The postsynaptic density (PSD) is a macromolecular signaling assembly anchored in the postsynaptic membrane of nerve cells. It contains receptors, scaffold and signaling molecules, and cytoskeletal elements. Mass spectrometry of isolated PSDs reveals several hundred protein species [1]. The postsynaptic signal pathways have a major role in controlling synaptic strength, and ultimately may underlie the mechanisms involved in learning and memory. The fundamental molecular organization of the PSD in cultured hippocampal spines has recently been resolved by EM tomography. Three-dimensional reconstructions show an orthogonal assembly of horizontal scaffolding molecules associated with the vertically oriented filaments that in turn associate with major transmembrane structures [2]. Now that core individual proteins can be visualized with tomography, methods are needed to identify them. Structures can be matched with predicted sizes and shapes of proteins at specific cellular compartment, but a direct identifying label would be reassuring. Here, we label a key scaffolding molecule in the postsynaptic density, PSD-95 [3], by combining electron microscopic tomography with immunolabeling on cultured rat hippocampal neurons prepared by high pressure freezing, freeze substitution and cryoembedding. Dissociated cultured neurons grown on astrocytes in a 3 mm gold chamber for three weeks were initial fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and incubated with primary antibody to PSD-95, followed by a Nanogold conjugated secondary antibody. After a short (6–8 min) silver enhancement, the cells underwent preparation by high pressure freezing, and Lowicryl HM-20 sections of thickness 100–200 nm were cut en face, photographed for dual axis tomography. We find that PSD-95 molecules can be individually labeled in the tomographic reconstructions. Our methods could have broad applications for identifying individual molecules in large protein complexes in neuronal cells.
References
- 1.Cheng DM, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5:1158. doi: 10.1074/mcp.D500009-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen X, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008 in press. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kim E, Sheng M. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:771. doi: 10.1038/nrn1517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Work supported by NINDS, NIBIB intramural programs. We thank Dr. Susan Cheng (NINDS) for PSD-95 labeling and Fig. 1 (A–C).
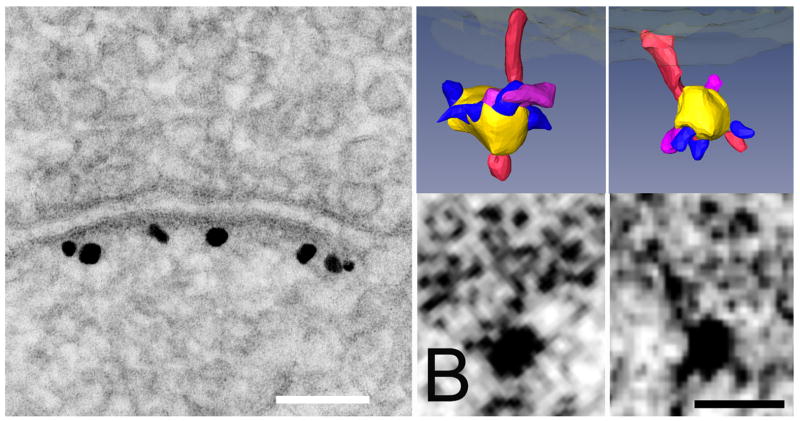
Fig. 1.
(A) Conventional enhanced label for PSD-95 showing high specificity of the polyclonal antibody made to the region of PSD-95 lying between PDZ2 and PDZ3. Scale bar: 100 nm. (B) Parallel specimens of hippocampal culture were silver enhanced for shorter times before preparation for tomography by freeze-substitution, resulting in smaller and less frequent silver grains. Label associated with filaments in single tomographic slices is shown below, and surface renderings above. Vertical filaments are rendered in red, and silver-enhanced gold particles are rendered in yellow. Structures rendered in purple are the correct size to represent the primary antibody contacting the vertical filaments. Smaller structures rendered in blue appear to represent the secondary Fab fragment protruding from the silver encrustation around the original gold particle. Scale bar: 10 nm.