Full text
PDF


















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
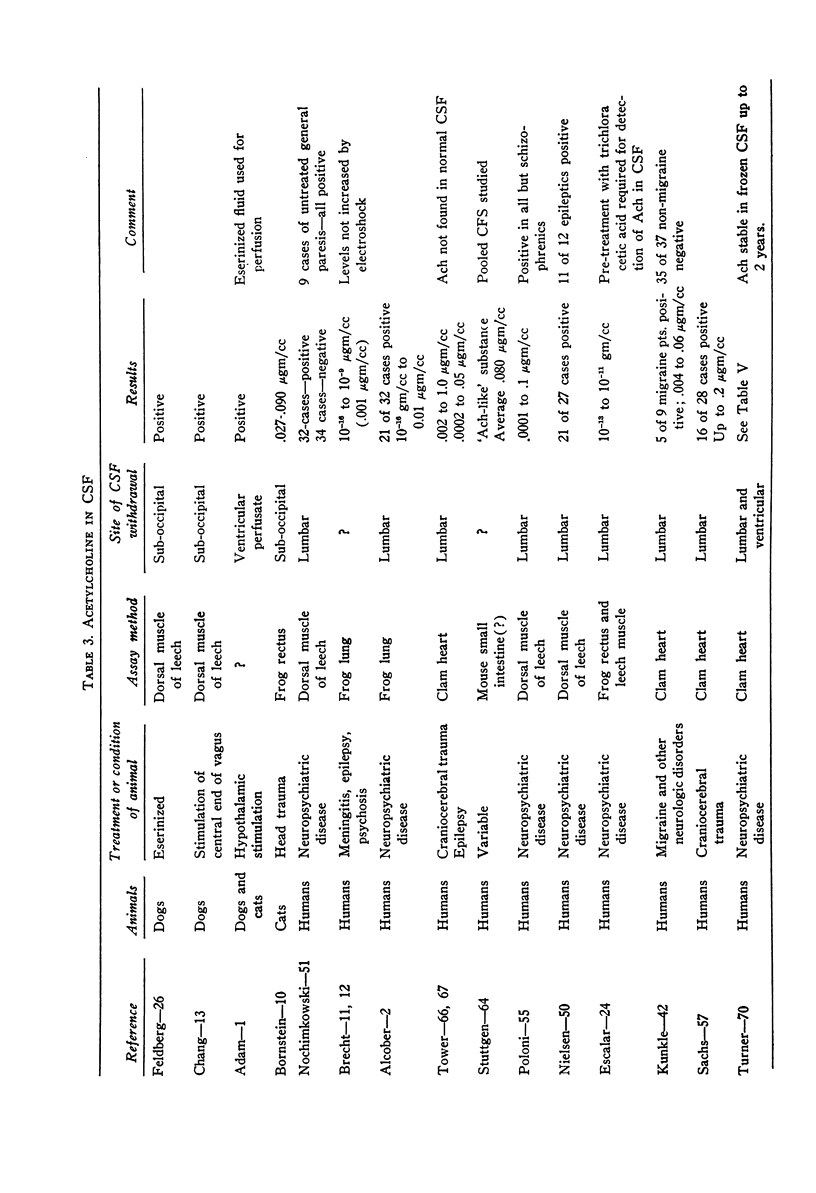
- ALCOBER T. Ueber den Nachweis von Acetylcholin im Liquor cerebrospinalis, besonders bei Psychosen. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr. 1948;180(1-2):202–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00353009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACCARINI V., VOLPICELLI M. L'istamina nel liquido cerebro-spinale. Rass Neurol Veg. 1951 Mar;9(5-6):483–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHATTACHARYA B. K., FELDBERG W. Perfusion of cerebral ventricles: assay of pharmacologically active substances in the effluent from the cisterna and the aqueduct. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Jun;13(2):163–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHATTACHARYA B. K., FELDBERG W., VOGT W. Some properties of the substance in human cerebrospinal fiuid sensitizing the frog rectus muscle to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 6;137(3):460–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOGDANSKI D. F., WEISSBACH H., UDENFRIEND Pharmacological studies with the serotonin precursor, 5-hydroxytryptophan. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958 Feb;122(2):182–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONVALLET M., DELL P., HIEBEL G. Tonus sympathique et activité électrique corticale. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1954 Feb;6(1):119–144. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(54)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN L. F., WOLFF H. G. Property of cerebrospinal fluid associated with disturbed metabolism of central nervous system. Science. 1958 Nov 14;128(3333):1208–1209. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3333.1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN L. F., WOLFF H. G. Studies of proteolytic enzymes in cerebrospinal fluid: capacity of incubated mixtures of cerebrospinal fluid and plasma proteins to form vasodilator substances that contract the isolated rat uterus. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1959 Jan;103(1):86–94. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1959.00270010092012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELL P., BONVALLET M., HUGELIN A. Tonus sympathique, adrénaline et contróle réticulaire de la motricité spinale. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1954 Nov;6(4):599–618. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(54)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
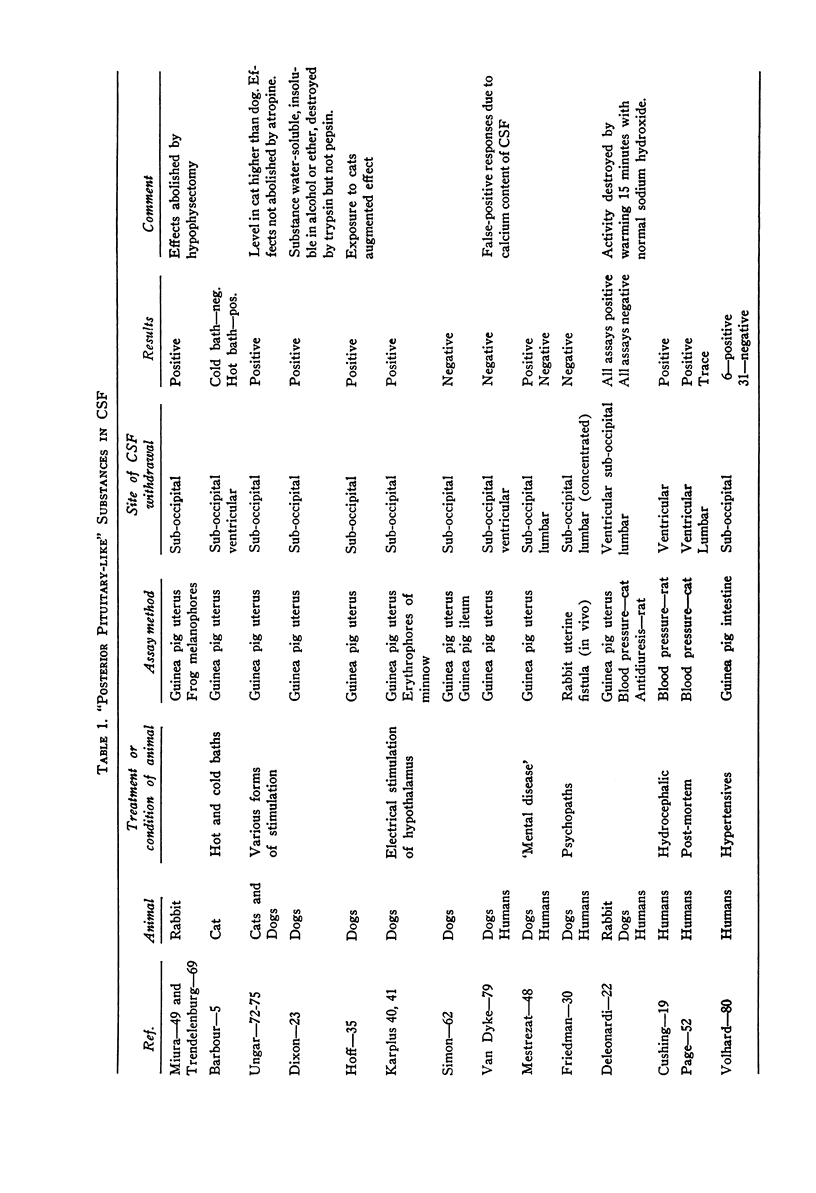
- Dixon W. E. Pituitary secretion. J Physiol. 1923 Mar 21;57(3-4):129–138. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1923.sp002048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESCALAR G., GALLI G. Ricerche sul contenuto di acetilcolina libera e legata in liquores normali e patologici. Sist Nerv. 1957 Sep-Oct;9(5):379–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., SHERWOOD S. L. Injections of drugs into the lateral ventricle of the cat. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):148–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Schriever H. The acetylcholine content of the cerebro-spinal fluid of dogs. J Physiol. 1936 Mar 9;86(3):277–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIARMAN N. J. Neurohumors in the brain. Yale J Biol Med. 1959 Nov;32:73–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. B. Recent advances in the chemistry of the cerebrospinal fluid. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1958 Oct;127(4):359–373. doi: 10.1097/00005053-195810000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON I. J., ROSE B. Observations on the histamine content of the cerebrospinal fluid in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1949 Feb;34(2):250–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKNER F. L., LECHNER H. Zur Frage der anticholinergen Therapie bei geschlossenem Schädel-Hirntrauma. Langenbecks Arch Klin Chir Ver Dtsch Z Chir. 1955;280(4):354–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKNER F. L. Neue Wege in der Behandlung der Commotio cerebri. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1954 Jun 26;104(26-27):546–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKLE E. C. Acetylcholine in the mechanism of headaches of migraine type. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1959 Feb;81(2):135–141. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1959.02340140001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACHNIT V., WEIS I. ACTH-Aktivität des Liquors bei hypophysären und interrenalen Erkrankungen. Dtsch Arch Klin Med. 1955;202(3):275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERNER A. B., CASE J. D. Pigment cell regulatory factors. J Invest Dermatol. 1959 Feb;32(2 Pt 2):211–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANGER W. M., SCHWARZ B. E., BAARS C. W., WAKIM K. G., BOLLMAN J. L., PETERSEN M. C., BERKSON J. Epinephrine and arterenol (norepinephrine) in mental disease; plasme and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1957 Oct;78(4):396–412. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1957.02330400070010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIELSEN A., DERBYSHIRE A. J., GERBER C. Acetylcholine in convulsive disorders. Harper Hosp Bull. 1953 Mar-Apr;11(2):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAASONEN M. K., MACLEAN P. D., GIARMAN N. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin, enteramine) content of structures of the limbic system. J Neurochem. 1957;1(4):326–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPIUS H. M., ELLIOTT K. A. Acetylcholine metabolism in normal and epileptogenic brain tissue; failure to repeat previous findings. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Mar;12(2):319–323. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.12.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page I. H. A HIGHLY ACTIVE PRESSOR SUBSTANCE FROM CEREBRAL VENTRICULAR FLUID OF HUMAN BEINGS. Science. 1935 Dec 6;82(2136):550–551. doi: 10.1126/science.82.2136.550-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBALLER A. B. Studies on the adrenaline-sensitive component of the reticular activating system. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1956 Nov;8(4):603–621. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(56)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHS E., Jr Acetylcholine and serotonin in the spinal fluid. J Neurosurg. 1957 Jan;14(1):22–27. doi: 10.3171/jns.1957.14.1.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCAVO D. Le sostanze antidiuretiche dei liquidi organici; sintesi critica. Rass Fisiopatol Clin Ter. 1954 Oct;26(10):773–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOWER D. B., McEACHERN D. Acetylcholine and neuronal activity; acetylcholine and cholines terase activity in the cerebrospinal fluids of patients with epilepsy. Can J Res. 1949 Mar;27(2):120–131. doi: 10.1139/cjr49e-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOWER D. B., McEACHERN D. Acetylcholine and neuronal activity; cholinesterase patterns and acetylcholine in the cerebrospinal fluids of patients with craniocerebral trauma. Can J Res. 1949 Mar;27(2):105–119. doi: 10.1139/cjr49e-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
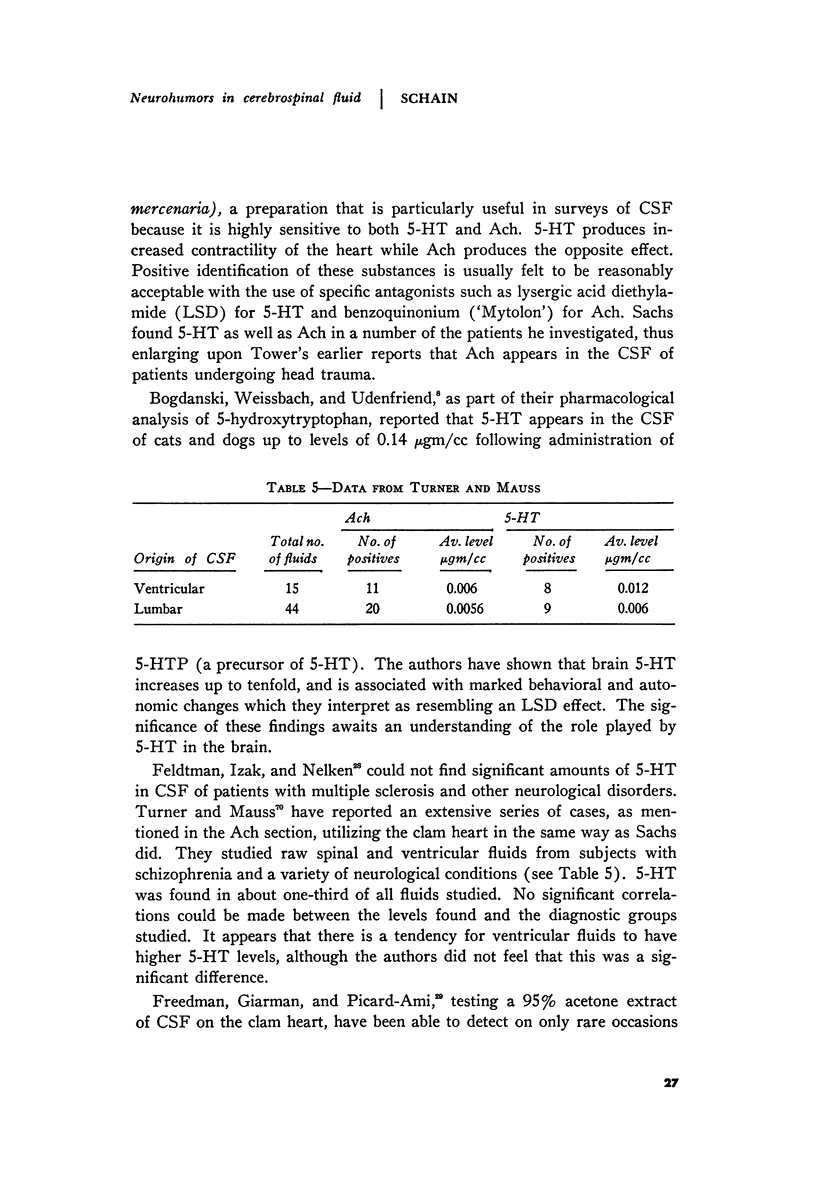
- TURNER W. J., MAUSS E. A. Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) and acetylcholine in human ventricular and spinal fluids. AMA Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1959 Dec;1:646–650. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1959.03590060108012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD A., Jr Atropine in the treatment of closed head injury. J Neurosurg. 1950 Sep;7(5):398–402. doi: 10.3171/jns.1950.7.5.0398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL-MALHERBE H., LIDDELL D. W. Adrenaline and noradrenaline in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1954 Nov;17(4):247–249. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.17.4.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


