Abstract
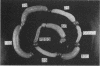
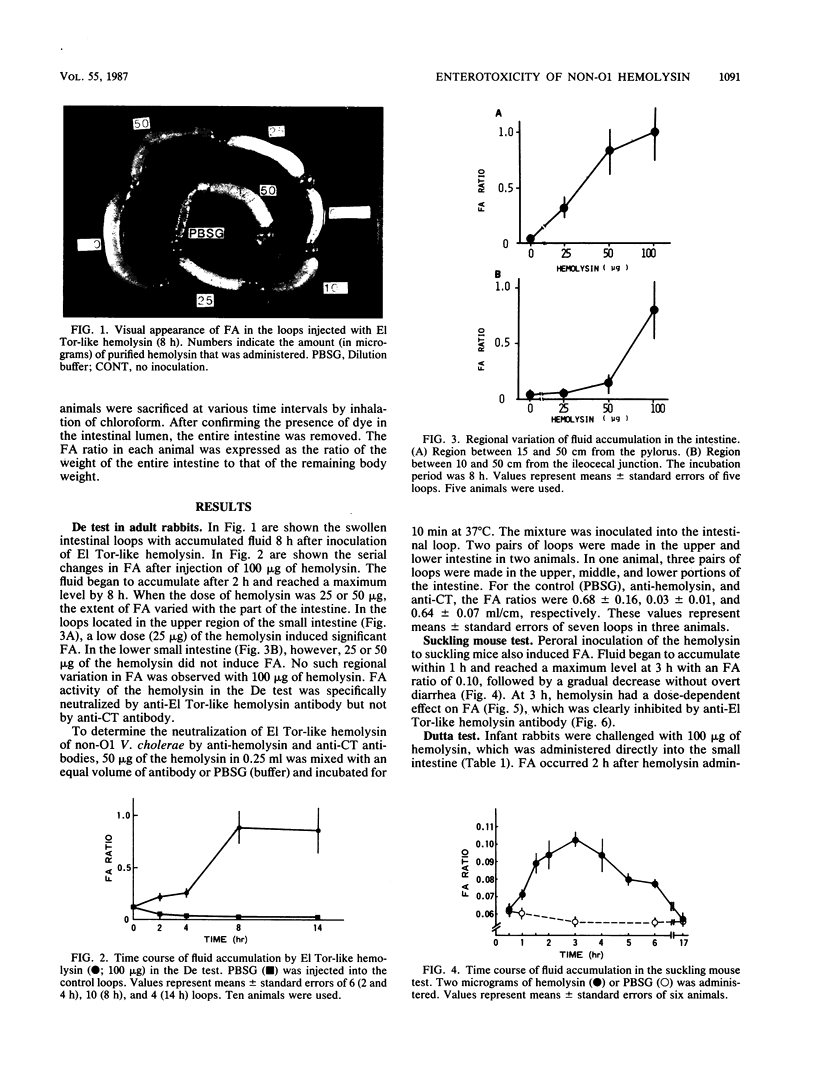
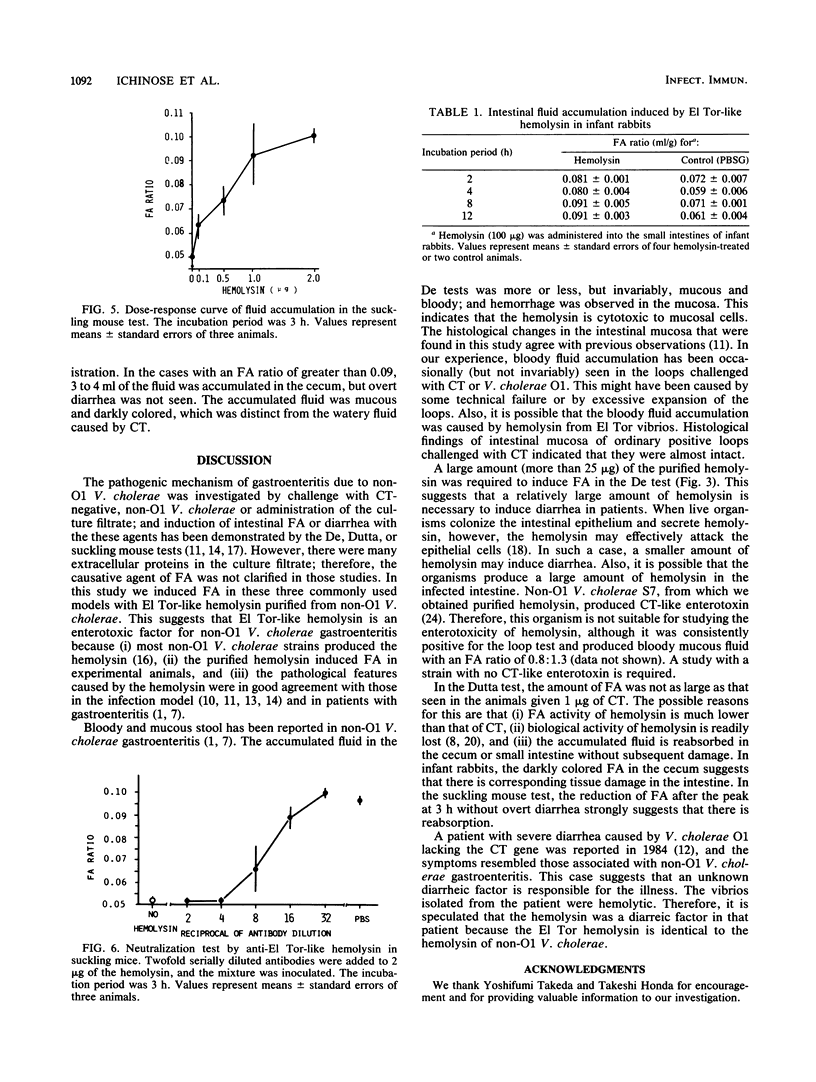
The enterotoxicity of an El Tor-like hemolysin purified from non-O1 Vibrio cholerae was investigated. Fluid accumulation was induced by injection of purified hemolysin into the ligated intestinal loops in adult rabbits (De test), intraintestinal administration in infant rabbits (Dutta test), and oral inoculation in suckling mice. The accumulated fluid was invariably mucous and bloody, and a histological change in the mucosa was observed. These results suggest that the hemolysin is an enterotoxic factor that is responsible for non-O1 V. cholerae gastroenteritis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P., Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Production of cholera-like enterotoxin by a Vibrio cholerae non-O1 strain isolated from the environment. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.90-97.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTTA N. K., HABBU M. K. Experimental cholera in infant rabbits: a method for chemotherapeutic investigation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1955 Jun;10(2):153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1955.tb00074.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Finkelstein R. A. Purification and characterization of a hemolysin produced by Vibrio cholerae biotype El Tor: another toxic substance produced by cholera vibrios. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1020-1027.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Hollis D. G., Gangarosa E. J., Weaver R. E. Non-cholera vibrio infections in the United States. Clinical, epidemiologic, and laboratory features. Ann Intern Med. 1978 May;88(5):602–606. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-5-602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsow C. M., Newman F. S. Comparison of hemolysin, hemolysin-destructive factor and hemodigestive enzyme production by strains of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio cholerae type El Tor. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1968 Winter;26(4):507–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of environmental and nontoxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.661-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden J. M., McCardell B. A., Shah D. B. Cytotoxin production by members of genus Vibrio. Lancet. 1984 Nov 24;2(8413):1217–1218. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden J. M., Nematollahi W. P., Hill W. E., McCardell B. A., Twedt R. M. Virulence of three clinical isolates of Vibrio cholerae non-O-1 serogroup in experimental enteric infections in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):616–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.616-619.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Picardi J. L., Lieb S., Lee J. V., Roberts A., Hood M., Gunn R. A., Blake P. A. Isolation of nontoxigenic Vibrio cholerae O group 1 from a patient with severe gastrointestinal disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):296–297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.296-297.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Seidler R. J. Medium-dependent production of extracellular enterotoxins by non-O-1 Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio mimicus, and Vibrio fluvialis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):228–231. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.228-231.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Seidler R. J., Rollins D. M., Joseph S. W. Vibrio factors cause rapid fluid accumulation in suckling mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1083–1091. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1083-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oashi M., Shimada T., Fukumi H. In vitro production of enterotoxin and hemorrhagic principle by Vibrio cholerae, NAG. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1972 Jun;25(3):179–194. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.25.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Fedorka-Cray P. J., Pettebone P. Colonization of the rabbit small intestine by clinical and environmental isolates of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio mimicus. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1175–1183. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1175-1183.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake A., Yamamoto M. Hemolysin-destructive factor of Vibrio cholerae (Vibrio comma). J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):461–462. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.461-462.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Al-Omani M., Honda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae hemolysin: purification, partial characterization, and immunological relatedness to El Tor hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):192–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.192-196.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Ichinose Y., Nakasone N., Tanabe M., Nagahama M., Sakurai J., Iwanaga M. Identity of hemolysins produced by Vibrio cholerae non-O1 and V. cholerae O1, biotype El Tor. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):927–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.927-931.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Craig J. P. Evidence that a non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produces enterotoxin that is similar but not identical to cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.896-901.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Craig J. P. Purification and some properties of a non-o1 Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin that is identical to cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1128–1135. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1128-1135.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinnaka Y., Carpenter C. C., Jr An enterotoxin produced by noncholera vibrios. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1972 Dec;131(6):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]