Abstract
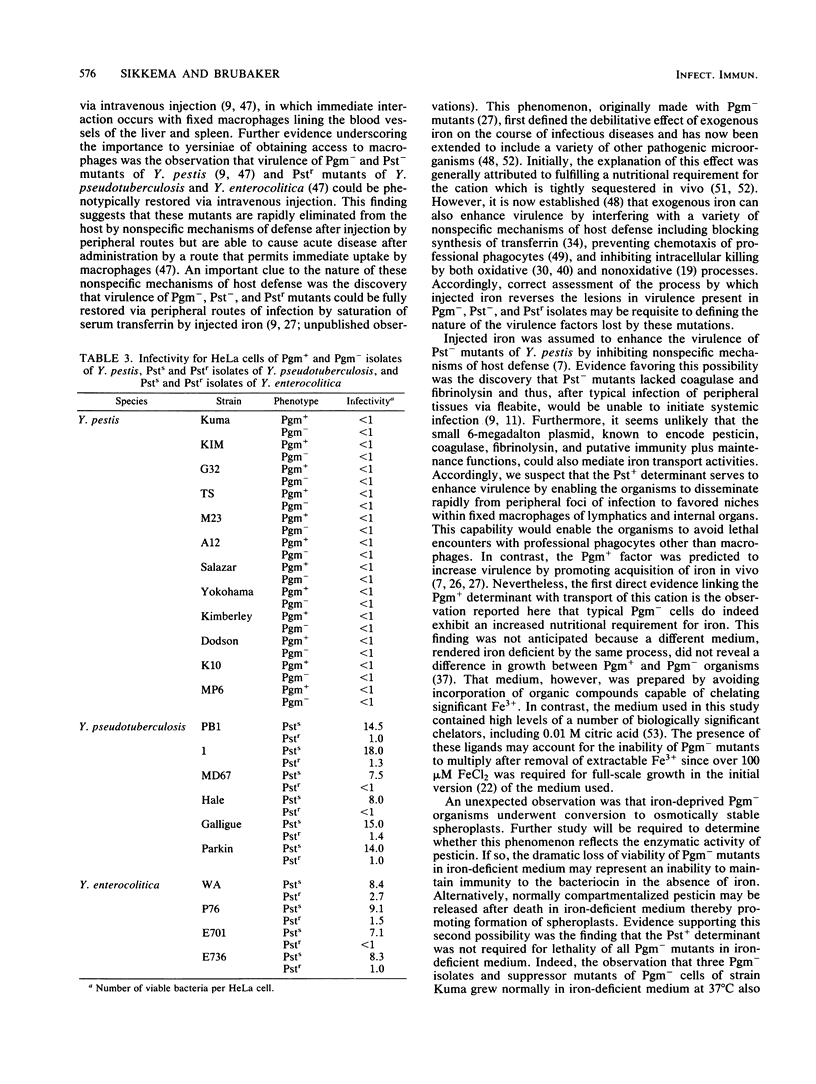
The independent abilities of Yersinia pestis to absorb exogenous pigments including hemin and Congo red (Pgm+) and to produce the bacteriocin pesticin with genetically linked invasive enzymes (Pst+) are established virulence factors of the species. Pst- Pgm+ strains of Y. pestis are sensitive to pesticin (Psts), and mutation of these isolates to pesticin resistance (Pstr) is known to result in concomitant conversion to Pgm-. Wild-type cells of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica are Pgm- but may be Psts; mutation of the latter to Pstr also results in avirulence. In this study, typical Pgm- mutants of Y. pestis exhibited a dramatic nutritional requirement at 37 degrees C but not 26 degrees C for iron which could be fulfilled by either Fe3+ or hemin. Iron privation of Pgm- yersiniae resulted in formation of osmotically stable spheroplasts similar to those previously observed after exposure of Psts bacteria to pesticin. At 37 degrees C, Pgm+ organisms rapidly overgrew initially predominant Pgm- populations in iron-deficient medium. However, Pgm-isolates could undergo a second mutation that permitted successful competition with Pgm+ cells in this environment. The mutation to Pstr in Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. enterocolitica did not promote a similar requirement for iron but rather prevented these organisms from penetrating HeLa cells. The ability to invade these nonprofessional phagocytes was not shared by Pgm+ or Pgm- cells of Y. pestis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEN-GURION R., HERTMAN I. Bacteriocin-like material produced by Pasteurella pestis. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):289–297. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. The effects of loss of different virulence determinants on the virulence and immunogenicity of strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Jun;39(3):278–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The pigmentation of Pasteurella pestis on a defined medium containing haemin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):570–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The pigmentation of Pasteurella pestis on a defined medium containing haemin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):570–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The virulence-enhancing effect of iron on nonpigmented mutants of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):577–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Gurion R., Shafferman A. Essential virulence determinants of different Yersinia species are carried on a common plasmid. Plasmid. 1981 Mar;5(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin W. H., Jr, Turnbough C. L., Jr, Posey B. S., Briles D. E. The ability of Salmonella typhimurium to produce the siderophore enterobactin is not a virulence factor in mouse typhoid. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):392–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.392-397.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhoff H. A., Vinal A. C. Congo red medium to distinguish between invasive and non-invasive Escherichia coli pathogenic for poultry. Avian Dis. 1986 Jan-Mar;30(1):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovallius A., Nilsson G. Ingestion and survival of Y. pseudotuberculosis in HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Dec;21(12):1997–2007. doi: 10.1139/m75-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R., Beesley E. D., Surgalla M. J. Pasteurella pestis: Role of Pesticin I and Iron in Experimental Plague. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Mutation rate to nonpigmentation in Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1404–1406. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1404-1406.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowart R. E., Foster B. G. Differential effects of iron on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes: minimum requirements and mechanism of acquisition. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):721–730. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J. A., Schiemann D. A. HeLa cell infection by Yersinia enterocolitica: evidence for lack of intracellular multiplication and development of a new procedure for quantitative expression of infectivity. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.48-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Mode of action of pesticin: N-acetylglucosaminidase activity. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):495–501. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.495-501.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Fowler J. M., Brubaker R. R. Mutations to tolerance and resistance to pesticin and colicins in Escherichia coli phi. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):506–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.506-511.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladstone G. P., Walton E. The effect of iron and haematin on the killing of staphylococci by rabbit polymorphs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Oct;52(5):452–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTMAN I., BEN-GURION R. A study on pesticin biosynthesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:135–143. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., CARLIN C. E. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. I. A casein hydrolyzate medium for the growth of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):122–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.122-129.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. J., Brubaker R. R. Pesticin-dependent generation of somotically stable spheroplast-like structures. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):786–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.786-789.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Brubaker R. R. Characterization of pesticin. Separation of antibacterial activities. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4749–4753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Yang G. C., Brubaker R. R. Specificity, induction, and absorption of pesticin. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):212–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.212-219.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen W. A., Surgalla M. J. Plague bacillus: survival within host phagocytes. Science. 1969 Feb 28;163(3870):950–952. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3870.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. S., Quie P. G., Basford R. E. Effect of iron on leukocyte function: inactivation of H2O2 BY IRON. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):303–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.303-308.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kol'tsova E. G., Suchkov Y. G., Lebedeva S. A. Transmission of a bacteriocinogenic factor in Pasteurella pestis. Sov Genet. 1971 Apr;7(4):507–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McGrath P. P., Carter P. H., Eide E. L. The ability of some Yersinia enterocolitica strains to invade HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1714–1722. doi: 10.1139/m77-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Loss of pigmentation in Shigella flexneri 2a is correlated with loss of virulence and virulence-associated plasmid. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.397-401.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane H., Okubadejo M., Reddy S. Transferrin and Staphylococcus aureus in kwashiorkor. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 May;57(5):587–591. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/57.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Detection and differentiation of iron-responsive avirulent mutants on Congo red agar. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.94-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Accumulation of iron by yersiniae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1290-1298.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Vwa+ phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.166-171.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ J., ROSENTHAL S. Iron (II) inactivation of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2486–2490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Brener D., DeVoe I. W. Expression of a high-affinity mechanism for acquisition of transferrin iron by Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.107-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Localization in Yersinia pestis of peptides associated with virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):129–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.129-135.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surgalla M. J., Beesley E. D. Congo red-agar plating medium for detecting pigmentation in Pasteurella pestis. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):834–837. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.834-837.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. In vivo comparison of avirulent Vwa- and Pgm- or Pstr phenotypes of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):895–900. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.895-900.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T. Studies on the pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. I. Experimental infection in rabbits. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(7):341–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T. Studies on the pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. II. Interaction with cultured cells in vitro. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(7):365–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T. Studies on the pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. III. Comparative studies between Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(9):505–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Goldschmidt P., Greene N. D. Suppressive effects of metal salts on leukocyte and fibroblastic function. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Nov;18(5):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and susceptibility to infectious disease. Science. 1974 May 31;184(4140):952–956. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4140.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahorchak R. J., Brubaker R. R. Effect of exogenous nucleotides on Ca2+ dependence and V antigen synthesis in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):953–959. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.953-959.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Asbeck B. S., Verhoef J. Iron and host defence. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;2(1):6–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02019915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]