Mesenteric lymph node B lymphoblasts which home to the small intestine are precommitted to IgA synthesis. J Exp Med. 1977 Apr 1;145(4):866–875. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.4.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Sato S., Ohya T., Suzuki S., Ikeda S., Koeda T. Plasmid-cured Salmonella enteritidis AL1192 as a candidate for a live vaccine. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):586–587. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.586-587.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L. Sequential uptake of horseradish peroxidase by lymphoid follicle epithelium of Peyer's patches in the normal unobstructed mouse intestine: an ultrastructural study. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Sacci J. B., Jr, Craig J. P., Germanier R., Fürer E. Procholeragenoid: a safe and effective antigen for oral immunization against experimental cholera. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1112-1118.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. Induction of optimal mucosal antibody responses: effects of age, immunization route(s), and dosing schedule in rats. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):341–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.341-346.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Graeff A. S., Yarchoan R., Strober W. Simultaneous induction of antigen-specific IgA helper T cells and IgG suppressor T cells in the murine Peyer's patch after protein feeding. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2079–2083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner A. J., Keren D. F. Demonstration of M cells in the specialized follicle-associated epithelium overlying isolated lymphoid follicles in the gut. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Apr;35(4):397–404. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.4.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Shigella sonnei plasmids: evidence that a large plasmid is necessary for virulence. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.75-83.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliabue A., Nencioni L., Villa L., Keren D. F., Lowell G. H., Boraschi D. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated antibacterial activity of intestinal lymphocytes with secretory IgA. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):184–186. doi: 10.1038/306184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



