Abstract
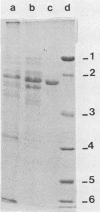
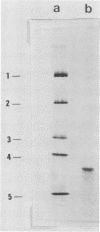
An immunogenic and skin-reactive protein called P64 was purified from Sauton zinc-deficient culture filtrate of Mycobacterium bovis BCG by using successively hydrophobic chromatography on phenyl-Sepharose, ion exchange on DEAE-Sephacel, and molecular sieving on Sephadex G-200. The final P64 preparation was found to be homogeneous based on several analyses. Protein P64 was a constituent of BCG cells since it was present in soluble cellular extract from normally grown BCG cells. It represented 8 to 9% of the soluble proteins of the extract and appeared as the major soluble protein antigen of BCG. This protein was found to have a molecular weight of 64,000 by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, but in molecular sieving it eluted at a volume corresponding to a molecular weight of 246,000. An abnormal UV spectrum was observed for this protein. Its amino acid composition showed an abundance of acidic amino acids (or their amides). Aromatic amino acids represented only 3% of the total amino acid residues. The NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of this protein (10 amino acids) was determined. Its sugar content measured with the phenol-sulfuric acid test was lower than 0.3% (wt/wt.) Isolated P64 was tested by various crossed-immunoelectrophoresis techniques and was shown to correspond to antigen 82 in the reference system for BCG antigens. The protein antigen P64 elicited a delayed cutaneous reaction in guinea pigs sensitized with either living or heat-killed BCG. Its potency in skin reaction was, respectively, two- and threefold that of the BCG purified protein derivative. The two types of sensitization used for skin test reactions promoted significant immunoglobulin G antibody production against the protein antigen P64 in guinea pigs 7 weeks after sensitization.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R. G., Daniel T. M. Serodiagnosis of tuberculosis using the enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay (ELISA) of antibody to Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 5. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Dec;126(6):1013–1016. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.6.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Jacobs W. R., Docherty M. A., Ritchie L. R., Curtiss R., 3rd Molecular analysis of DNA and construction of genomic libraries of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1093-1102.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs O., Harboe M., Axelsen N. H., Bunch-Christensen K., Magnusson M. The antigens of Mycobacterium bovis, strain BCG, studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: a reference system. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(3):249–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. M., Anderson P. A. The isolation by immunoabsorbent affinity chromatography and physicochemical characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 5. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Mar;117(3):533–539. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.3.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. M., Balestrino E. A., Balestrino O. C., Davidson P. T., Debanne S. M., Kataria S., Kataria Y. P., Scocozza J. B. The tuberculin specificity in humans of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 5. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Oct;126(4):600–606. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.4.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. M., Janicki B. W. Mycobacterial antigens: a review of their isolation, chemistry, and immunological properties. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):84–113. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.84-113.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn J., Johannes A., Weckx M., Beumer-Jochmans M. P. Partial purification and characterization of an alcohol dehydrogenase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. bovis (BCG). J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jun;124(2):359–363. doi: 10.1099/00221287-124-2-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn J., Weckx M., Beumer-Jochmans M. P. Effect of zinc deficiency on Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. bovis (BCG). J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jun;124(2):353–357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-124-2-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duez C., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M., Van Beeumen J., Delcambe L., Dierickx L. Purification and properties of the exocellular beta-lactamase of Actinomadura strain R39. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 4;700(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis T. P., Miller R. A., Young D. B., Khanolkar S. R., Buchanan T. M. Immunochemical characterization of a protein associated with Mycobacterium leprae cell wall. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.371-377.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange J. M. The humoral immune response in tuberculosis: its nature, biological role and diagnostic usefulness. Adv Tuberc Res. 1984;21:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M. Antigens of PPD, old tuberculin, and autoclaved Mycobacterium bovis BCG studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):80–87. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Mshana R. N., Closs O., Kronvall G., Axelsen N. H. Cross-reactions between mycobacteria. II. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of soluble antigens of BCG and comparison with other mycobacteria. Scand J Immunol. 1979;9(2):115–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb02713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Nagai S., Patarroyo M. E., Torres M. L., Ramirez C., Cruz N. Properties of proteins MPB64, MPB70, and MPB80 of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):293–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.293-302.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasløv K., Closs O., Møller S., Bentzon M. W. Studies on the development of tuberculin sensitivity in immunized guinea pigs with demonstration of a close relationship between results of skin tests and the lymphocyte transformation technique. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1984;73(2):114–122. doi: 10.1159/000233450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Direct microsequence analysis of polypeptides using an improved sequenator, a nonprotein carrier (polybrene), and high pressure liquid chromatography. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2124–2133. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: nucleotide binding and toxin heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):267–271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai S., Matsumoto J., Nagasuga T. Specific skin-reactive protein from culture filtrate of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1152–1160. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1152-1160.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. B., Lampen J. O. Glyceride-cysteine lipoproteins and secretion by Gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):315–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.315-322.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penke B., Ferenczi R., Kovács K. A new acid hydrolysis method for determining tryptophan in peptides and proteins. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W., Dobbelaer R., Dam A., Jørgensen J. B., Gayot G., Augier J., Haagsma J., Rees W. H., Lesslie I. W., Hebert C. N. Collaborative assay of EEC standards for bovine tuberculins. J Biol Stand. 1979 Jan;7(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(79)80037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. A simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Dauwerse H. G., Das P. K., Groothuis D. G., Schouls L. M., van Embden J. D. Cloning of Mycobacterium bovis BCG DNA and expression of antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):800–806. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.800-806.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano O., Fukuda T., Abe H., Sudo T. Purification and characterization of a tuberculin-active substance from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Biochem. 1984 Aug;96(2):523–531. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]