Abstract
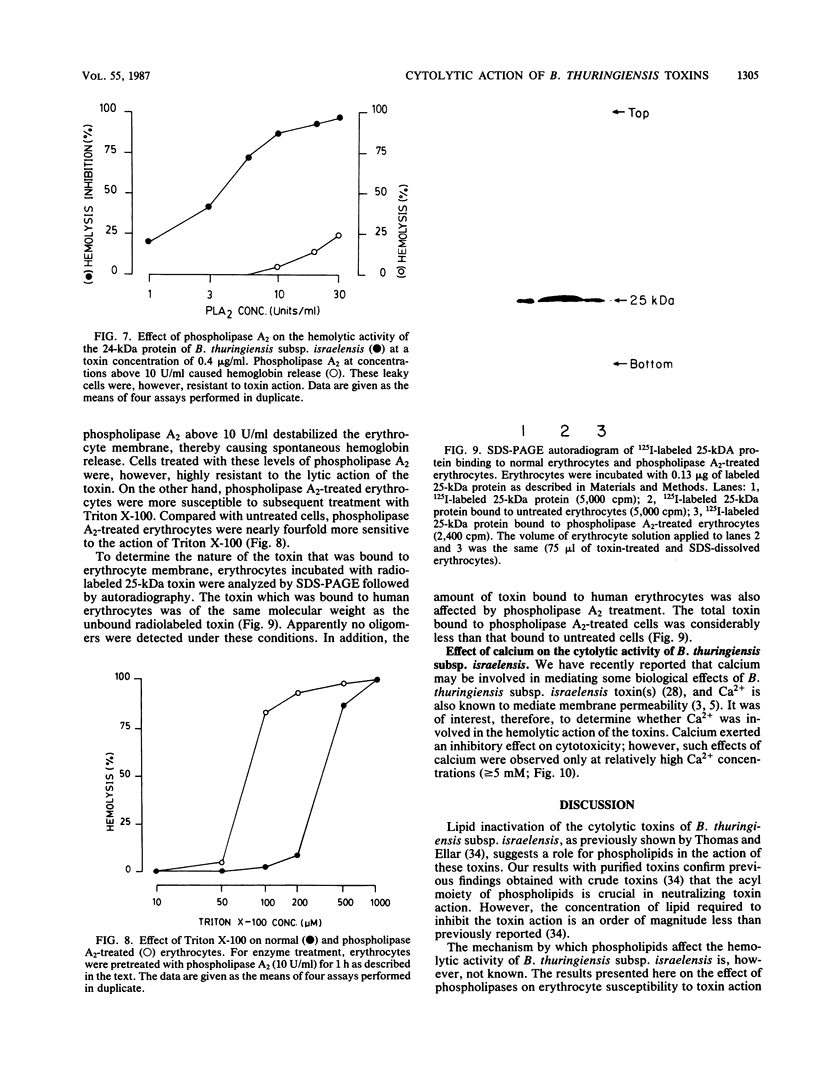
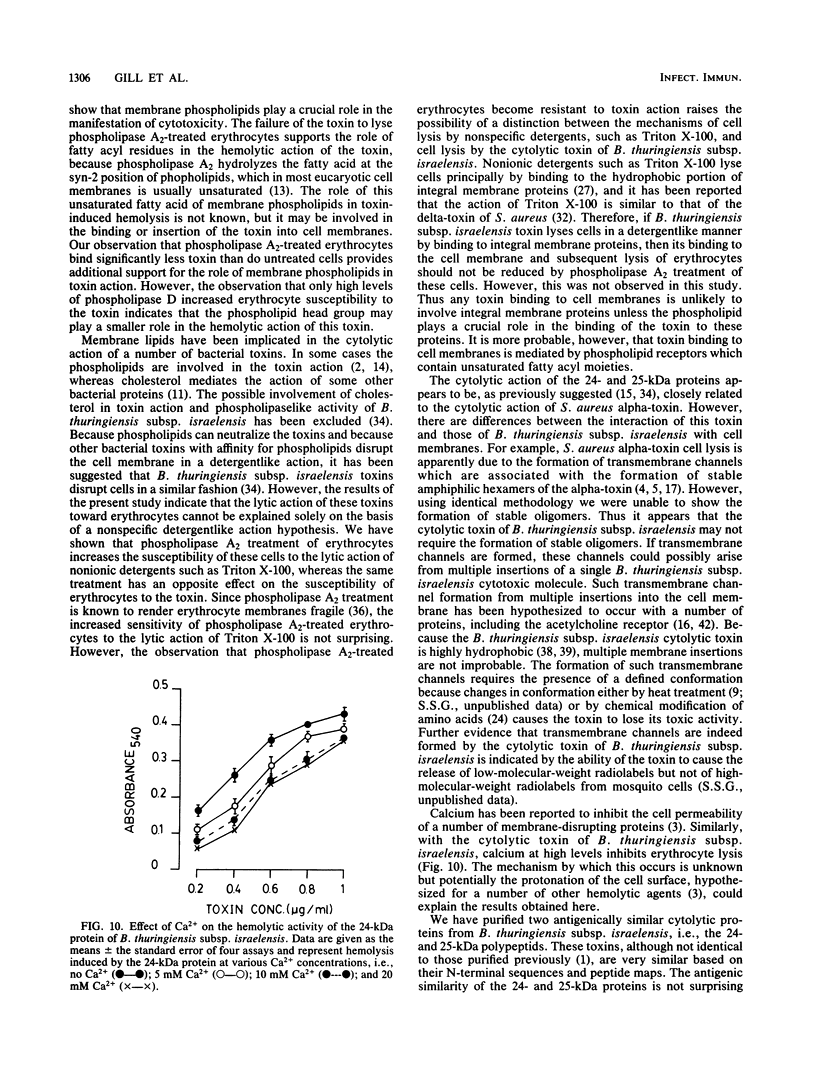
Two toxic polypeptides of 24 and 25 kilodaltons (kDa) were purified from parasporal proteinaceous crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Both of these polypeptides, which are antigenically similar and have identical N terminals, lysed human erythrocytes and cultured mosquito cells. Although the 24-kDa peptide was more toxic than the 25-kDa peptide, both were less toxic than the crude alkali-solubilized crystal toxin. However, a 1:1 mixture of these 24- and 25-kDa proteins was more toxic than either of these polypeptides individually, indicating a possible interaction between these proteins at the cell membrane. Both the 24- and the 25-kDa proteins were inactivated by aqueous suspensions of dioleolylphosphatidylcholine, indicating the involvement of phospholipids in the cytotoxic action of these toxins. Thus the role of cell membrane phospholipids in mediating the toxin action was studied by using phospholipases as probes. Treatment of erythrocytes with high levels of phospholipase D increased their susceptibility to the toxin; however, phospholipase A2-treated erythrocytes were less susceptible to the toxin. These erythrocytes also bound less 125I-labeled 25-kDa toxin. These results support the role of fatty acyl residues at the syn-2 position of membrane phospholipids in toxin action. The cytolytic toxin of B. thuringiensis subsp. israelensis is thought to damage cell membranes in a detergentlike manner. However, there was a difference between the cytolytic action of this toxin and that of a nonionic detergent such as Triton X-100 because phospholipase A2-treated erythrocytes were more susceptible to Triton X-100, whereas such erythrocytes were less sensitive to the toxin. Thus, the cytolytic toxin apparently did not act as a nonspecific detergent, but rather interacted with phospholipid receptors on the cell membrane. Such an interaction of the toxin with phospholipid receptors probably results in the increased cell permeability, thereby causing cell lysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. L., Rohrmann G. F., Beaudreau G. S. Delta endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):39–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.39-46.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangham A. D., Standish M. M., Weissmann G. The action of steroids and streptolysin S on the permeability of phospholipid structures to cations. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):253–259. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford C. L., Alder G. M., Menestrina G., Micklem K. J., Murphy J. J., Pasternak C. A. Membrane damage by hemolytic viruses, toxins, complement, and other cytotoxic agents. A common mechanism blocked by divalent cations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9300–9308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Füssle R., Tranum-Jensen J. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: oligomerization of hydrophilic monomers to form amphiphilic hexamers induced through contact with deoxycholate detergent micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Mechanism of complement cytolysis and the concept of channel-forming proteins. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):311–324. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles J. F., de Barjac H. Action des cristaux de Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis sur l'intestin moyen des larves de Aedes aegypti L., en microscopie électronique. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Mar-Apr;134A(2):197–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. L., Bernheimer A. W. Role of cholesterol in the action of cereolysin on membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Buckingham L. Effect of streptolysin S on liposomes. Influence of membrane lipid composition on toxin action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 20;648(1):6–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M. Amphipathic analysis and possible formation of the ion channel in an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur S., Gill S. S. Distribution and nature of epoxide hydrolase activity in subcellular organelles of mouse liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 15;35(8):1299–1308. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin B., Chiu D. Membrane phospholipid organization in pathologic human erythrocytes. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;97:137–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfannenstiel M. A., Couche G. A., Muthukumar G., Nickerson K. W. Stability of the larvicidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis: amino acid modification and denaturants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Nov;50(5):1196–1199. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.5.1196-1199.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson K. D., Nishimoto A. Y. Stimulation of Na+-Ca2+ exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles by phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):16–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Helenius A., Garoff H. Solubilization of the membrane proteins from Semliki Forest virus with Triton X100. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 15;80(1):119–133. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G. J., Schouest L. P., Jr, Gill S. S. Action of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis delta-endotoxin on the ultrastructure of the house fly larva neuromuscular system in vitro. J Invertebr Pathol. 1986 Mar;47(2):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(86)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Comparative properties and methods of preparation of lipid vesicles (liposomes). Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:467–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Determination of toxin-induced leakage of different-size nucleotides through the plasma membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):640–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.640-648.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. E., Ellar D. J. Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis crystal delta-endotoxin: effects on insect and mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Sci. 1983 Mar;60:181–197. doi: 10.1242/jcs.60.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. E., Ellar D. J. Mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis insecticidal delta-endotoxin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 18;154(2):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Dullemans A. M., van Workum M. E., Visser B. Molecular cloning and the nucleotide sequence of the Mr 28 000 crystal protein gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8207–8217. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. S., Ellar D. J. Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis delta-endotoxin. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the transcripts in Bacillus thuringiensis and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90417-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. F., Ralston E., Blake J., Ramachandran J., Hall Z. W., Stroud R. M. Topological mapping of acetylcholine receptor: evidence for a model with five transmembrane segments and a cytoplasmic COOH-terminal peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):626–630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]