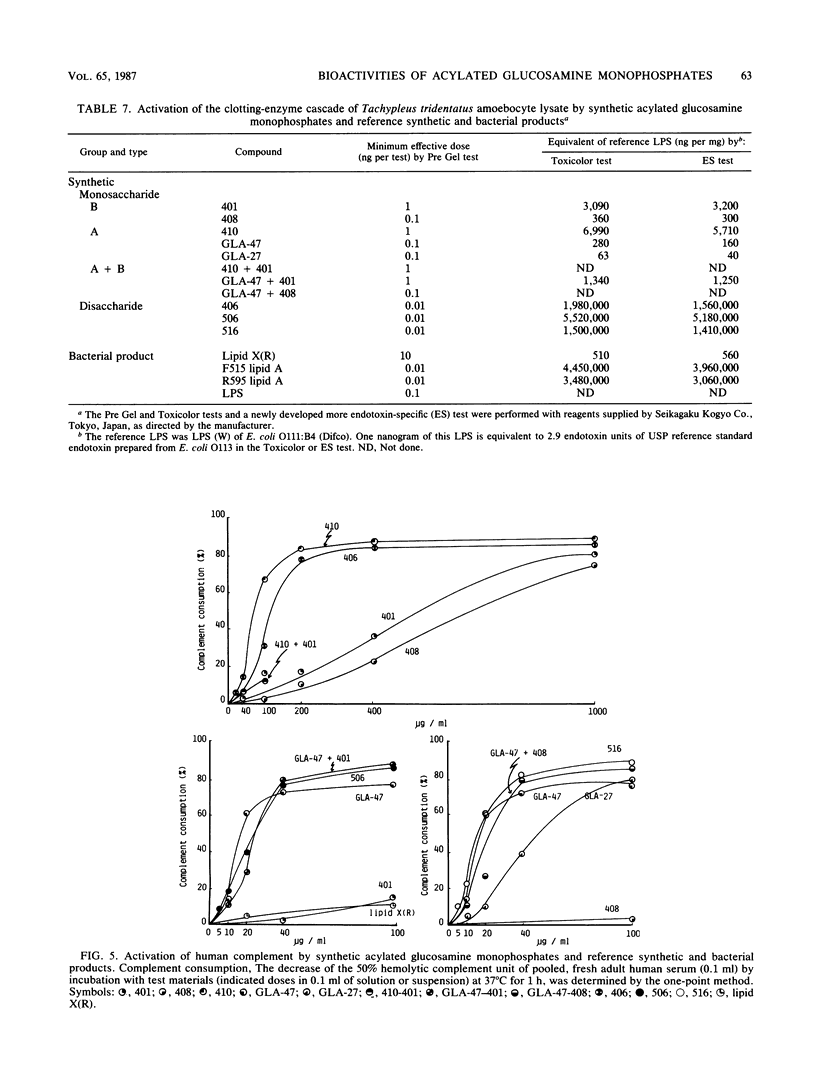
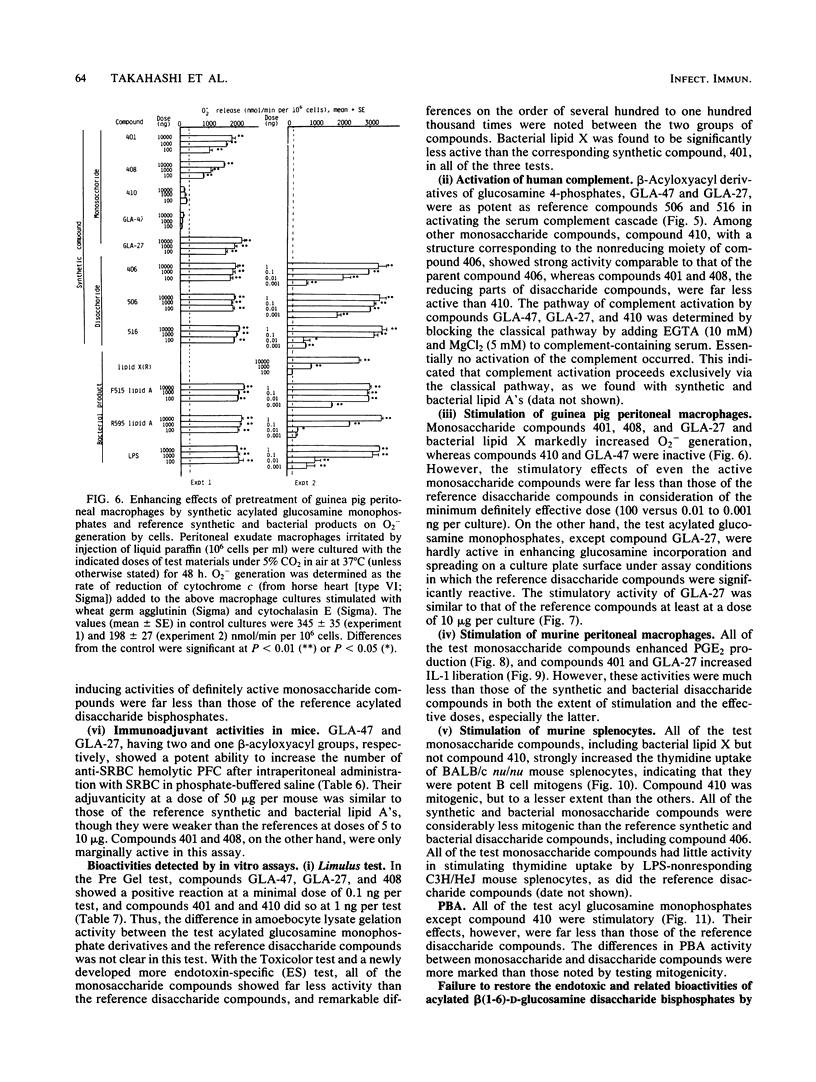
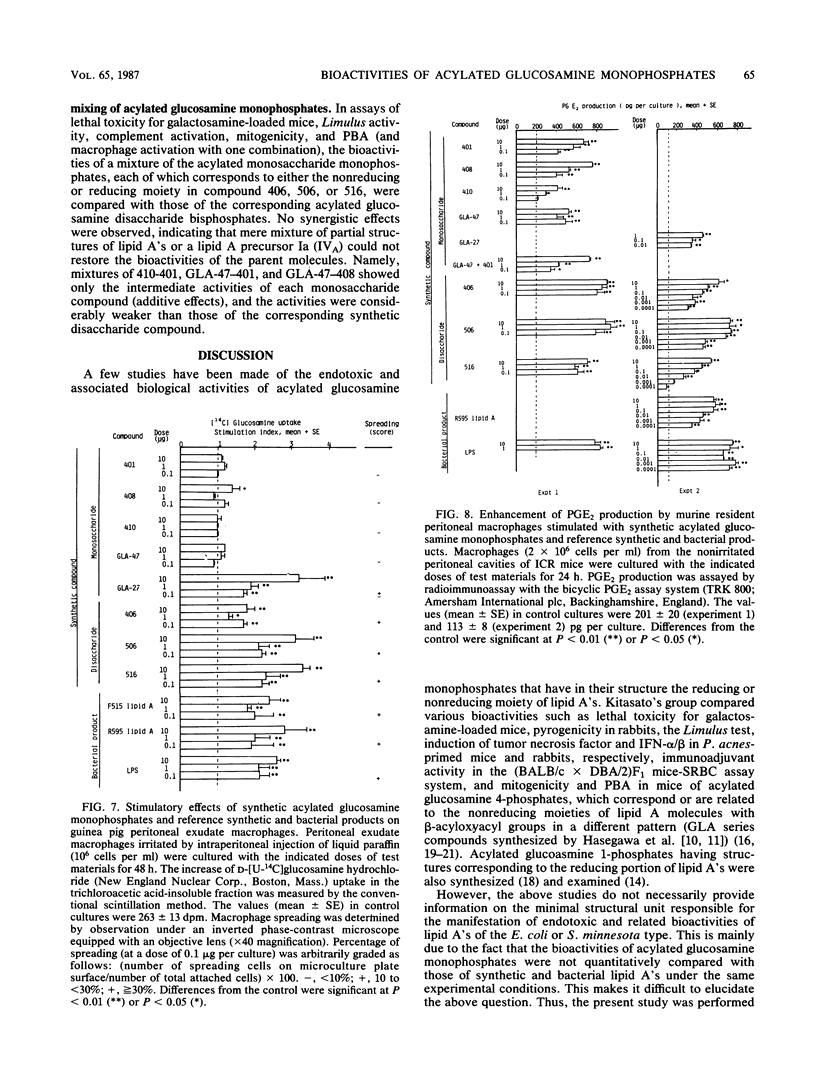
Abstract
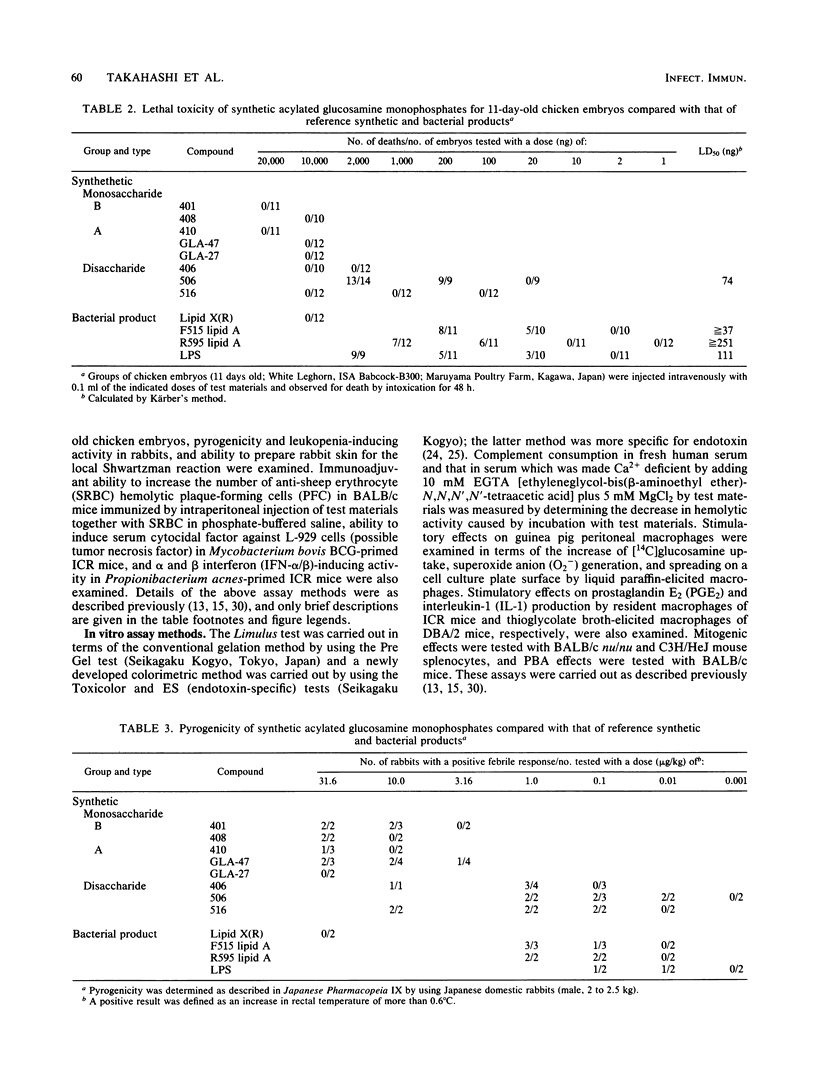
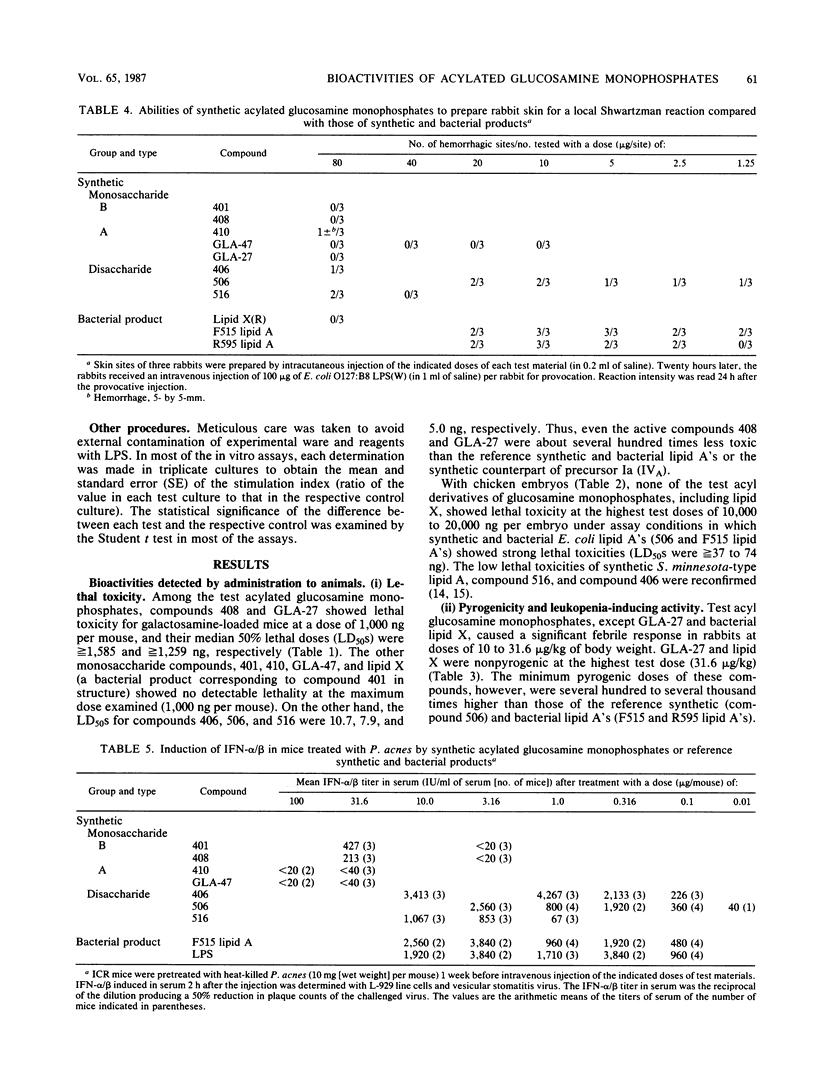
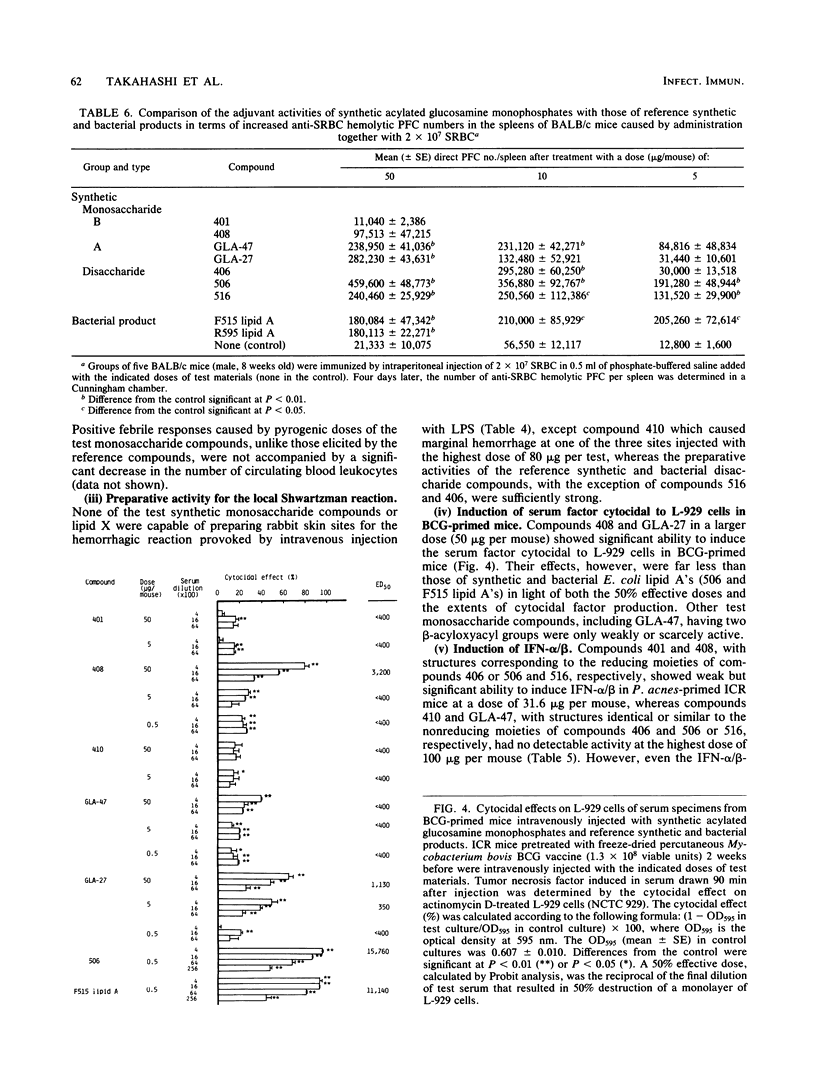
Several synthetic acylated glucosamine monophosphates, with structures corresponding to the nonreducing or reducing moiety of the lipid A of the Escherichia coli or Salmonella minnesota type, and a synthetic compound corresponding to a biosynthetic disaccharide lipid A precursor (designated Ia or IVA) were examined for their endotoxic and related bioactivities in comparison with those of the synthetic and bacterial parent molecules, i.e., acylated beta(1-6)-D-glucosamine disaccharide bisphosphates. Some of the test monosaccharide compounds were definitely active in most of the in vitro assays. Their activities, except for complement activation, however, were weaker than those of the reference compounds, synthetic and bacterial acylated disaccharide bisphosphates. The differences between the test monosaccharide and disaccharide compounds were much more apparent in in vivo assays, in which the test acylated glucosamine monophosphates were scarcely active, though some test compounds exhibited weak lethal toxicity in galactosamine-loaded mice and were weakly active in pyrogenicity, immunoadjuvant activity, and possible tumor necrosis factor and alpha and beta interferon-inducing ability in Mycobacterium bovis BCG- and Propionibacterium acnes-primed mice, respectively. Mixture at an equimolar ratio of acyl glucosamine monophosphates, each of which has the structure of the reducing or nonreducing moiety of the reference disaccharide compound, did not restore the endotoxic or associated bioactivities of the corresponding parent molecules. No essential differences in bioactivity were noted between synthetic and bacterial monosaccharide compounds, i.e., lipid X, whose structure corresponds to the reducing moiety of E. coli-type lipid A.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano F., Nishijima M., Akagawa K., Akamatsu Y. Enhancement of O2- generation and tumoricidal activity of murine macrophages by a monosaccharide precursor of Escherichia coli lipid A. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 18;192(2):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T., Westphal O., Brade H., Brade L., Freudenberg M., Schade U., Imoto M., Yoshimura H. Synthetic and natural Escherichia coli free lipid A express identical endotoxic activities. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen-Hagge T., Lehmann V., Seydel U., Lindner B., Zähringer U. Isolation and structural analysis of two lipid A precursors from a KDO deficient mutant of Salmonella typhimurium differing in their hexadecanoic acid content. Arch Microbiol. 1985 May;141(4):353–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00428849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Matsuura M., Kanegasaki S., Kawakubo Y., Kojima Y., Shibukawa N., Kumazawa Y., Yamamoto A., Tanamoto K., Yasuda T. Structural requirements of lipid A responsible for the functions: a study with chemically synthesized lipid A and its analogues. J Biochem. 1985 Aug;98(2):395–406. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegasaki S., Kojima Y., Matsuura M., Homma J. Y., Yamamoto A., Kumazawa Y., Tanamoto K., Yasuda T., Tsumita T., Imoto M. Biological activities of analogues of lipid A based chemically on the revised structural model. Comparison of mediator-inducing, immunomodulating and endotoxic activities. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 3;143(2):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegasaki S., Tanamoto K., Yasuda T., Homma J. Y., Matsuura M., Nakatsuka M., Kumazawa Y., Yamamoto A., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Structure-activity relationship of lipid A: comparison of biological activities of natural and synthetic lipid A's with different fatty acid compositions. J Biochem. 1986 Apr;99(4):1203–1210. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Takahashi I., Ogawa T., Tsujimoto M., Shimauchi H., Ikeda T., Okamura H., Tamura T., Harada K. Immunobiological activities of synthetic lipid A analogs with low endotoxicity. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):673–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.673-682.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Harada K., Mori Y., Kawasaki A., Tanaka A., Nagao S., Tanaka S. Immunobiologically active lipid A analogs synthesized according to a revised structural model of natural lipid A. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):293–296. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.293-296.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Takahashi I., Ikeda T., Otsuka K., Shimauchi H., Kasai N., Mashimo J. Synthetic lipid A with endotoxic and related biological activities comparable to those of a natural lipid A from an Escherichia coli re-mutant. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):225–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.225-237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa Y., Matsuura M., Homma J. Y., Nakatsuru Y., Kiso M., Hasegawa A. B cell activation and adjuvant activities of chemically synthesized analogues of the nonreducing sugar moiety of lipid A. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Feb;15(2):199–201. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura M., Kojima Y., Homma J. Y., Kubota Y., Yamamoto A., Kiso M., Hasegawa A. Biological activities of chemically synthesized analogues of the nonreducing sugar moiety of lipid A. FEBS Lett. 1984 Feb 27;167(2):226–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura M., Kojima Y., Homma J. Y., Kumazawa Y., Yamamoto A., Kiso M., Hasegawa A. Effects of backbone structures and stereospecificities of lipid A-subunit analogues on their biological activities. J Biochem. 1986 May;99(5):1377–1384. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura M., Yamamoto A., Kojima Y., Homma J. Y., Kiso M., Hasegawa A. Biological activities of chemically synthesized partial structure analogues of lipid A. J Biochem. 1985 Nov;98(5):1229–1237. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima M., Amano F., Akamatsu Y., Akagawa K., Tokunaga T., Raetz C. R. Macrophage activation by monosaccharide precursors of Escherichia coli lipid A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):282–286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima M., Raetz C. R. Characterization of two membrane-associated glycolipids from an Escherichia coli mutant deficient in phosphatidylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10690–10696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T. Addition of perchloric acid to blood samples for colorimetric limulus test using chromogenic substrate: comparison with conventional procedures and clinical applications. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Sep;104(3):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T., Tamura H., Tanaka S., Ohki M., Takahashi S., Arai M., Masuda M., Kawai T. A new chromogenic endotoxin-specific assay using recombined limulus coagulation enzymes and its clinical applications. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Jun 30;149(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Mascagni P., Ribi E., Takayama K. Monophosphoryl lipid A obtained from lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella minnesota R595. Purification of the dimethyl derivative by high performance liquid chromatography and complete structural determination. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5271–5278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R., Purcell S., Takayama K. Molecular requirements for B-lymphocyte activation by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4624–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seydel U., Lindner B., Wollenweber H. W., Rietschel E. T. Structural studies on the lipid A component of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides by laser desorption mass spectrometry. Location of acyl groups at the lipid A backbone. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):505–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain S. M., Armitage I. M., Anderson L., Takayama K., Qureshi N., Raetz C. R. Location of polar substituents and fatty acyl chains on lipid A precursors from a 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid-deficient mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Studies by 1H, 13C, and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16089–16098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Kotani S., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Takahashi I., Harada K., Katsukawa C., Tanaka S., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Immunopharmacological activities of a synthetic counterpart of a biosynthetic lipid A precursor molecule and of its analogs. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):219–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.219-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Mascagni P., Anderson L., Raetz C. R. Glucosamine-derived phospholipids in Escherichia coli. Structure and chemical modification of a triacyl glucosamine 1-phosphate found in a phosphatidylglycerol-deficient mutant. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14245–14252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Mascagni P., Nashed M. A., Anderson L., Raetz C. R. Fatty acyl derivatives of glucosamine 1-phosphate in Escherichia coli and their relation to lipid A. Complete structure of A diacyl GlcN-1-P found in a phosphatidylglycerol-deficient mutant. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7379–7385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Raetz C. R., Ribi E., Peterson J., Cantrell J. L., Pearson F. C., Wiggins J., Johnson A. G. Influence of fine structure of lipid A on Limulus amebocyte lysate clotting and toxic activities. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):350–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.350-355.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




