Abstract
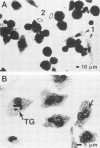
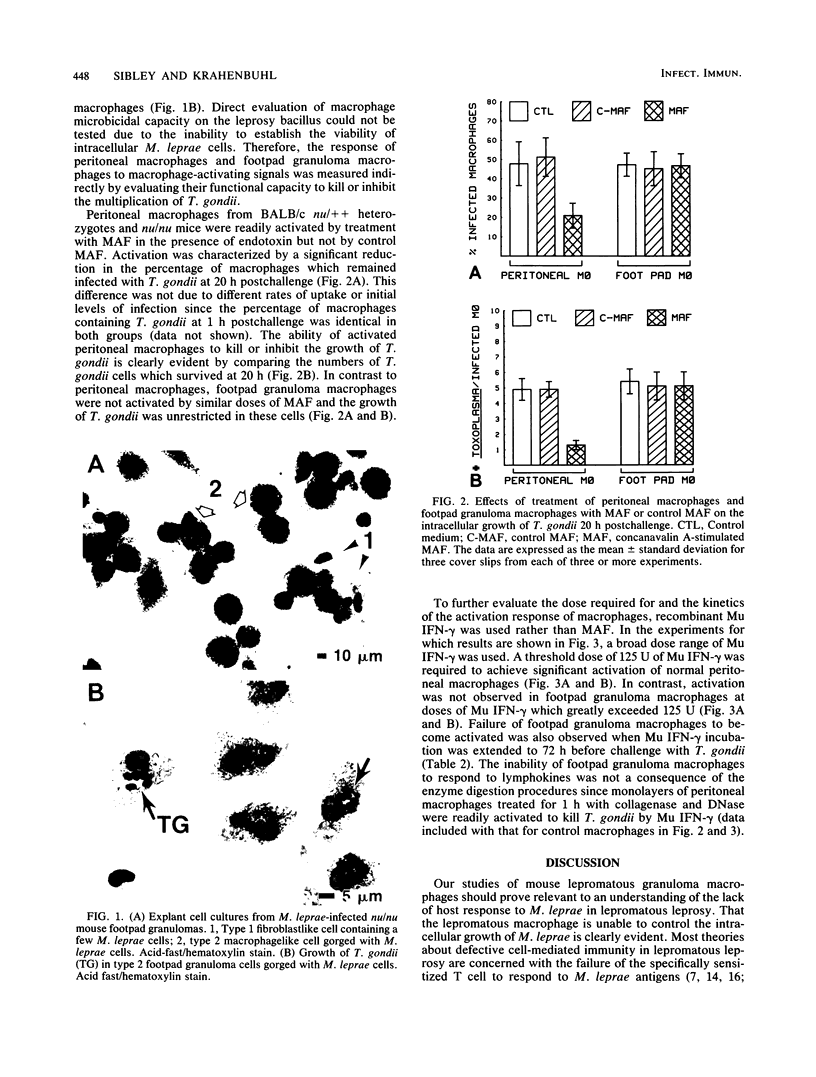
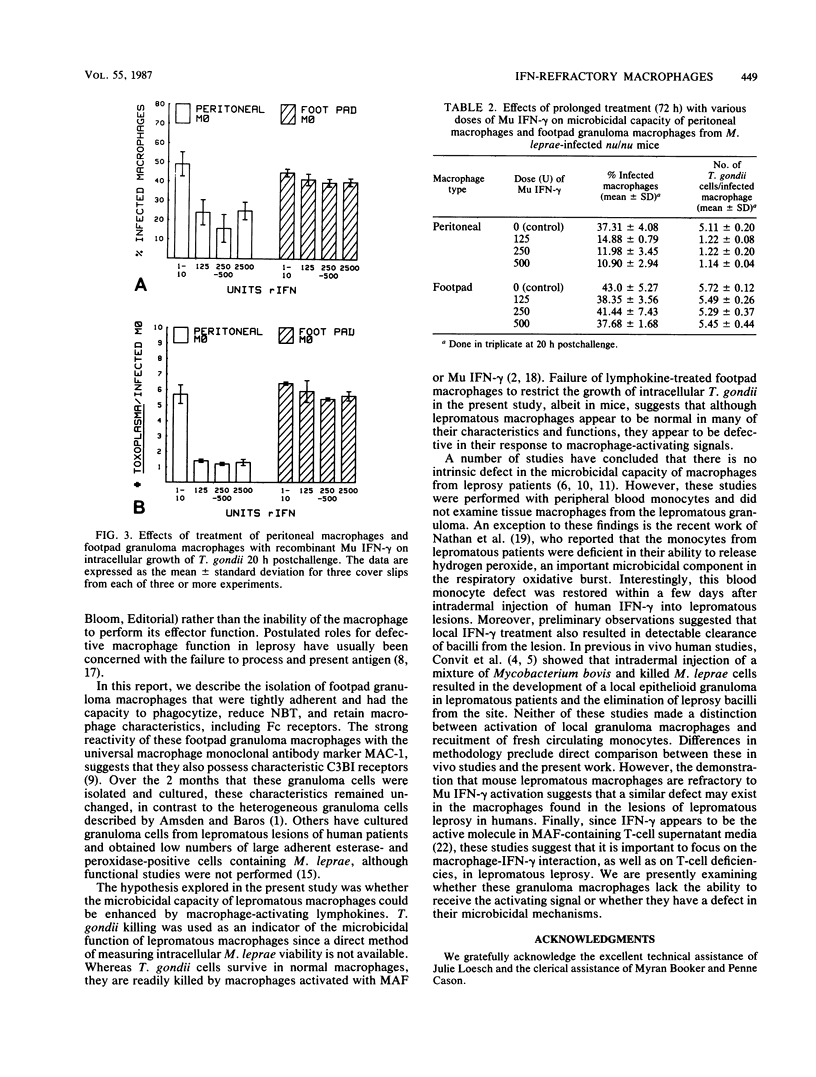
Mycobacterium leprae grows to enormous numbers in the nu/nu mouse footpad, producing granulomas resembling those of lepromatous leprosy in humans. Footpad granuloma cells gorged with M. leprae were established in primary cell culture to examine their functional capabilities. These cells were classified as macrophages by the following criteria: positive staining for nonspecific esterase, reduction of Nitro Blue Tetrazolium during phagocytosis of Candida albicans, possession of Fc receptors, and possession of Mac-1 antigen. Footpad macrophages also phagocytized and supported the intracellular growth of Toxoplasma gondii. However, unlike peritoneal macrophages, footpad macrophages could not be activated to kill or inhibit T. gondii by macrophage-activating factor produced by mitogen-stimulated spleen cells or by recombinant gamma interferon. Thus, although the lepromatous macrophages appeared to be normal in many of their functions, they were defective in response to macrophage-activating signals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsden A. F., Boros D. L. Fc-receptor-bearing macrophages isolated from hypersensitivity and foreign-body granulomas. Delineation of macrophage dynamics, fc receptor density/avidity and specificity. Am J Pathol. 1979 Aug;96(2):457–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of normal and activated human macrophages on Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1154–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehl S., Ruby J., Job C. K., Hastings R. C. The growth of Mycobacterium leprae in nude mice. Lepr Rev. 1983 Dec;54(4):283–304. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19830035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convit J., Aranzazu N., Zúiga M., Ulrich M., Pinardi M. E., Castellazzi Z., Alvarado J. Immunotherapy and immunoprophylaxis of leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1983 Jun;Spec No:47–60. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19830048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convit J., Pinardi M. E., Rodríguez Ochoa G., Ulrich M., Avila J. L., Goihman M. Elimination of Mycobacterium leprae subsequent to local in vivo activation of macrophages in lepromatous leprosy by other mycobacteria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jun;17(2):261–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Cline M. J., Levy L. Leukocyte antimicrobial function in patients with leprosy. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):380–386. doi: 10.1172/JCI107570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T. Immunological aspects of leprosy--present status. Prog Allergy. 1978;25:211–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H. The role of macrophages in the lymphoproliferative response to Mycobacterium leprae in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Oct;34(1):46–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Levis W. R., Cohn Z. A. Defective production of monocyte-activating cytokines in lepromatous leprosy. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):666–678. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Cohn Z. A. The immunobiology of leprosy. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1986;28:45–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. The role of activated macrophages in specific and nonspecific cytostasis of tumor cells. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):507–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Mason L. H., Rothman W., Reinherz E., Schlossman S. F., Bloom B. R. Delineation of a human T cell subset responsible for lepromin-induced suppression in leprosy patients. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1183–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R. B., Girdhar B. K., Sengupta U., Desikan K. V. In vitro studies on dermal granulomas of human leprosy--cellular characteristics. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1985 Mar;53(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Narayanan R. B., Mehra N. K., Sharma A. K., Gupte M. D. Concanavalin A induced suppressor activity in human leprosy. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Nov;2(4):319–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Van Rood J. J., Mehra N. K., Vaidya M. C. Natural suppressor cells in human leprosy: the role of HLA-D-identical peripheral lymphocytes and macrophages in the in vitro modulation of lymphoproliferative responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):203–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Kaplan G., Levis W. R., Nusrat A., Witmer M. D., Sherwin S. A., Job C. K., Horowitz C. R., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Local and systemic effects of intradermal recombinant interferon-gamma in patients with lepromatous leprosy. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 3;315(1):6–15. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607033150102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. R., Bryan V. M., Oi V. T., Herzenberg L. A. Antigen-specific identification and cloning of hybridomas with a fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1962–1966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. W., McIntosh A. T. Macrophages isolated from regressing Moloney sarcomas are more cytotoxic than those recovered from progressing sarcomas. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):69–71. doi: 10.1038/268069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Pace J. L., Russell S. W., Altman A., Katz D. H. Macrophage-activating factor produced by a T cell hybridoma: physiochemical and biosynthetic resemblance to gamma-interferon. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):826–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., McRae D. H. A method for counting acid-fast bacteria. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Jan-Mar;36(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Krahenbuhl J. L., Weidner E. Lymphokine activation of J774G8 cells and mouse peritoneal macrophages challenged with Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.760-764.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]