Abstract
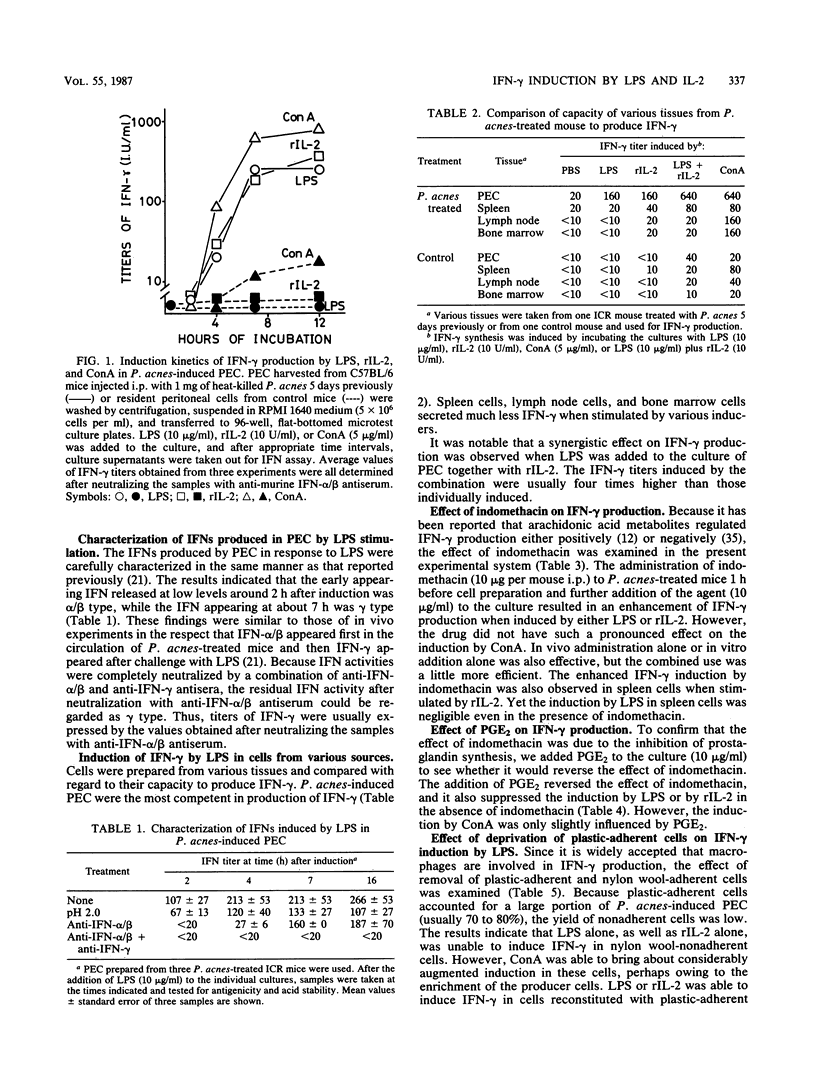
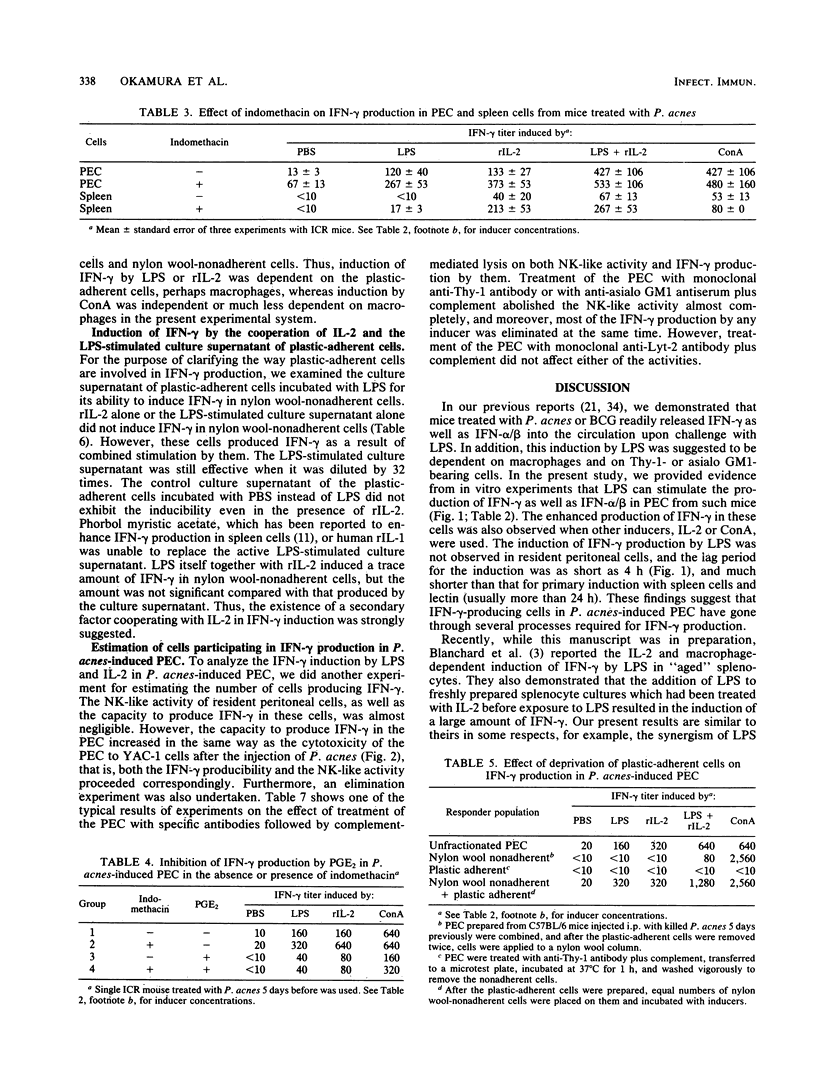
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces high levels of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) in the circulation of mice pretreated with heat-killed Propionibacterium acnes. The following results were obtained in the present study. LPS, as well as interleukin-2 (IL-2), was also able to induce IFN-gamma in vitro in peritoneal exudate cells (PEC) from such mice. Splenocytes and lymph node cells from these mice or resident peritoneal cells from control mice produced trace or undetectable amount of IFN-gamma upon exposure to LPS. A synergistic effect on IFN-gamma induction was observed when LPS was added to a culture of PEC together with IL-2. Indomethacin augmented the induction of IFN-gamma by LPS or IL-2, and prostaglandin E2 reversed its effect. Deprivation of plastic-adherent or nylon wool-adherent cells abolished the induction by LPS or IL-2, whereas it did not affect that by concanavalin A. Culture supernatant of plastic-adherent cells incubated with LPS stimulated the nylon wool-nonadherent cells to produce IFN-gamma in the presence of IL-2, but interleukin-1 or phorbol myristic acetate did not replace the LPS-stimulated supernatant. The ability of PEC to produce IFN-gamma measured as a function of time after P. acnes injection increased in proportion to their natural killer (NK)-like activity against YAC-1 cells. Moreover, treatment of PEC with monoclonal anti-Thy-1 antibody or with anti-asialo GM1 antiserum plus complement eliminated the production of IFN-gamma and the NK-like activity simultaneously, whereas treatment with monoclonal anti-Lyt-2 antibody plus complement did not. These results suggest that IL-2 and some unidentified factor released from plastic-adherent cells by LPS stimulation cooperatively induce IFN-gamma production in activated, Thy-1- and asialo GM1-positive NK-like cells appearing in inflammatory reactions and that prostaglandin E2 regulates IFN-gamma production in these cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Klein T. W., Friedman H., Stewart W. E., 2nd Interferon-gamma induction by lipopolysaccharide: dependence on interleukin 2 and macrophages. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):963–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner K. T., Mauel J., Cerottini J. C., Chapuis B. Quantitative assay of the lytic action of immune lymphoid cells on 51-Cr-labelled allogeneic target cells in vitro; inhibition by isoantibody and by drugs. Immunology. 1968 Feb;14(2):181–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber P. A., Glasgow L. A. Effect of Corynebacterium acnes on interferon production in mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):272–276. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.272-276.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M., Farrar J. J. Regulation of the production of immune interferon and cytotoxic T lymphocytes by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1120–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Webb D. R. Regulation of the immune response by prostaglandins. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Jan;15(1):106–122. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Morganelli P. M., Miller R. Recombinant immune interferon increases immunoglobulin G Fc receptors on cultured human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):393–397. doi: 10.1172/JCI110980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa K., Suzuki R., Matsui H., Shimizu Y., Kumagai K. Natural killer (NK) cells as a responder to interleukin 2 (IL 2). II. IL 2-induced interferon gamma production. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):988–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Augmented induction of interferons during Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):960–969. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Torres B. A. Leukotrienes: positive signals for regulation of gamma-interferon production. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):413–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Torres B. A. Phorbol ester replacement of helper cell and interleukin 2 requirements in gamma interferon production. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):911–914. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.911-914.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Hooks J. J., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 2-mediated immune interferon (IFN-gamma) production by human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawade Y. An analysis of neutralization reaction of interferon by antibody: a proposal on the expression of neutralization titer. J Interferon Res. 1980 Fall;1(1):61–70. doi: 10.1089/jir.1980.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawase I., Brooks C. G., Kuribayashi K., Olabuenaga S., Newman W., Gillis S., Henney C. S. Interleukin 2 induces gamma-interferon production: participation of macrophages and NK-like cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):288–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. P., Jones P. P. Induction of Ia and H-2 antigens on a macrophage cell line by immune interferon. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):315–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibson H. J., Gefter M., Zlotnik A., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Role of gamma-interferon in antibody-producing responses. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):799–801. doi: 10.1038/309799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukaida N., Kasahara T., Hosoi J., Shioiri-Nakano K., Kawai T. Effects of anti-Tac antibody on the response of large granular lymphocytes to interleukin-2. Immunology. 1986 Jan;57(1):137–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T. Sequential production of alpha and beta interferons and gamma interferon in the circulation of Listeria monocytogenes-infected mice after stimulation with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(7):659–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb00869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojo E., Haller O., Wigzell H. Corynebacterium parvum-induced peritoneal exudate cells with rapid cytolytic activity against tumour cells are non-phagocytic cells with characteristics of natural killer cells. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(3):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura H., Kawaguchi K., Shoji K., Kawade Y. High-level induction of gamma interferon with various mitogens in mice pretreated with Propionibacterium acnes. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):440–443. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.440-443.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Heterogeneity of natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:359–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne L. C., Georgiades J. A., Johnson H. M. Classification of interferons with antibody to immune interferon. Cell Immunol. 1980 Jul 15;53(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reem G. H., Yeh N. H. Interleukin 2 regulates expression of its receptor and synthesis of gamma interferon by human T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):429–430. doi: 10.1126/science.6429853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Marshall J. D., Shultz L. D., Gray P. W., Johnson H. M. Gamma-interferon is one of several direct B cell-maturing lymphokines. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):801–804. doi: 10.1038/309801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld G., Mandel A. D., Merigan T. C. In vitro production and cellular origin of murine type II interferon. Immunology. 1979 Apr;36(4):883–890. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Moore R. N., Johnson H. M., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of murine macrophage Ia antigen expression by a lymphokine with immune interferon activity. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanos S., Catinot L., Wietzerbin J., Falcoff E. Production of antibodies against mouse immune T (type II) interferon and their neutralizing properties. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):225–229. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch E., Kirchner H. Interferon inducibility in mice treated with Corynebacterium parvum. Antiviral Res. 1985 Apr;5(2):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey D. E., Wolfe S. A., Durdik J. M., Henney C. S. BCG-induced murine effector cells. I. Cytolytic activity in peritoneal exudates: an early response to BCG. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1145–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Matsumoto-Kobayashi M., Clark S. C., Seehra J., London L., Perussia B. Response of resting human peripheral blood natural killer cells to interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1147–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Weedon L. L., Moore R. N., Rosenstreich D. L. Correction of defective macrophage differentiation in C3H/HeJ mice by an interferon-like molecule. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):380–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Okamura H., Nagata K., Shimoyama T., Kawade Y. Cellular mechanisms in in vivo production of gamma interferon induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice infected with Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Interferon Res. 1985 Summer;5(3):431–443. doi: 10.1089/jir.1985.5.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakasugi N., Virelizier J. L., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Rothhut B., Huerta J. M., Russo-Marie F., Fiers W. Defective IFN-gamma production in the human neonate. II. Role of increased sensitivity to the suppressive effects of prostaglandin E. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):172–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto J. K., Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M. Interleukin 2 regulation of mitogen induction of immune interferon (IFN gamma) in spleen cells and thymocytes. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jan 15;66(2):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Stinebring W. R. Interferon appearance stimulated by endotoxin, bacteria, or viruses in mice pre-treated with Escherichia coli endotoxin or infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nature. 1965 Oct 30;208(5009):456–458. doi: 10.1038/208456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



