Abstract
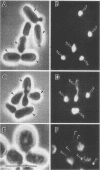
The total DNA per cell and DNA synthetic cycle phases were determined by flow cytometry in five Candida isolates including three species: Candida albicans 208R1, Candida tropicalis ATCC 750, and Candida parapsilosis 970, 3138, and ATCC 22019. The cells were prepared for flow cytometry by fixation in Carnoy fixative followed by staining with mithramycin. Marked but stable and reproducible inter- and intraspecific differences in total DNA per cell of stationary-phase cultures were found which did not correlate directly to diphenylamine estimates of the same parameter. This discrepancy was resolved by mathematically converting flow cytometry data into diphenylamine data. The reason for the discrepancy was found in studies of the DNA synthetic cycle of these yeasts: a large but isolate-specific variable proportion of the population is arrested in the S and G2-M phases after the culture passes from exponential to stationary phase. Histograms of exponential-growth-phase Candida isolates demonstrate that the majority of the population is in the G2-M phase of the DNA synthetic cycle. The DNA content of the C. tropicalis and C. parapsilosis isolates studied is as high as or higher than that of C. albicans. Extranuclear fluorescent particles were observed in the C. tropicalis isolate. No equivalent particles could be detected in the other four Candida isolates. The nature of the particles is unknown.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beach D., Rodgers L., Gould J. ran1+ controls the transition from mitotic division to meiosis in fission yeast. Curr Genet. 1985;10(4):297–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00365626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak J. A., Hall T. E., Crane M. S., Engel J. C., McDaniel J. P., Uriegas R. Trypanosoma cruzi: flow cytometric analysis. I. Analysis of total DNA/organism by means of mithramycin-induced fluorescence. J Protozool. 1982 Aug;29(3):430–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb05427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak J. A. The natural heterogeneity of Trypanosoma cruzi: biological and medical implications. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(4):357–371. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J. W. Opportunistic fungal infections in patients with neoplastic disease. Am J Med. 1984 Mar;76(3):458–463. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90665-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert R. D., Jett J. H., Salzman G. C. Modular electronics for flow cytometry and sorting: the LACEL system. Cytometry. 1981 Mar;1(5):337–341. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990010506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter K. J., Eipel H. E. Microbial determinations by flow cytometry. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Aug;113(2):369–375. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerker M., Van Dilla M. A., Brunsting A., Kratohvil J. P., Hsu P., Wang D. S., Gray J. W., Langlois R. G. Is the central dogma of flow cytometry true: that fluorescence intensity is proportional to cellular dye content? Cytometry. 1982 Sep;3(2):71–78. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990030202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Cortelyou M. W., Kirsch D. R. Integrative transformation of Candida albicans, using a cloned Candida ADE2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke P. A., Kugleman B., Morimoto H., Jacobs E. C., Ellison J. Fluorescent staining of fungal nuclei with a benzimidazol derivative. J Cell Sci. 1978 Feb;29:77–84. doi: 10.1242/jcs.29.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Carpentier F., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Fungemia in the immunocompromised host. Changing patterns, antigenemia, high mortality. Am J Med. 1981 Sep;71(3):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaiya A. F., Sogin S. J. Ploidy determination of Canadida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1043–1049. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1043-1049.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaiya A. F., Steed J. R., Sogin S. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid-deficient strains of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1284–1290. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1284-1290.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggsby W. S., Torres-Bauza L. J., Wills J. W., Townes T. M. DNA content, kinetic complexity, and the ploidy question in Candida albicans. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):853–862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuette W. H., Shackney S. E., Plowman F. A., Tipton H. W., Smith C. A., MacCollum M. A. Design of flow chamber with electronic cell volume capability and light detection optics for multilaser flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1984 Nov;5(6):652–656. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990050616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. L. Rapid nuclear staining method for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1339–1341. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1339-1341.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. C., Reich E., Goldberg I. H. Base specificity in the interaction of polynucleotides with antibiotic drugs. Science. 1965 Sep 10;149(3689):1259–1263. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3689.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Magee P. T. Natural heterozygosity in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):896–903. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.896-903.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Markie D. M., Simpkin K. G., Poulter R. M. Instability of Candida albicans hybrids. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1131–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1131-1136.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Partridge R. M., Magee P. T. Heterozygosity and segregation in Candida albicans. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(1):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00267358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Fennell D. J. The use of fluorescent DNA-binding agent for detecting and separating yeast mitochondrial DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:335–351. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60963-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]