Abstract
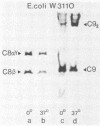
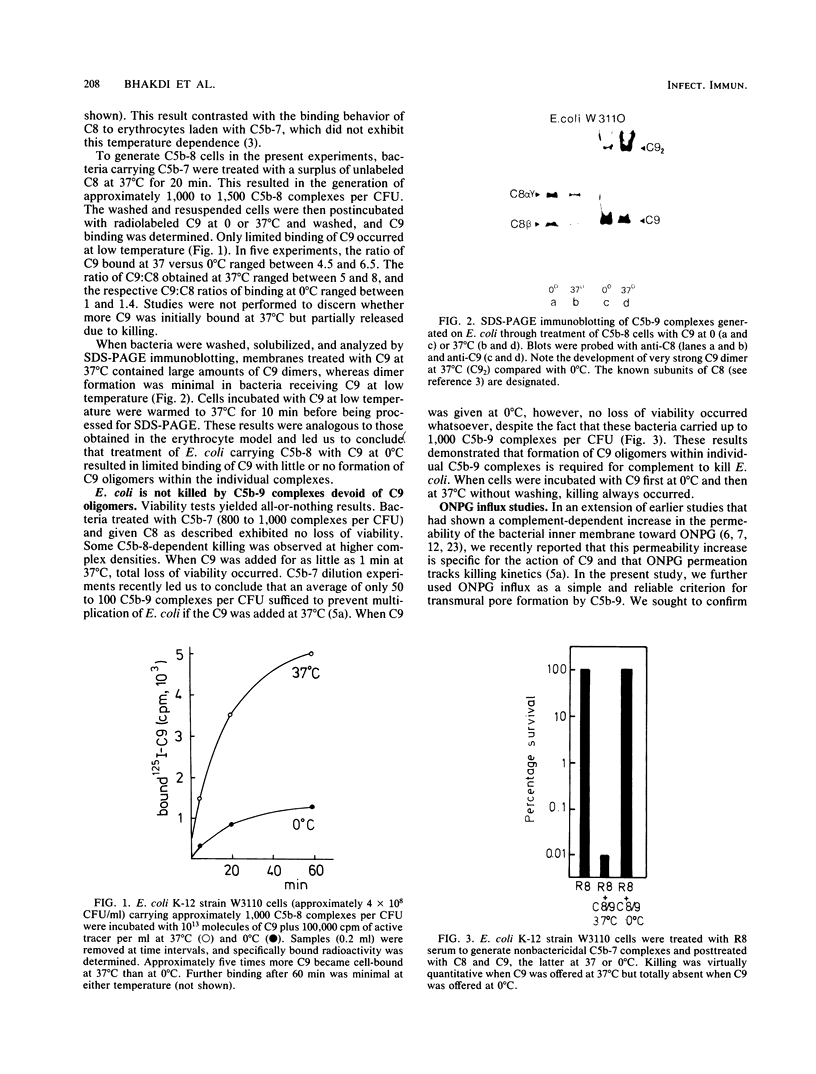
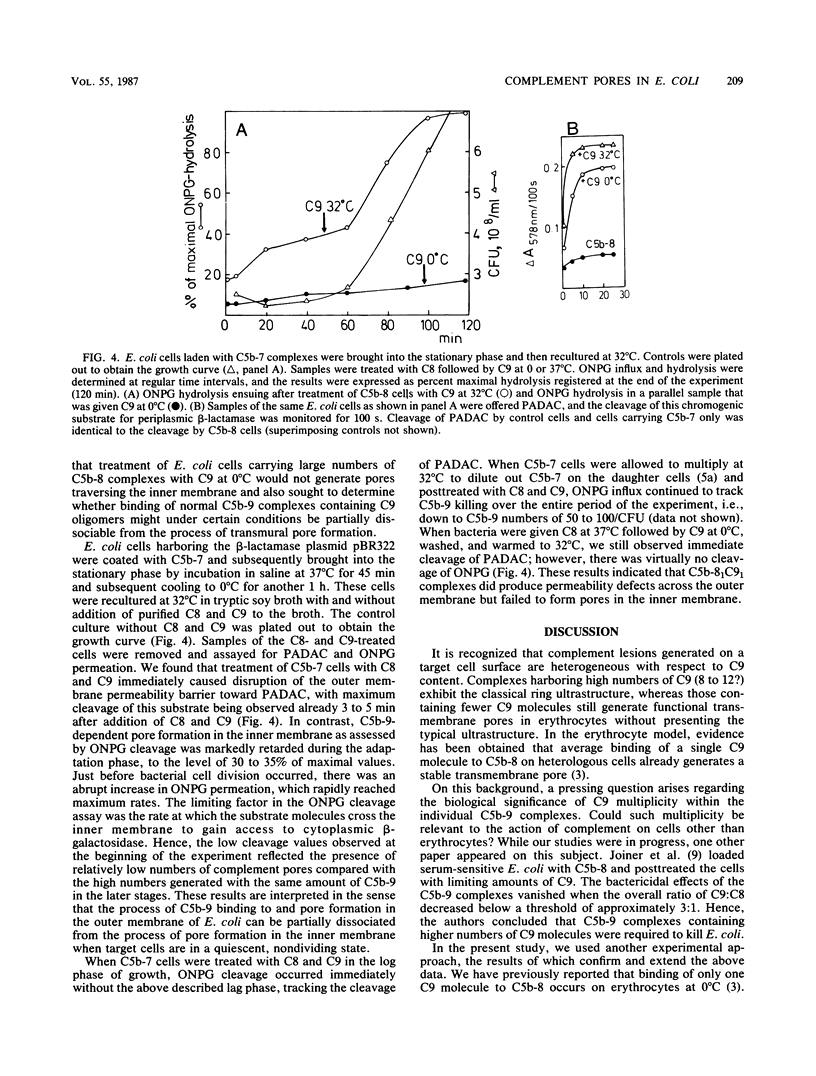
The binding of C9 at 0 and 37 degrees C to viable Escherichia coli K-12 cells carrying C5b-8 complexes was quantified. At low temperature, limited average binding of only 1 to 1.4 molecules of C9 per C8 molecule occurred, whereas 6 to 8 C9 molecules were bound per C8 molecule at 37 degrees C. Despite incorporation of C9 into C5b-9 complexes at 0 degrees C, these terminal complexes caused no loss of bacterial viability even when present in very large numbers (1,000 to 1,500 per CFU) on the bacterial cells. In contrast, generation of 50 to 100 C5b-9 complexes carrying multiple C9 molecules per CFU caused loss of viability. The failure of C5b-81C91 complexes to generate transmural pores was confirmed by measurements of o-nitrophenyl-beta-D-galactoside influx into the cells. Whereas treatment of C5b-8-laden cells with C9 at 32 degrees C caused virtually instantaneous influx of the marker, almost no influx was registered in cells receiving C9 at 0 degrees C. When cells carrying C5b-7 were brought into the stationary phase and given C8 and C9 at 32 degrees C, a C9-dependent disruption of the outer membrane permeability barrier immediately occurred as demonstrated by cleavage of a chromogenic substrate by periplasmic beta-lactamase. In sharp contrast, o-nitrophenyl-beta-D-galactoside influx was markedly retarded over a prolonged period, with abrupt permeability increases of the inner membrane toward this molecule being noted just before bacterial cell division occurred. We conclude that killing of E. coli requires binding of C5b-9 complexes containing C9 oligomers to the outer membrane and suggest that formation of pores in the inner membrane occurs when these complexes are "hit" by transiently forming zones of bioadhesion. Formation of the latter may be a dynamic process that is accentuated during cell division and quiescent during the stationary phase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E. Adsorption of bacteriophages to adhesions between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):346–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.346-356.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. C5b-9 assembly: average binding of one C9 molecule to C5b-8 without poly-C9 formation generates a stable transmembrane pore. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2999–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. On the cause and nature of C9-related heterogeneity of terminal complement complexes generated on target erythrocytes through the action of whole serum. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1453–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born J., Bhakdi S. Does complement kill E. coli by producing transmural pores? Immunology. 1986 Sep;59(1):139–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the action of serum and the role of lysozyme in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2118–2126. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2118-2126.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the lethal event in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2127-2131.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giavedoni E. B., Chow Y. M., Dalmasso A. P. The functional size of the primary complement lesion in resealed erythrocyte membrane ghosts. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Schmetz M. A., Sanders M. E., Murray T. G., Hammer C. H., Dourmashkin R., Frank M. M. Multimeric complement component C9 is necessary for killing of Escherichia coli J5 by terminal attack complex C5b-9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4808–4812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll H. P., Bhakdi S., Taylor P. W. Membrane changes induced by exposure of Escherichia coli to human serum. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1055–1066. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1055-1066.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J., Carroll S. F. Sequential metabolic expressions of the lethal process in human serum-treated Escherichia coli: role of lysozyme. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):735–745. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.735-745.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels D. W., Abramovitz A. S., Hammer C. H., Mayer M. M. Increased ion permeability of planar lipid bilayer membranes after treatment with the C5b-9 cytolytic attack mechanism of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2852–2856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Whitlow M. B., Mayer M. M. The relationship between channel size and the number of C9 molecules in the C5b-9 complex. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2594–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibert G., Biebach A. Eine enzymatische Methode zur Bestimmung von Cefotaxim in Serum- und Harnproben. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1981 May;19(5):279–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J. Complement pores in erythrocyte membranes. Analysis of C8/C9 binding required for functional membrane damage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 10;732(3):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. L., Monahan J. B., Brickner A., Sodetz J. M. Measurement of the ratio of the eighth and ninth components of human complement on complement-lysed membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4016–4022. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Bactericidal and bacteriolytic activity of serum against gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):46–83. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.46-83.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack complex of complement: C5b-8 complex as accelerator of C9 polymerization. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):495–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Levine R. P. How complement kills E. coli. I. Location of the lethal lesion. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1146–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]