Abstract
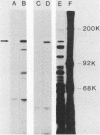
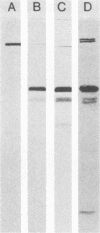
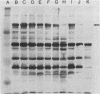
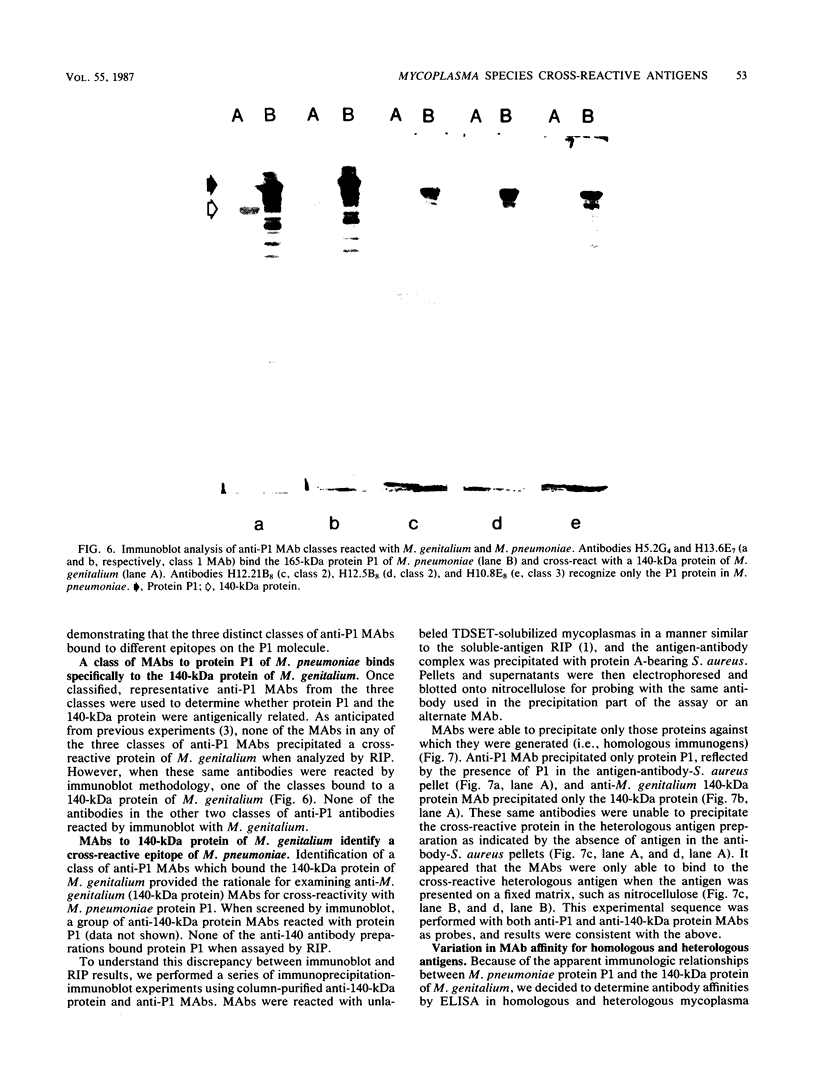
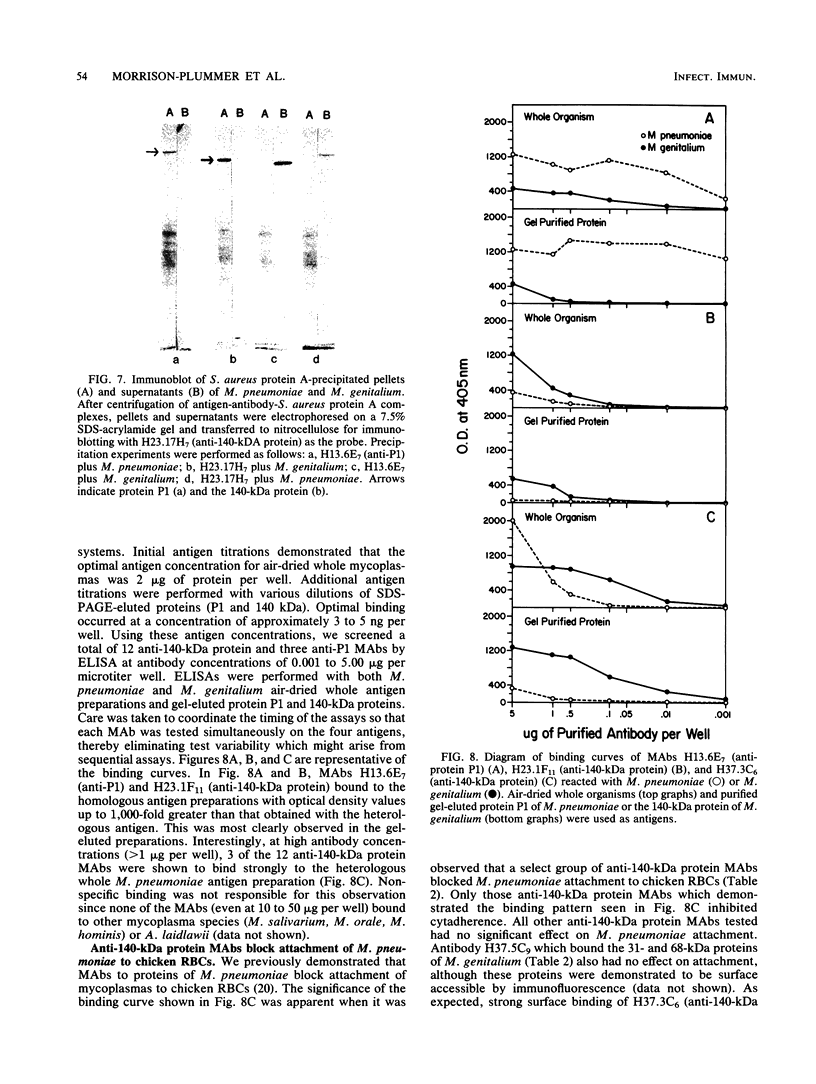
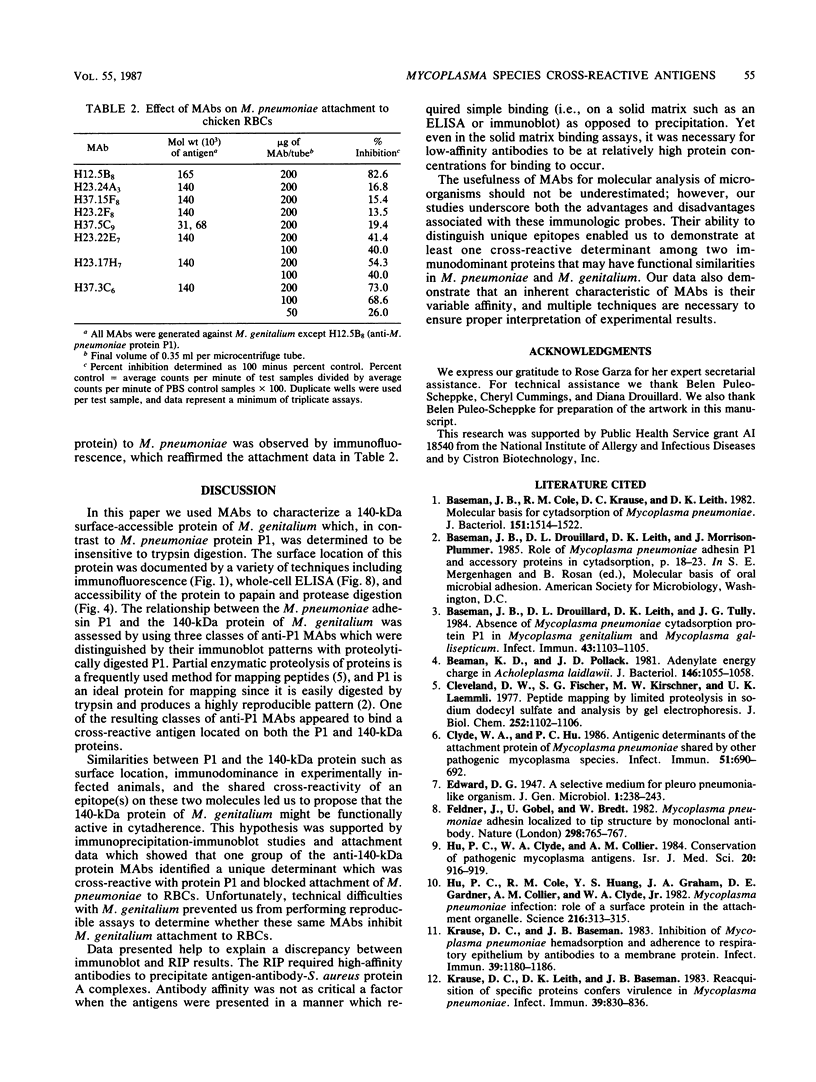
Previous serological data have demonstrated cross-reactive antigens between two pathogenic species of mycoplasmas, M. pneumoniae and M. genitalium. Preliminary analysis of sera and monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to protein antigens of these species showed an immunodominance of adhesin P1 (165 kilodaltons [kDa]) of M. pneumoniae in mice and hamsters and a 140-kDa protein of M. genitalium in mice and experimentally infected chimpanzees. To further characterize these two proteins, we assayed multiple anti-P1 and anti-140-kDa protein MAbs by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, immunoblot, and radioimmunoprecipitation techniques. The 140-kDa M. genitalium protein was shown to be surface accessible and insensitive to levels of trypsin which readily degrade protein P1. Peptide mapping was used to identify a unique class of MAbs which bound a cross-reactive molecule common to both the major adhesin protein P1 of M. pneumoniae and the 140-kDa protein of M. genitalium. MAbs generated against both M. pneumoniae and M. genitalium which were reactive with this determinant blocked M. pneumoniae attachment to chicken erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Cole R. M., Krause D. C., Leith D. K. Molecular basis for cytadsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1514–1522. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1514-1522.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Drouillard D. L., Leith D. K., Tully J. G. Absence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadsorption protein P1 in Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1103–1105. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1103-1105.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman K. D., Pollack J. D. Adenylate energy charge in Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1055–1058. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1055-1058.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyde W. A., Jr, Hu P. C. Antigenic determinants of the attachment protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae shared by other pathogenic Mycoplasma species. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):690–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.690-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldner J., Göbel U., Bredt W. Mycoplasma pneumoniae adhesin localized to tip structure by monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):765–767. doi: 10.1038/298765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Clyde W. A., Jr, Collier A. M. Conservation of pathogenic mycoplasma antigens. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Oct;20(10):916–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Cole R. M., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: role of a surface protein in the attachment organelle. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.6801766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Baseman J. B. Inhibition of mycoplasma pneumoniae hemadsorption and adherence to respiratory epithelium by antibodies to a membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1180–1186. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1180-1186.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Baseman J. B. Reacquisition of specific proteins confers virulence in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):830–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.830-836.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Identification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteins associated with hemadsorption and virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):809–817. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.809-817.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leith D. K., Trevino L. B., Tully J. G., Senterfit L. B., Baseman J. B. Host discrimination of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteinaceous immunogens. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):502–514. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Lindhardt B. O., Schütten H. J., Blom J., Christiansen C. Serological cross-reactions between Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1036-1043.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K. Serological cross-reactions between "Mycoplasma genitalium" and M. pneumoniae. Lancet. 1982 Nov 20;2(8308):1158–1159. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92809-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison-Plummer J., Jones D. H., Baseman J. B. An ELISA to detect monoclonal antibodies specific for lipid determinants of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 11;64(1-2):165–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison-Plummer J., Leith D. K., Baseman J. B. Biological effects of anti-lipid and anti-protein monoclonal antibodies on Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):398–403. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.398-403.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Taylor-Robinson D., Cole R. M., Rose D. L. A newly discovered mycoplasma in the human urogenital tract. Lancet. 1981 Jun 13;1(8233):1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92461-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Taylor-Robinson D., Rose D. L., Furr P. M., Graham C. E., Barile M. F. Urogenital challenge of primate species with Mycoplasma genitalium and characteristics of infection induced in chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1046–1054. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Whitcomb R. F., Clark H. F., Williamson D. L. Pathogenic mycoplasmas: cultivation and vertebrate pathogenicity of a new spiroplasma. Science. 1977 Mar 4;195(4281):892–894. doi: 10.1126/science.841314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]