Abstract
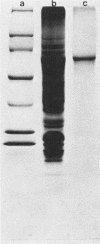
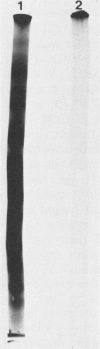
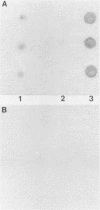
Purified preparations of adenylate cyclase were obtained from crude urea extracts of Bordetella pertussis by a one-step calmodulin affinity chromatography technique. Diluted extract was loaded onto the column and washed, and adenylate cyclase was eluted with 10mM EGTA [ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid]. A 104-fold purification was accomplished in one step. By sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the affinity-purified adenylate cyclase was dissociated into one major protein band with an apparent molecular weight of 60,000 and a minor band at 200,000. The affinity-purified adenylate cyclase was observed to have adenylate cyclase enzymatic activity which was activated by calmodulin, to bind 125I-calmodulin, and to be free of pertussis toxin as determined by in vivo and in vitro assays.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai H., Sato Y. Separation and characterization of two distinct hemagglutinins contained in purified leukocytosis-promoting factor from Bordetella pertussis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 22;444(3):765–782. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin R. K., Grab D. J., Siekevitz P. Function of a calmodulin in postsynaptic densities. III. Calmodulin-binding proteins of the postsynaptic density. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):449–455. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. D. The epidemiology of pertussis and pertussis immunization in the United Kingdom and the United States: a comparative study. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1984 Feb;14(2):1–78. doi: 10.1016/0045-9380(84)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody C. L., Baraff L. J., Cherry J. D., Marcy S. M., Manclark C. R. Nature and rates of adverse reactions associated with DTP and DT immunizations in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1981 Nov;68(5):650–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer D. L., Eaton J. W. Phagocyte impotence caused by an invasive bacterial adenylate cyclase. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.6287574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperstock M., Riegle L. Polymyxin B inactivation of lipopolysaccharide in vaccines of Gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):315–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.315-318.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando-Warnakulasuriya G. J., Eckerson M. L., Clark W. A., Wells M. A. Lipoprotein metabolism in the suckling rat: characterization of plasma and lymphatic lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1983 Dec;24(12):1626–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan S. D., Yost B. Calmodulin-binding proteins: visualization by 125I-calmodulin overlay on blots quenched with Tween 20 or bovine serum albumin and poly(ethylene oxide). Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):510–519. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Fiederlein R. L., Glasser L., Galgiani J. N. Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase: effects of affinity-purified adenylate cyclase on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.135-140.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman W. E., Klapper D. G., Baseman J. B. Detection, isolation, and analysis of a released Bordetella pertussis product toxic to cultured tracheal cells. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):782–794. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.782-794.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee D. V., Andreasen T. J., Storm D. R. Calcium-independent stimulation of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase by calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2759–2764. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes W. J., Greegor S. Carbohydrate compositions of normal, spontaneously transformed, and virally transformed cells derived from BALB/c mice. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 1):3905–3910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Farfel Z. Bordetella pertussis invasive adenylate cyclase. Partial resolution and properties of its cellular penetration. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5526–5532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Sauer K. T., Myers G. A., Cowell J. L., Guerrant R. L. Induction of a novel morphological response in Chinese hamster ovary cells by pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1198-1203.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E., Wolff J. Soluble adenylate cyclase from the culture medium of Bordetella pertussis: purification and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):890–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.890-898.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Moribayashi A., Yano I. Ornithine-containing lipid of Bordetella pertussis that carries hemagglutinating activity. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):907–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.907-910.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessin R. H., Franke J. Secreted adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis: calmodulin requirements and partial purification of two forms. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):290–296. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.290-296.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilhoffer M. C., Cook G. H., Wolff J. Calcium-independent activation of adenylate cyclase by calmodulin. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):11–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Anthrax toxin edema factor: a bacterial adenylate cyclase that increases cyclic AMP concentrations of eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3162–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Ross E. M., Alderslade R., Bellman M. H., Rawson N. S. Pertussis immunisation and serious acute neurological illness in children. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 May 16;282(6276):1595–1599. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6276.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Bergman R. K., Sadowski P. L. Biological activities of crystalline pertussigen from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. C. Pertussis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 Nov;54(6):427–469. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197511000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman M., Furman B. L., Wardlaw A. C. Bordetella pertussis respiratory tract infection in the mouse: pathophysiological responses. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):56–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman M. The concept of pertussis as a toxin-mediated disease. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;3(5):467–486. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser J., Stark G. R. Immunologic detection of specific proteins in cell extracts by fractionation in gels and transfer to paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:205–215. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Izumiya K., Sato H., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Role of antibody to leukocytosis-promoting factor hemagglutinin and to filamentous hemagglutinin in immunity to pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1223–1231. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1223-1231.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Kimura M., Fukumi H. Development of a pertussis component vaccine in Japan. Lancet. 1984 Jan 21;1(8369):122–126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R. D., Fish F., Manclark C. R., Meade B., Zhang Y. L. Pertussis toxin. Affinity purification of a new ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14647–14651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Tam S. W., Waisman D. M., Wang J. H. Differential interaction of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase isozymes with calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11102–11103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Wang T. H., Wirch E., Wang J. H. Purification and properties of bovine brain calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5916–5923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattuck R. L., Oldenburg D. J., Storm D. R. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase from Bordetella pertussis. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6356–6362. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Yajima M., Ase K., Ui M. A role of the B-oligomer moiety of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in development of the biological effects on intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6756–6761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi S., Sonoda S., Imagawa T., Kanoh M. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte-inhibitory factor of Bordetella pertussis. I. Extraction and partial purification of phagocytosis- and chemotaxis-inhibitory activities. Biken J. 1978 Dec;21(4):121–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A., Warren K. S. Selective primary health care: an interim strategy for disease control in developing countries. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 1;301(18):967–974. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911013011804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. C., Parton R. Bordetella pertussis toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1982;19(1):1–53. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(82)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Pertussis toxin and extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase as virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):219–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westcott K. R., La Porte D. C., Storm D. R. Resolution of adenylate cyclase sensitive and insensitive to Ca2+ and calcium-dependent regulatory protein (CDR) by CDR-sepharose affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):204–208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H., Goldhammer A. R., Berkowitz S. A. Calmodulin activates prokaryotic adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3841–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heyningen S. Bacterial toxins and cyclic AMP. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):782–782. doi: 10.1038/299782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]