Abstract
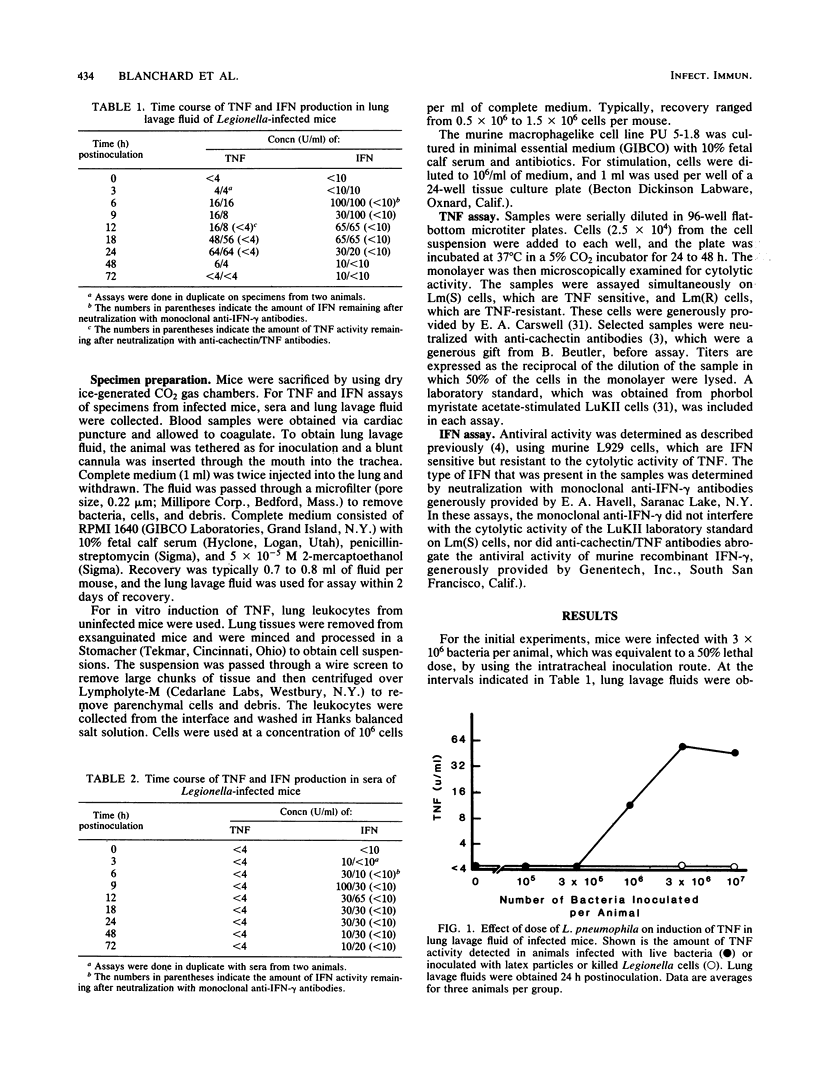
Mice were inoculated with Legionella pneumophila via an intratracheal route to establish an experimental model of infection. Lung lavage fluid obtained from infected mice contained a cytolytic factor identified as tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Peak levels of TNF were produced at about 24 h postinfection and rapidly declined thereafter. Treatment of the mice with dextran sulfate before inoculation with the bacteria resulted in lowered amounts of TNF in the lung lavage fluid, suggesting that macrophages were responsible for production of the cytokine. Furthermore, cultures of adherent lung leukocytes and a macrophage cell line, PU 5-1.8, were stimulated to produce TNF by exposure to Legionella antigens. In addition, adherent lung leukocytes from Legionella-infected mice spontaneously released TNF into the culture supernatant. Inoculation of mice with saline or latex particles failed to induce TNF in vivo, indicating that bacterial antigens or products were the stimulating signals. Since there was no detectable TNF activity in sera at any time after intratracheal inoculation, TNF production appeared to be confined to the site of infection. Pretreatment of PU 5-1.8 cultures with gamma interferon, which was detected in the lung lavage fluid before TNF, resulted in augmented TNF production, suggesting cooperativity may exist between the two cytokines, either in the pathogenicity of the bacterium or in a possible immunomodulatory function of TNF and interferon during infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Holtmann H., Toker L., Hahn T., Wallach D. Tumor necrosis factor induction by Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2938–2942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Klein T. W., Friedman H., Stewart W. E., 2nd Kinetics and characterization of interferon production by murine spleen cells stimulated with Legionella pneumophila antigens. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):719–723. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.719-723.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Ikeda Y., Le Trang N., Hotez P. J., Beutler B. Weight loss associated with an endotoxin-induced mediator from peritoneal macrophages: the role of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor). Immunol Lett. 1985;11(3-4):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daisy J. A., Benson C. E., McKitrick J., Friedman H. M. Intracellular replication of Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):460–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerling P., Finger H., Hof H. Cell-mediated resistance to infection with Listeria monocytogenes in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):382–385. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.382-385.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Heymer B., Wirsing C. H., Emmerling P., Hof H. Reversion of dextran sulfate-induced loss of antibacterial resistance by Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):950–960. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.950-960.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman F., Widen R., Klein T., Friedman H. Lymphoid cell blastogenesis as an in vitro indicator of cellular immunity to Legionella pneumophila antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):834–837. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.834-837.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Bierther M. Morphological changes induced by dextran sulfate 500 in mononuclear phagocytes of listeria-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1110–1119. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1110-1119.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1618–1635. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Interaction of the legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) with human phagocytes. II. Antibody promotes binding of L. pneumophila to monocytes but does not inhibit intracellular multiplication. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):398–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kildahl-Andersen O., Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. IFN-gamma-induced production of monocyte cytotoxic factor. Cell Immunol. 1985 Oct 15;95(2):392–406. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A., Harlan J. M., Sparks L. H., Gamble J. R., Agosti J. M., Waltersdorph A. M. Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4220–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Moore R. N., Mergenhagen S. E. Macrophages as a source of tumoricidal activity (tumor-necrotizing factor). Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):523–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.523-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. F., Carswell E. A., Kassel R. L., Fiore N., Williamson B., Hoffmann M. K., Haranaka K., Old L. J. Endotoxin-induced tumor necrosis factor. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1980;75:207–212. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81491-4_32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason L. H., Mathieson B. J., Liang S. M., Flick D. A., Herberman R. B. Mediation of mouse natural cytotoxic activity by tumour necrosis factor. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):700–702. doi: 10.1038/321700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Broxmeyer H. E., Nakoinz I. Immunostimulators induce granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating activity and block proliferation in a monocyte tumor cell line. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):611–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero V., Tavernier J., Fiers W., Baglioni C. Induction of the synthesis of tumor necrosis factor receptors by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2445–2450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M., Inagawa H., Minagawa H., Kajikawa T., Oshima H., Abe S., Yamazaki M., Mizuno D. Endogenous production of TNF in mice with immune complex as a primer. J Biol Response Mod. 1986 Apr;5(2):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein D. S., David J. R. Tumor necrosis factor enhances eosinophil toxicity to Schistosoma mansoni larvae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1055–1059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Matthews N., Depledge P., Playfair J. H. Malarial parasites and tumour cells are killed by the same component of tumour necrosis serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):293–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Interferon-gamma enhances expression of cellular receptors for tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2441–2444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Palombella V. J., Henriksen-DeStefano D., Swenson C., Feinman R., Hirai M., Tsujimoto M. Fibroblast growth enhancing activity of tumor necrosis factor and its relationship to other polypeptide growth factors. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):632–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson B. D., Carswell E. A., Rubin B. Y., Prendergast J. S., Old L. J. Human tumor necrosis factor produced by human B-cell lines: synergistic cytotoxic interaction with human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5397–5401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Nagamuta M., Usami H., Sugawara Y., Watanabe N., Niitsu Y., Urushizaki I. Release of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) into mouse peritoneal fluids by OK-432, a streptococcal preparation. Immunopharmacology. 1986 Apr;11(2):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(86)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



