Abstract
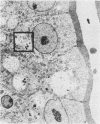
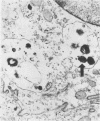
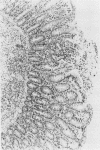
Epidemiologic evidence suggests that Plesiomonas shigelloides is an enteric pathogen. We conducted in vitro, animal, and volunteer studies on P. shigelloides isolates from patients with diarrhea. Five strains gave a negative keratoconjunctivitis reaction in guinea pigs and did not invade HeLa cells. Genetic probes for heat-stable enterotoxins related to those of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and for gene sequences common to the invasiveness plasmids of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive E. coli were negative. Heat-labile enterotoxins were not found when a modified GM1-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used. Rabbits did not develop diarrhea but were transiently colonized when inoculated with up to 10(11) P. shigelloides CFU using the reversible intestinal tie adult rabbit diarrhea model. A very large plasmid (between 118 and 312 megadaltons) was found in all isolates. Strain P012 was cured of its plasmid by novobiocin. This strain, but not its cured derivative, invaded the mucosa of the distal ileum of gnotobiotic piglets given 10(10) CFU. At a lower inoculum (10(9) CFU), strain P012 induced inflammation of the colonic mucosa and diarrhea at day 6. The same isolate was fed to 33 healthy volunteers in doses of 1 X 10(3) to 4 X 10(9) CFU. Thirty-six percent of the volunteers shed the organism, but none became ill. These data are only weakly supportive of a role for P. shigelloides in diarrheal illness and suggest the need for more studies with other strains to better understand its pathogenicity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avendano A., Herrera P., Horwitz I., Duarte E., Prenzel I., Lanata C., Levine M. L. Duodenal string cultures: practicality and sensitivity for diagnosing enteric fever in children. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):359–362. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns M. M., Vaughan S., Sanyal S. C., Timmis K. N. Invasive ability of Plesiomonas shigelloides. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 Aug;257(3):343–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boileau C. R., d'Hauteville H. M., Sansonetti P. J. DNA hybridization technique to detect Shigella species and enteroinvasive escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):959–961. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.959-961.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R. A., Music S. I., Libonati J. P., Snyder M. J., Wenzel R. P., Hornick R. B. Response of man to infection with Vibrio cholerae. I. Clinical, serologic, and bacteriologic responses to a known inoculum. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):45–52. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. G., Brown G. W. Plesiomonas shigelloides in South Australia. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Nov;21(6):715–718. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.6.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. A., 2nd, Chretien J. H., Garagusi V. F., Goldstein M. A. Snake-to-human transmission of Aeromonas (Pl) shigelloides resulting in gastroenteritis. South Med J. 1978 Apr;71(4):474–476. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197804000-00038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey D. J., Clark J. N. A case of diarrhoea associated with Plesiomonas shigelloides. N Z Med J. 1984 Feb 8;97(749):92–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Sethabutr O., Taylor D. N. DNA hybridization in the diagnosis of bacterial diarrhea. Clin Lab Med. 1985 Sep;5(3):447–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Protein synthesis in HeLa or Henle 407 cells infected with Shigella dysenteriae 1, Shigella flexneri 2a, or Salmonella typhimurium W118. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.137-144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides as causes of intestinal infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6(5):633–639. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.5.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Blake P. A., Farmer J. J., 3rd Plesiomonas enteric infections in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):690–694. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. D., Tung C., Swartz M. N. Elimination of plasmid pMG110 from Escherichia coli by novobiocin and other inhibitors of DNA gyrase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):586–590. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostacká A., Ciznár I., Korych B., Karolcek J. Toxic factors of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Sep;252(4):525–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huq M. I., Islam M. R. Microbiological & clinical studies in diarrhoea due to Plesiomonas shigelloides. Indian J Med Res. 1983 Jun;77:793–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H. Cytotoxicity and suckling mouse reactivity of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from human sources. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Oct;27(10):1019–1027. doi: 10.1139/m81-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., Sotman S. Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Takeuchi A., Gangarosa E. J., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P. Pathogenesis of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) dysentery. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):261–270. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Popoff M., Wadstrom T. Aeromonas hydrophila in acute diarrheal disease: detection of enterotoxin and biotyping of strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):96–100. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.96-100.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makin T. J., Tzipori S. Inexpensive techniques for the production and maintenance of gnotobiotic piglets, calves and lambs. Aust Vet J. 1980 Aug;56(8):353–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1980.tb09558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeeley D., Ivy P., Craft J. C., Cohen I. Plesiomonas: biology of the organism and diseases in children. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. R., Johnson P. C., DuPont H. L., Satterwhite T. K., Wood L. V. Lack of correlation between known virulence properties of Aeromonas hydrophila and enteropathogenicity for humans. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):62–65. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.62-65.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Hardy J. W., Hug M. I., Echeverria P., Falkow S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene encoding a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1167-1174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S. Pathological changes in the small intestine of neonatal pigs infected with a pig reovirus-like agent (rotavirus). J Comp Pathol. 1977 Jul;87(3):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(77)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitarangsi C., Echeverria P., Whitmire R., Tirapat C., Formal S., Dammin G. J., Tingtalapong M. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides: prevalence among individuals with and without diarrhea in Thailand. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.666-673.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt J. F., George W. L. Plesiomonas shigelloides-associated diarrhea. JAMA. 1985 Jun 14;253(22):3294–3295. doi: 10.1001/jama.253.22.3294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristaino P. A., Levine M. M., Young C. R. Improved GM1-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):808–815. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.808-815.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Tzipori S., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., Prpic J. K. The pathogenesis of Yersinia enterocolitica infection in gnotobiotic piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):297–308. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutala W. A., Sarubi F. A., Jr, Finch C. S., McCormack J. N., Steinkraus G. E. Oyster-associated outbreak of diarrhoeal disease possibly caused by Plesiomonas shigelloides. Lancet. 1982 Mar 27;1(8274):739–739. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92647-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Shigella sonnei plasmids: evidence that a large plasmid is necessary for virulence. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.75-83.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Singh S. J., Sen P. C. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):195–198. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraswathi B., Agarwal R. K., Sanyal S. C. Further studies on enteropathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides. Indian J Med Res. 1983 Jul;78:12–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Sack R. B., Froehlich J. L. Simple adult rabbit model for Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):739–747. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.739-747.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. R. Immunoperoxidase techniques: practical and theoretical aspects. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Mar;102(3):113–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Brose E. C. Restriction endonuclease mapping of R27 (TP117), an incompatibility group HI subgroup 1 plasmid from Salmonella typhimurium. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):75–77. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Echeverria P., Blaser M. J., Pitarangsi C., Blacklow N., Cross J., Weniger B. G. Polymicrobial aetiology of travellers' diarrhoea. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):381–383. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto T., Kinoshita Y., Shimada T., Sakazaki R. Two epidemics of diarrhoeal disease possibly caused by Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Apr;80(2):275–280. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Chandler D., Smith M., Makin T., Halpin C. Experimental colibacillosis in gnotobiotic piglets exposed to 3 enterotoxigenic serotypes. Aust Vet J. 1982 Sep;59(3):93–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1982.tb02736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., McCartney E., Lawson G. H., Rowland A. C., Campbell I. Experimental infection of piglets with cryptosporidium. Res Vet Sci. 1981 Nov;31(3):358–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Robins-Browne R. M., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., McCartney E. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli enteritis: evaluation of the gnotobiotic piglet as a model of human infection. Gut. 1985 Jun;26(6):570–578. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandepitte J., Makulu A., Gatti F. Plesiomonas shigelloides. Survey and possible association with diarrhoea in Zaïre. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1974;54(6):503–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Graevenitz A., Mensch A. H. The genus aeromonas in human bacteriology report of 30 cases and review of the literature. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 1;278(5):245–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802012780504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]