Abstract
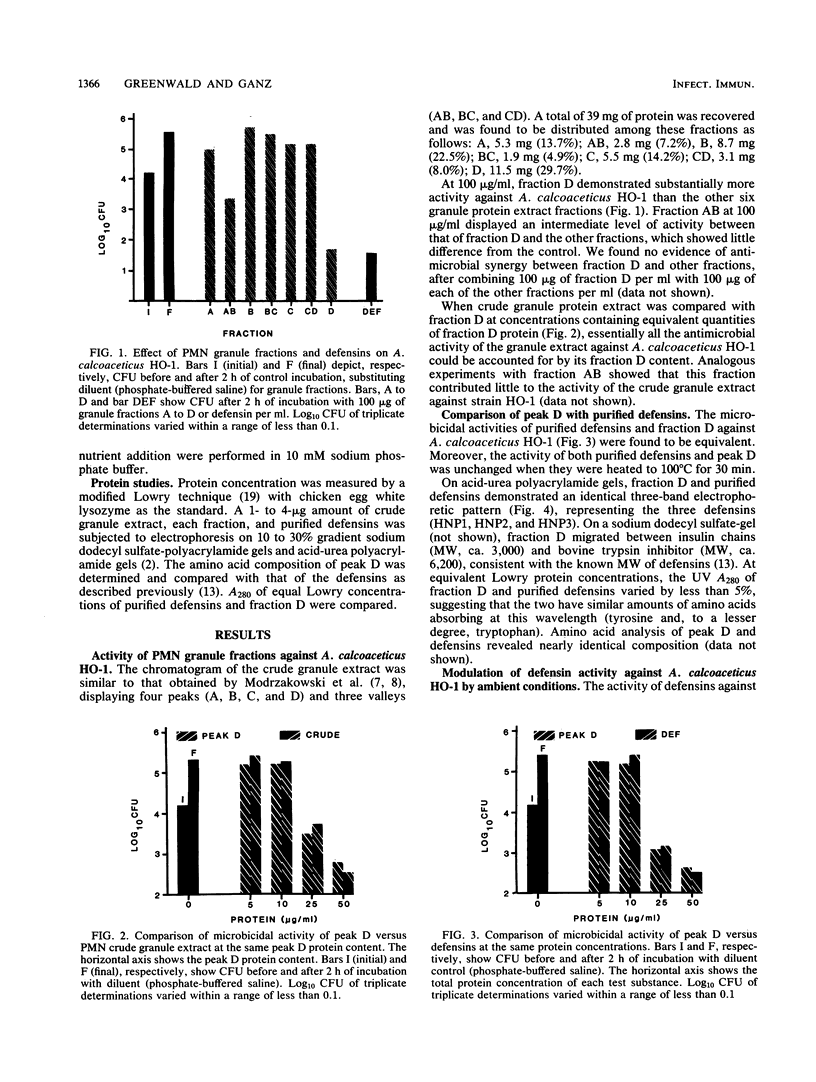
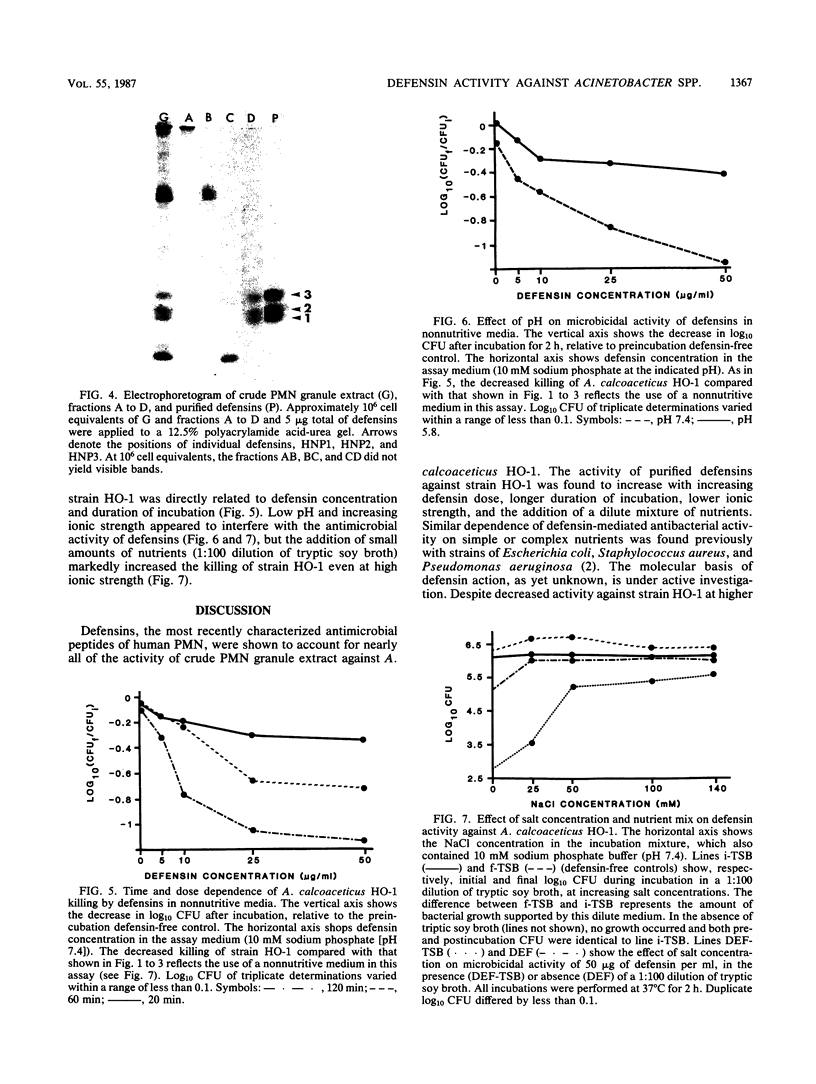
An acid extract of human neutrophil granules was fractionated on a Sephadex G-100 column and tested for microbicidal activity against Acinetobacter calcoaceticus HO-1 as described previously (M.C. Modrzakowski and C. M. Paranavitana, Infect. Immun. 32:668-674, 1981). The low-molecular-weight protein fraction, peak D, accounted for about 30% of the protein and nearly all of the activity of the crude extract against strain HO-1. Peak D protein proved to be a mixture of the three human defensin peptides HNP1, HNP2, and HNP3. Purified defensins reproduced the microbicidal activity of peak D. The data suggest that defensins could play a major role in the killing of A. calcoaceticus by human neutrophils.
Full text
PDF

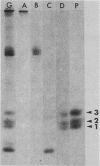
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elsbach P., Weiss J. A reevaluation of the roles of the O2-dependent and O2-independent microbicidal systems of phagocytes. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):843–853. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.5.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Antimicrobial activity of phagocyte granule proteins. Semin Respir Infect. 1986 Jun;1(2):107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovde C. J., Gray B. H. Characterization of a protein from normal human polymorphonuclear leukocytes with bactericidal activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):142–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.142-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ladra K. M. Fungicidal components of mammalian granulocytes active against Cryptococcus neoformans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):96–99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ladra K. M., Hake R. B. Nonoxidative fungicidal mechanisms of mammalian granulocytes: demonstration of components with candidacidal activity in human, rabbit, and guinea pig leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1226–1234. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1226-1234.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrzakowski M. C., Cooney M. H., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. Bactericidal activity of fractionated granule contents from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):587–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.587-591.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrzakowski M. C., Paranavitana C. M. Bactericidal activity of fractionated granule contents from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: role of bacterial membrane lipid. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):668–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.668-674.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Antibacterial activity of cationic proteins from human granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1118–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Cooney M. H., Spitznagel J. K. Bactericidal activity of specific and azurophil granules from human neutrophils: studies with outer-membrane mutants of Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):131–137. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.131-137.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Cooney M. H., Spitznagel J. K. Susceptibility of lipopolysaccharide mutants to the bactericidal action of human neutrophil lysosomal fractions. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.145-151.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Cohen M. S. The microbicidal mechanisms of human neutrophils and eosinophils. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):565–598. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S., Ganz T., Schilling J. W., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of three human neutrophil defensins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1436–1439. doi: 10.1172/JCI112121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic antimicrobial proteins isolated from human neutrophil granulocytes in the presence of diisopropyl fluorophosphate. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):29–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.29-35.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Onunka V. C., Martin L. E. Antigonococcal activity of human neutrophil cathepsin G. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):184–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.184-188.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smego R. A., Jr Endemic nosocomial Acinetobacter calcoaceticus bacteremia. Clinical significance, treatment, and prognosis. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Dec;145(12):2174–2179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K. Nonoxidative antimicrobial reactions of leukocytes. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1984;14:283–343. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4862-8_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Olsson I., Odeberg H. Purification and characterization of a potent bactericidal and membrane active protein from the granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2664–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUCKER-FRANKLIN D., HIRSCH J. G. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON THE DEGRANULATION OF RABBIT PERITONEAL LEUKOCYTES DURING PHAGOCYTOSIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:569–576. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]