Abstract
An Escherichia coli deep rough lipopolysaccharide (LPS), biosynthetically labeled with 32PO4 and [3H]glucosamine, was used to study dephosphorylation of the lipid A moiety by murine macrophages. Over a 48-h incubation period, the macrophages removed approximately two-thirds of the 32P from [3H32P]LPS that was added to the culture medium. The LPS-derived phosphate was incorporated into cell components (e.g., phospholipids), as well as released from the cells. Cell lysates were also able to remove phosphate from [3H32P]LPS. The phosphatase activity was optimal at acidic pH and was greatly reduced by 10 mM sodium fluoride or heating at 80 degrees C. There was no evident difference in the LPS-dephosphorylating ability of macrophages from LPS-responsive and -hyporesponsive mice. The results indicate that murine macrophages dephosphorylate the lipid A moiety of deep rough E. coli LPS and raise the possibility that enzymatic dephosphorylation may modify LPS bioactivity.
Full text
PDF
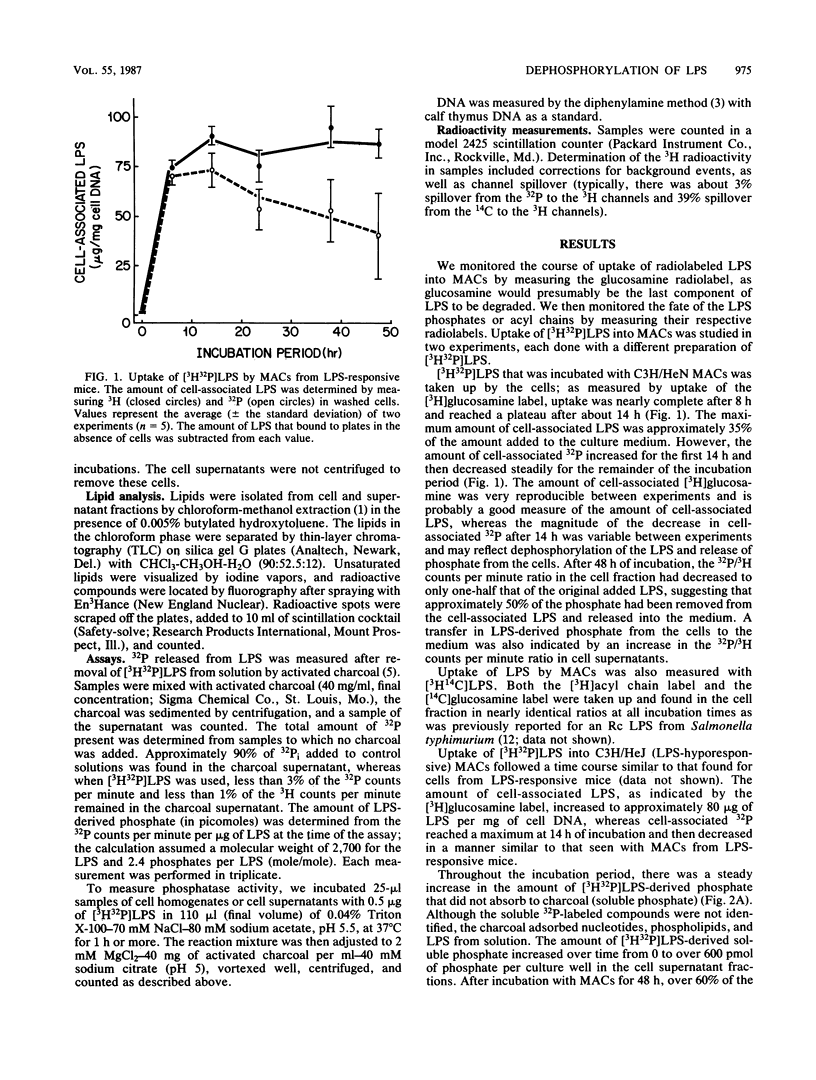
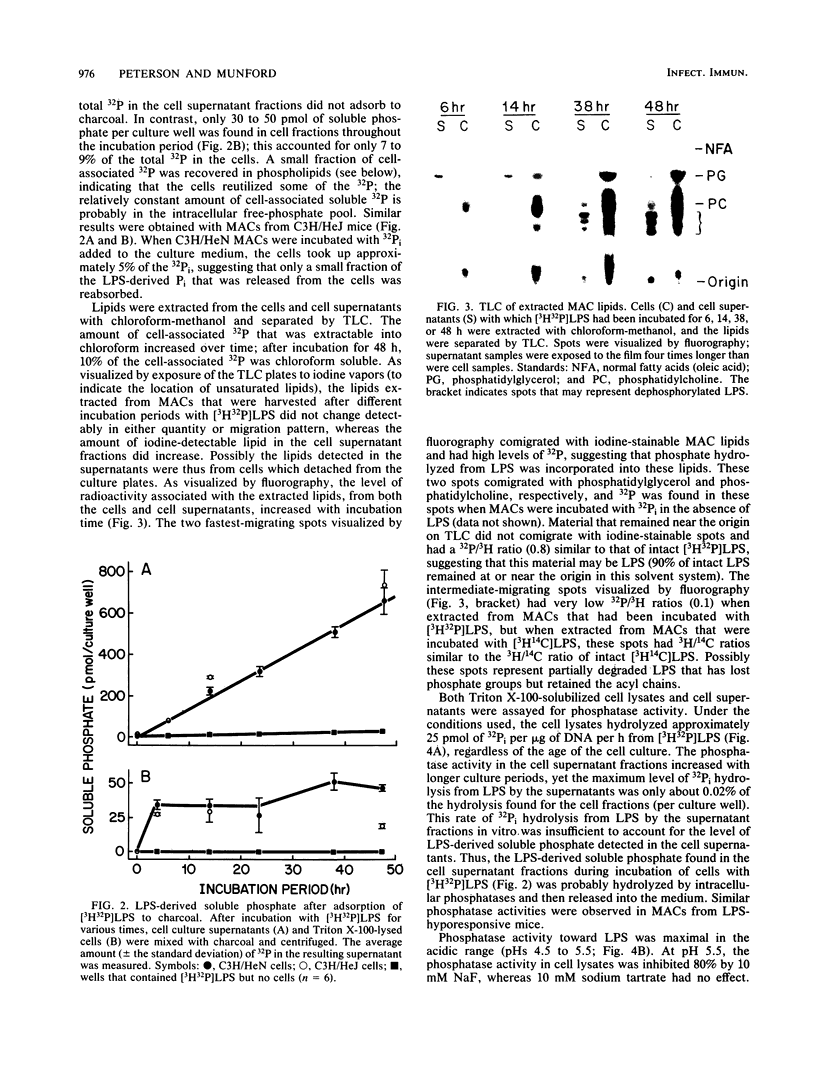
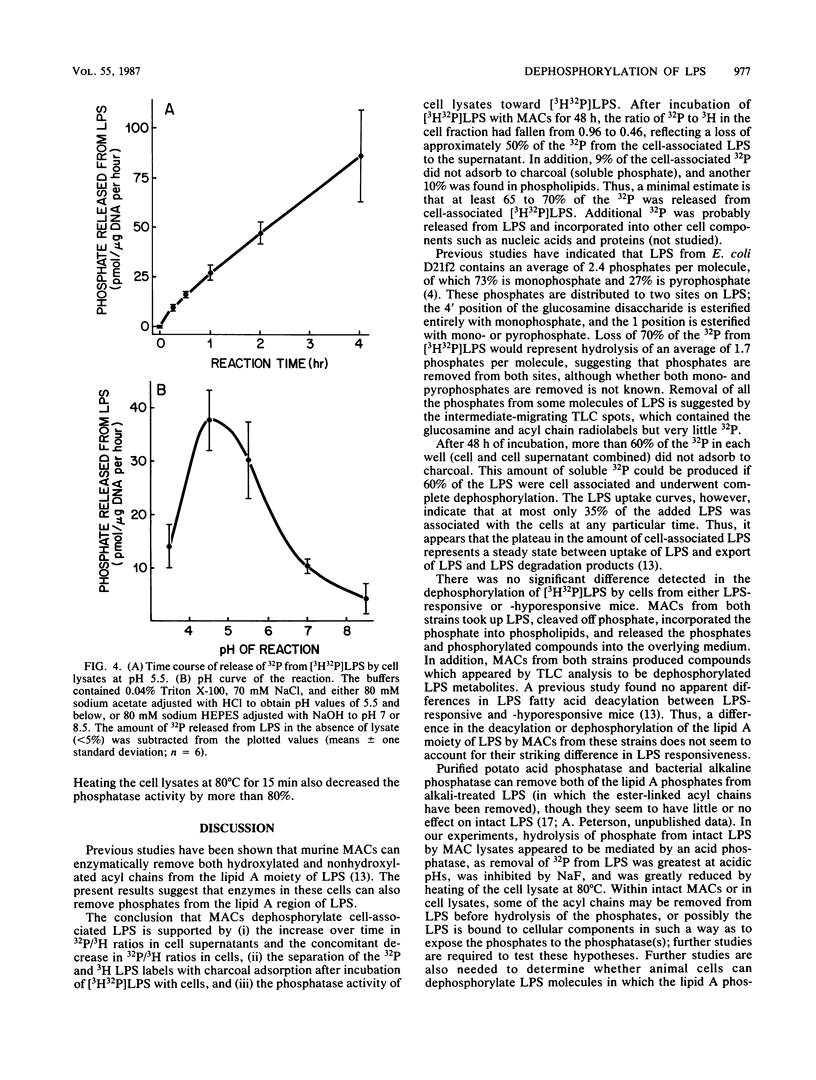

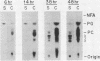
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Lipids of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: structure and metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):833–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.833-843.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Monner D. A. Characterization of lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli K-12 mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):455–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.455-464.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE R. K., LIPMANN F. The effect of arsenate on aerobic phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):235–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson S. L., Adams D. O. A simple, sensitive assay for determining DNA in mononuclear phagocytes and other leukocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1978;23(1-2):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Peterson A. A., Haug A., Pownall H. J., McGroarty E. J. A pH titration study on the ionic bridging within lipopolysaccharide aggregates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 19;821(3):404–412. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Alterations in rats in vivo of the chemical structure of lipopolysaccharide from Salmonella abortus equi. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):353–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Munford R. S. Enzymatic deacylation of the lipid A moiety of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides by human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleine B., Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Excretion of radioactivity in faeces and urine of rats injected with 3H,14C-lipopolysaccharide. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Jun;66(3):303–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Takahashi I., Ikeda T., Otsuka K., Shimauchi H., Kasai N., Mashimo J. Synthetic lipid A with endotoxic and related biological activities comparable to those of a natural lipid A from an Escherichia coli re-mutant. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):225–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.225-237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L. Uptake and deacylation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides by macrophages from normal and endotoxin-hyporesponsive mice. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):464–473. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.464-473.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. Physical properties of short- and long-O-antigen-containing fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111:B4. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.116-122.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Takayama K., Ribi E. Purification and structural determination of nontoxic lipid A obtained from the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11808–11815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D., HOWARD J. G., JENKIN C. R. The fate of 32P-labelled bacterial lipopolysaccharide in laboratory animals. Lancet. 1956 Apr 7;270(6919):366–367. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. R., Tang J., Barzilay I., Khorana H. G. Structure of the lipopolysaccharide from an Escherichia coli heptose-less mutant. I. Chemical degradations and identification of products. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5906–5917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. R., Verret R. C., Khorana H. G. The structure of lipopolysaccharide from an Escherichia coli heptose-less mutant. III. Two fatty acyl amidases from Dictyostelium discoideum and their action on lipopolysaccharide derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5926–5933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain S. M., Fesik S. W., Armitage I. M. Characterization of lipopolysaccharide from a heptoseless mutant of Escherichia coli by carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2906–2910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain S. M., Fesik S. W., Armitage I. M. Structure and metal-binding properties of lipopolysaccharides from heptoseless mutants of Escherichia coli studied by 13C and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13466–13477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Raetz C. R., Ribi E., Peterson J., Cantrell J. L., Pearson F. C., Wiggins J., Johnson A. G. Influence of fine structure of lipid A on Limulus amebocyte lysate clotting and toxic activities. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):350–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.350-355.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]