Abstract
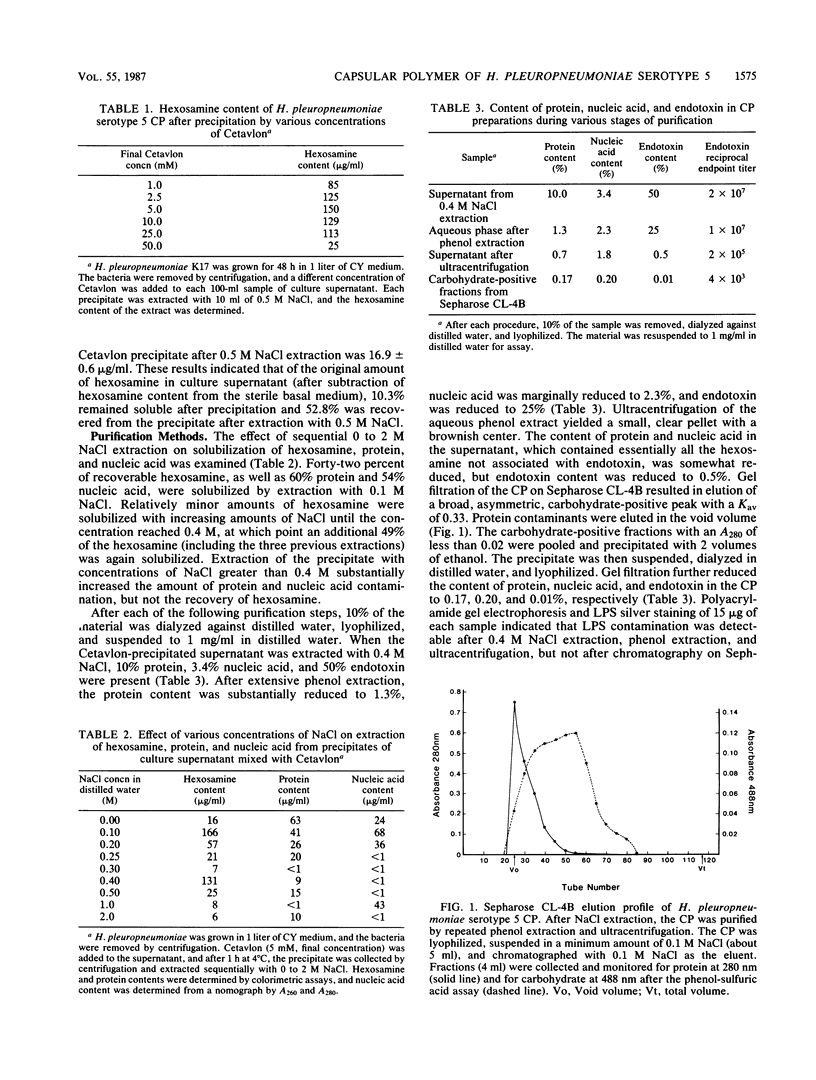
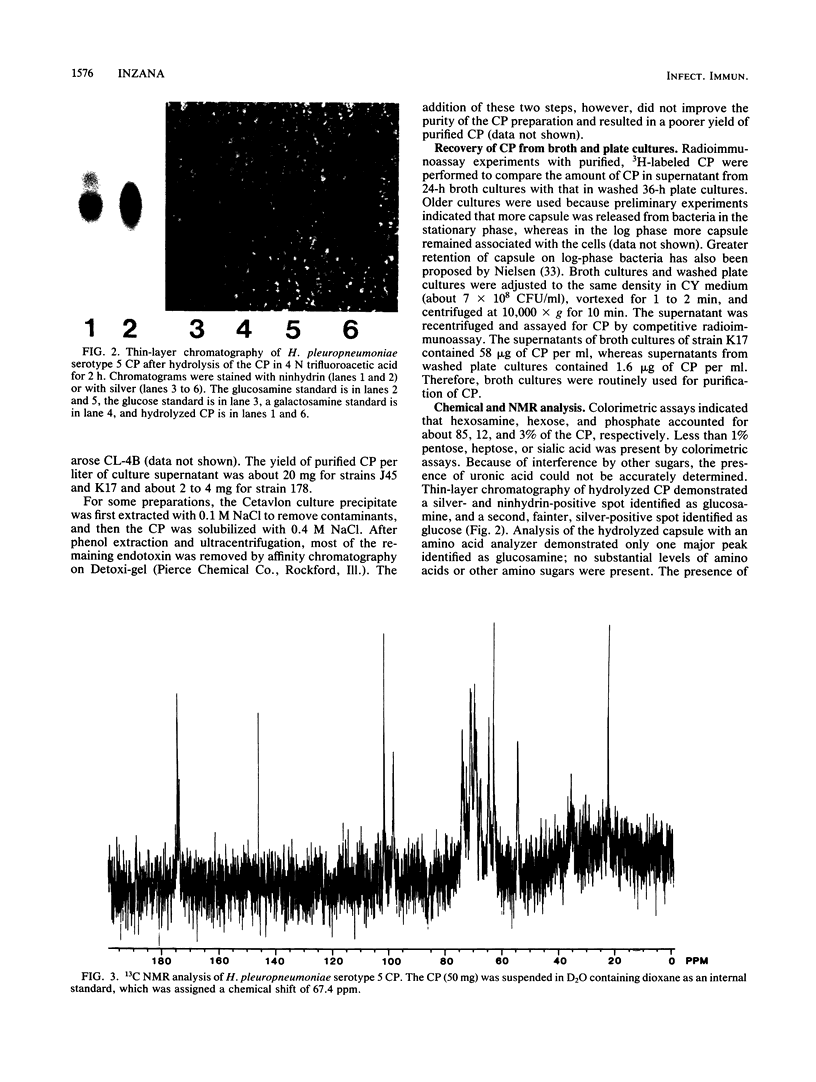
The capsular polymer (CP) of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotype 5 was purified, and its chemical composition was analyzed. Radioimmunoassay experiments showed that the maximum amount of CP could be obtained from broth cultures of bacteria in the late stationary phase, rather than from bacteria washed off agar plates. The CP was precipitated from culture supernatant with 5 mM hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (Cetavlon) and solubilized with 0.4 M NaCl. Ninety percent of the CP in the culture supernatant was precipitated with Cetavlon, although some material remained insoluble after NaCl extraction. The CP was further purified by phenol extraction, ultracentrifugation, and Sepharose CL-4B gel filtration. The Kav of the CP from Sepharose CL-4B chromatography was 0.33. The CP preparation contained 85% hexosamine, 12% hexose, 3% phosphate, 0.17% protein, 0.20% nucleic acid, and 0.01% endotoxin. Thin-layer chromatography, an amino acid analyzer, and a glucose oxidase colorimetric kit were used to identify the sugar components of the hydrolyzed CP as glucosamine and glucose. Analysis of the native CP by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance indicated that amino, N-acetyl, and carboxyl groups were present and that the CP was a disaccharide.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman E., Brisson J. R., Perry M. B. Structural studies of the capsular polysaccharide from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotype 1. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;64(8):707–716. doi: 10.1139/o86-097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. Intrinsic tritium labeling of the capsular polysaccharide antigen of Haemophilus influenzae type B. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):866–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Pitt J., Smith D. H. Synthesis and release of polyribophosphate by Haemophilus influenzae type b in vitro. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):581–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.581-589.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Smith D. H. Isolation of the capsular polysaccharide from culture supernatant of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):472–477. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.472-477.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendixen P. H., Shewen P. E., Rosendal S., Wilkie B. N. Toxicity of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae for porcine lung macrophages, peripheral blood monocytes, and testicular cells. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):673–676. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.673-676.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Purification and vaccine potential of Klebsiella capsular polysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):225–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.225-230.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirks-Go S. I., Zanen H. C. Latex agglutination, counterimmunoelectrophoresis, and protein A co-agglutination in diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Dec;31(12):1167–1171. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.12.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I., Olander H. J. Isolation and biological characterization of two lipopolysaccharides and a capsular-enriched polysaccharide preparation from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1433–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I., Olander H. J. Resistance of C3H/HeJ mice to the effects of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):474–479. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.474-479.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C. A simplification of the radioactive antigen-binding test by a double label technique. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):910–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A. Evaluation of different antigens in the complement-fixation test for diagnosis of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae (parahaemolyticus) infections in swine. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Nov;40(11):1564–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A., Hurvell B., Biberstein E. L. Serologic studies of porcine strains of Haemophilus parahaemolyticus (pleuropneumoniae): antigenic specificity and relationship between serotypes. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Aug;39(8):1286–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A. Serologic studies on porcine strains of Haemophilus parahaemolyticus (pleuropneumoniae): extraction of type-specific antigens. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Apr;40(4):469–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Mathison B. Serotype specificity and immunogenicity of the capsular polymer of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotype 5. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1580–1587. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1580-1587.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen A. E., Bertram T. A. Morphological and biochemical comparison of virulent and avirulent isolates of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotype 5. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):419–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.419-424.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K., Nakai T., Sawata A. Efficacy of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae vaccine in pigs. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Apr;47(2):201–206. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K., Nakai T., Sawata A. Interaction between heat-stable hemolytic substance from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae and porcine pulmonary macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):563–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.563-570.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Lariviere S. Determination of antigenic specificity and relationship among Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotypes by an indirect hemagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):787–790. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.787-790.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J. Sur l'hémophilose du pore. 3. Différenciation sérologique de Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1971;216(4):487–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Pleuropneumonia of swine caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Studies on the protection obtained by vaccination. Nord Vet Med. 1976 Jul-Aug;28(7-8):337–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Serological characterization of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae (Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae) strains and proposal of a new serotype: serotype 10. Acta Vet Scand. 1985;26(4):581–585. doi: 10.1186/BF03546528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp V. J., Ross R. F., Erickson B. Z. Serotyping of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae by rapid slide agglutination and indirect fluorescent antibody tests in swine. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jan;46(1):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B. Vaccines for the prevention of encapsulated bacterial diseases: current status, problems and prospects for the future. Immunochemistry. 1978 Nov;15(10-11):839–854. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Boyd D. A. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):840–843. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.840-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. E. Aliphatic ammonium salts in the assay of acidic polysaccharides from tissues. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:145–197. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebunya T. N., Saunders J. R. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in swine: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jun 15;182(12):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Gilkerson E. Quantitation of glycosaminoglycan hexosamine using 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolone hydrazone hydrochloride. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):478–480. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFROM M. L., PATIN D. L., DELEDERKREMER R. M. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY ON MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE. J Chromatogr. 1965 Mar;17:488–494. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)99899-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. G., Rebers P. A. Procedure for determining heptose and hexose in lipopolysaccharides. Modification of the cysteine-sulfuric acid method. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]