Abstract
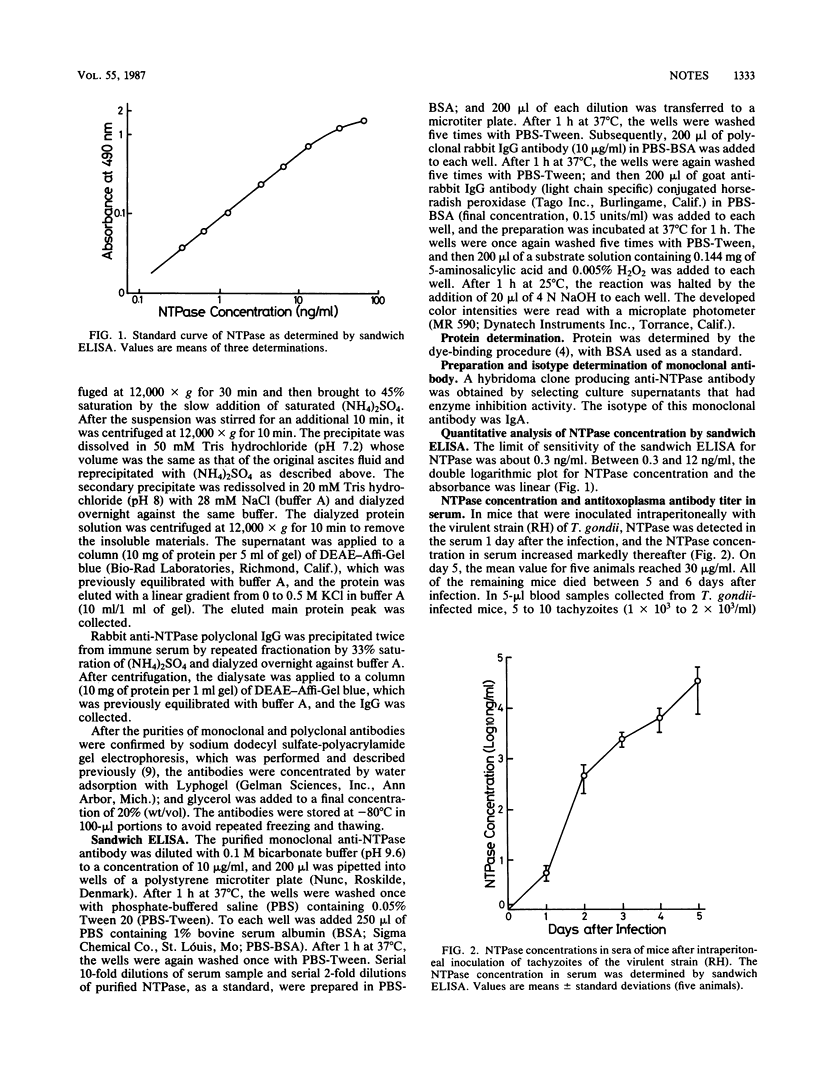
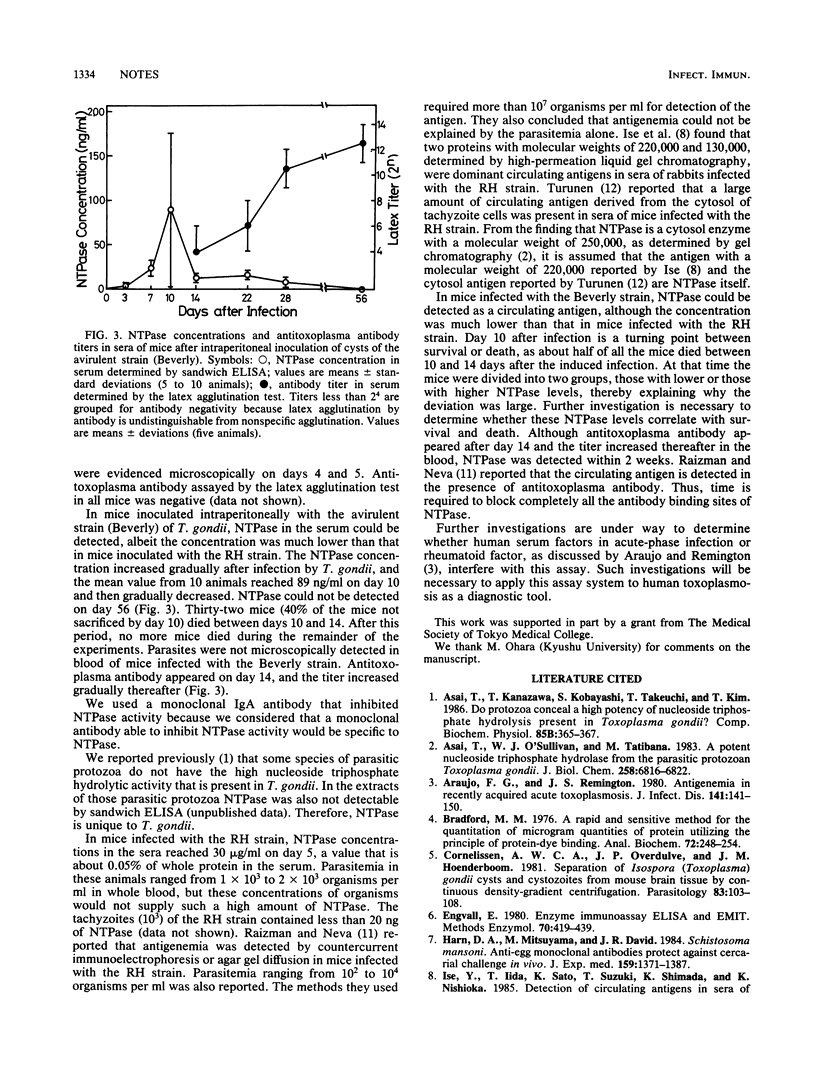
The nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase, which is present in the tachyzoite form of Toxoplasma gondii, was detected as a circulating antigen in sera of mice infected with a virulent (RH) or an avirulent (Beverly) strain of T. gondii. The enzyme was detected with a monoclonal antibody incorporated into an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The lower limit of sensitivity of the assay was about 0.3 ng/ml, and standard assays provided a linear plot of nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase concentration over a range of 0.3 to 12 ng/ml. In mice inoculated intraperitoneally with tachyzoites of the RH strain, nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase emerged in the serum 1 day after injection, and then the concentration increased and reached a value of 30 micrograms/ml on day 5. In mice inoculated intraperitoneally with cysts of the Beverly strain, nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase was detected at day 3 after injection, and a peak concentration of 89 ng/ml was seen on day 10. The concentration of enzyme decreased thereafter, and the enzyme disappeared from the circulation on day 56.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. Antigenemia in recently acquired acute toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):144–150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asai T., Kanazawa T., Kobayashi S., Takeuchi T., Kim T. Do protozoa conceal a high potency of nucleoside triphosphate hydrolysis present in Toxoplasma gondii? Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1986;85(2):365–367. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(86)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asai T., O'Sullivan W. J., Tatibana M. A potent nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase from the parasitic protozoan Toxoplasma gondii. Purification, some properties, and activation by thiol compounds. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6816–6822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen A. W., Overdulve J. P., Hoenderboom J. M. Separation of Isospora (Toxoplasma) gondii cysts and cystozoites from mouse brain tissue by continuous density-gradient centrifugation. Parasitology. 1981 Aug;83(Pt 1):103–108. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000050071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E. Enzyme immunoassay ELISA and EMIT. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):419–439. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harn D. A., Mitsuyama M., David J. R. Schistosoma mansoni. Anti-egg monoclonal antibodies protect against cercarial challenge in vivo. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1371–1387. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ise Y., Iida T., Sato K., Suzuki T., Shimada K., Nishioka K. Detection of circulating antigens in sera of rabbits infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):269–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.269-272.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenschmidt E. G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of soluble Toxoplasma gondii antigen in acute-phase toxoplasmosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;4(5):488–492. doi: 10.1007/BF02014430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raizman R. E., Neva F. A. Detection of circulating antigen in acute experimental infections with Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):44–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turunen H. J. Detection of soluble antigens of Toxoplasma gondii by a four-layer modification of an enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):768–773. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.768-773.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L. Production of antisera with small doses of immunogen: multiple intradermal injections. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Knapen F., Panggabean S. O. Detection of circulating antigen during acute infections with Toxoplasma gondii by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):545–547. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.545-547.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



