Abstract
The role of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) in the pathogenesis of HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains controversial. By understanding the transition from benign to malignant, we studied the gene expression patterns in liver tissues at different stages, including normal, cirrhosis, and different HCC stages.
One hundred and eight liver tissue samples obtained from 88 distinct patients were studied (41 HCV-cirrhotic tissues, 17 HCV-cirrhotic tissues from patients with HCC, 47 HCV-HCC tissues). Differentially expressed genes (DEG) were studied using high-density oligonucleotide arrays. Among probe sets identified as differentially expressed via the F test, all pairwise comparisons were performed. Cirrhotic tissues with and without concomitant HCC were further evaluated and a classifier to predict whether the tissue type was associated with HCC was used. Differential expression profiles were analyzed using Interaction Networks and Functional Analysis.
Characteristics gene signatures were identified when normal tissue was compared to cirrhosis, cirrhosis vs. early HCC, and normal vs. HCC. Pathway analysis classified the cellular and biological functions of the DEG as related to cellular growth and proliferation, cell death and inflammatory disease in cirrhosis; cell death, cell cycle, DNA replication, and immune response in early HCCs; and cell death, cell growth and proliferation, cell cycle, and DNA repair in advanced HCCs.
Characteristics gene signatures were identified at different stages of HCV-HCC progression. A set of genes were identified to predict whether the cirrhotic tissue was associated with HCC.
Keywords: hepatocarcinogenesis, molecular markers, microarrays, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma
Introduction
According to the most recently available worldwide estimates, liver cancer is the 6th leading cancer type with 626,162 cases estimated in 2002, and is the 3rd leading cause of cancer death, with an estimated 598,321 deaths that same year (www-dep.iarc.fr) (1). The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the USA is increasing because of the increased prevalence of Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (2–4). Surgical resection and liver transplantation still represents the only potentially curative treatments for HCC (5–7). Since 80% of HCC patients in the USA have cirrhosis, optimum care requires the complex analysis of cancer stage to predict recurrence, and the determination of liver reserve to predict suitability of resection vs. total hepatic replacement to prevent death from liver failure (5,6,8,9).
A vast amount of information regarding genetic markers, genomic aberrations, as well as gene expression is being accumulated for the study of HCC (9–15). The major risk factors for HCC development are now well defined and some of the multiple steps involved in hepatocarcinogenesis have been elucidated in recent years (16, 17). Though an association between HCV infection and later development of HCC has been established, currently the actual mechanisms that lead to malignant transformation are largely unknown.
Molecular genetic analyses have shown that genomic changes accumulate during the development and progression of HCC (18–23). The molecular pathogenesis of HCC is very complex (18–25). Furthermore, different risk factors (viral infections, alcohol consumption, aflatoxin, hemochromatosis, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) are implicated in HCC development. Each of these scenarios involves different genetic and epigenetic alterations, chromosome aberrations, gene mutations and altered molecular pathways (18–25). Moreover, the study of the step-by-step oncogenic process is particularly difficult, due to the fact that samples from pre-neoplastic lesions can almost only be prospectively collected in transplant centers using the whole explanted liver. Despite these complexities, DNA microarrays have been used recently to profile global changes in gene expression in liver samples obtained from patients with HCC identifying subgroups of HCC that differ according to etiological factors (26), rate of recurrence (27), and intrahepatic metastasis (28), as well as novel molecular markers for HCC diagnosis (26–28). However, most of these studies identified genes that are related to limited aspects of tumor pathogenesis. In addition, the majority of these studies looked at the wide variety of HCC tumors. In this study we studied the genes involved in viral tumorogenesis and tumor initiation in HCV-induced HCC.
Methods
Samples
Samples were obtained from patients awaiting and undergoing liver transplantation at Virginia Commonwealth University, UNC, UCLA, University of Pennsylvania, and Northwestern University as part of the Adult to Adult Living Donor Liver Transplant Cohort Study (A2ALL; NIDDK 1U01DK62531). Laboratory techniques were centralized in the Molecular Transplant Research of the Division of Transplant at the Virginia Commonwealth University. The research protocol was approved by the respective institutional review boards, and informed consent was obtained in all cases. In addition, normal livers and tumor samples were also obtained through the Liver Tissue Cell Distribution System (NO1-DK-7-0004/HHSN26700700004C). Patient and sample information was obtained through the Data Coordinator Center (DCC) at the University of Michigan (A2ALL: Adult to Adult Living Donor Liver Transplant Cohort Study 1U01DK62531).
Sample Characteristics
This study was restricted to HCV infected patients. The characteristics of the samples are described in the Supplemental Table I. The study included 108 liver tissue samples obtained from 88 distinct patients, 41 HCV-cirrhotic tissues from patients without HCC, 17 cirrhotic tissues from patients with HCC, 47 HCV-HCC tissues. Thirteen patients with HCC-cirrhosis who provided both tumor and cirrhotic tissue, and 3 patients contributed with duplicate cirrhotic or tumor tissue for array processing. Also, 19 normal livers were included. Liver function and histopathology for these liver donors were shown to be normal. All 19 patients were seronegative for HCV Ab.
Sample Collection and Pathological Data
Liver tissue samples were collected in liquid nitrogen or RNA later solution (Ambion, Inc, Austin, TX), and stored at −80°C until use. Explanted livers were sliced at 4-5mm intervals and all suspicious nodules for HCC processed for light microscopy. Sections from the tumor/tumors were also fixed in formalin and processed for light microscopy. The size, multiplicity, grade, infiltration into adjacent liver, encapsulation, and vascular invasion (micrometer vs. millimeter portal or hepatic vein) was determined for all tumors. Histopathological classification of HCC was performed according to the Edmondson grading system; clinical stages were determined according to the American Tumor Study Group modified TNM classification mandated by the UNOS (29). In the HCC cases, only samples with at least 85% of tumor were further studied. The cirrhotic tissues from explanted livers were classified using Knodell score and Ishak grade (30).
RNA isolation, cDNA Synthesis and In Vitro Transcription for Labeled cRNA probe
The sample preparation protocol follows the Affymetrix GeneChip® Expression Analysis Manual (Santa Clara, CA). To ensure processing of samples with a high percent of tumor and minimal/no necrosis, 5 μm frozen section slides were made and stained with H&E for Pathologist evaluation to determine tumor cell percentage. After the evaluation, normal/necrotic tissue was macrodissected. Sections were performed and total RNA was extracted using TRIzol (Life Technologies, Rockville, MD).
Briefly, total RNA was reverse-transcribed using T7-polydT primer and converted into double-stranded cDNA (One-Cycle Target Labeling and Control Reagents, Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA), with templates being used for an in vitro transcription reaction to yield biotin-labeled antisense cRNA. The labeled cRNA was chemically fragmented and made into the hybridization cocktail according to the Affymetrix GeneChip protocol, which was then hybridized to HG-U133A (N=9) and HG-U133A 2.0 (N=134) GeneChips. The array image was generated by the high-resolution GeneChip® Scanner 3000 by Affymetrix® (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA). The data was analyzed using Affymetrix Microarray Suite Software, Version 5.0 and Bioconductor packages (31) available in the R programming environment (32). Information about quality control (QC) procedures performed provided in QC Supplemental Data.
Data analysis
To mitigate any effect due to GeneChip type, prior to obtaining probe set expression summaries, the 9 HG-U133A GeneChips and 115 HG-U133A 2.0 GeneChips were independently read into the R programming environment (32) using the affy Bioconductor package (31,33). Thereafter, probe level data from the two GeneChip types were merged by probe sequence using matchprobes package in R (34). Subsequently, the robust multiarray average method was used to obtain probe set expression summaries (35, 36).
Due to the lack of independence among the 124 GeneChips present since some patients contributed more than one sample, for each probe set, a mixed effects analysis of variance model was fit considering probe set expression as the response, tissue type (normal liver, HCV cirrhosis without HCC, HCV cirrhosis with HCC, HCV-HCC) as the fixed effect of interest, and including subject as a random effect term. A group means parameterization of tissue type was included as the fixed effect term to facilitate extraction of linear contrasts of interest. To set the P-value threshold at which probe sets would be declared significantly differentially expressed, we first examined the P-values from the F test for all Affymetrix control probe sets. Since the expectation is that control probe sets are not differentially expressed, we selected the minimum P-value among control probe sets as our threshold for declaring a probe set significant (37). All probe sets with a P-value from the F test less than this threshold were retained.
Thereafter, among probe sets identified as differentially expressed via the F test, all six pairwise comparisons were performed. The limma package was used to fit the mixed effects models using restricted maximum likelihood procedure and an empirical Bayes method was applied to moderate probe set standard errors by borrowing information across the entire set of probe sets (38).
In addition to assessing significance across the three diagnostic groups, we performed a Jockheere-Terpstra test for trend to identify whether gene expression was significantly increasing or decreasing as the tissue progressed from normal to cirrhosis to early HCV-HCC to advanced HCV-HCC (early HCV-HCC was defined as TNM stage T1N0M0 or T2N0M0 while advanced HCV-HCC was defined as T3N0M0 or T4N0M0 or T4N0M1). Prior to performing the hypothesis tests, the gene expression matrix was filtered to include only independent samples, so for patients contributing both HCV-HCC and HCV cirrhotic tissues, only the HCV-HCC sample was used.
For those with replicate samples from the same tissue, the observed correlation among replicates was high (r̂ = 0.944, 0.962, and 0.923) so that the average probe set intensities for two replicates was used in place of either individual CEL file. The SAGx package in the R programming environment was used in performing the non-parametric test for trend.
It was also of interest to compare the cirrhotic tissues with and without concomitant HCC. The 58 CEL files representing the cirrhotic tissues were read into the R programming environment and normalized together using quantile normalization, and RMA expression summaries were obtained. There were two patients who contributed replicate cirrhotic samples, therefore subject was included as a random effect term in the linear model. A group means parameterized linear model was fit and an empirical Bayes method was used to adjust probe set variance by borrowing information across the entire set of probe sets. P-values from the modulated t-statistics were then obtained. It is known that the Affymetrix control probe sets should not be differentially expressed, thus the minimum P-value among the control probe sets was selected as the threshold for identifying differentially expressed probe sets.
Interaction Networks and Functional Analysis
Gene ontology and gene interaction analyses were executed using Ingenuity Pathways Analysis tools 3.0 (IPA) (http://www.ingenuity.com). The gene lists containing Entrez GeneIDs as clone identifiers, as well as fold-change values from corresponding supervised analyses, were mapped to their corresponding gene object in the Ingenuity Pathways Knowledge Base (IPKB). These so-called focus genes were then used in the network generation algorithm, based on the list of molecular interactions in IPKB. Significance for the enrichment of the genes in a network with particular biologic functions was determined by the right-tailed Fisher's exact test, using a list of all the genes on the array as a reference set.
Validation of microarray results
We carried out a quantitative reverse transcriptase-“real time” PCR (QPCR) for EDF1 (endothelial differentiation-related factor 1), tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), cadherin 4 (CDH4), and tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3) mRNAs from the same RNAs samples that were subjected to microarray study. Total RNA was subjected to reverse transcription using TaqMan® Reverse Transcription Reagents (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Real-time PCR reactions then were carried out in an ABI Prism 7700 Sequence Detection System, using TaqMan® Gene Expression Assays (Applied Biosystems) (EDF1: Hs00610152_m1, TFPI: Hs00196731_m1, CDH4: Hs00899698_m1, and TNFAIP3: Hs00234713_m1). Data was analyzed according to the comparative cycle threshold (Ct) method and was normalized by two different housekeeping genes as it was recently recommended for studies including HCC tissues (39, 40) including β2-microglobulin (B2M) and TATA box binding protein (TBP) expression in each sample. Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) was calculated to examine the relation between microarray and real-time PCR results. P<0.05 were considered significant.
Results
Samples
Liver tissue samples were classified for the analysis as normal livers (N=19), HCV cirrhosis (N=41), early HCCs (T1N0M0 and T2N0M0, N=26), advanced HCCs (T3N0M0 and T4N0M0, N=13), and very advanced HCCs (T4N0M1, N=7). For some of the analysis, HCV-HCC samples were associated in the same group (HCV-HCC samples).
Identifying differentially expressed genes among different tissue groups
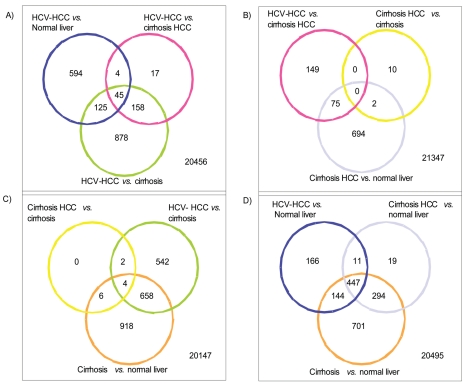
The minimum P-value among control probe sets which was used as our threshold was 1.037E-10. From this analysis, 2,262 probe sets were significantly differentially expressed among the four diagnostic groups (normal liver, HCV cirrhosis without HCC, HCV cirrhosis with HCC, HCV-HCC) (Figure-1).
Figure 1.
The gene expression matrix was filtered to include only the 2,262 probe sets represented in the Venn diagram illustrating the number of significant genes for the three pairwise comparisons. Thereafter, agglomerative hierarchical clustering using Ward’s method was applied to the filtered dataset using Pearson’s correlation as the similarity measure. Pink box: Normal livers, Yellow box: HCV-cirrhosis from patients without HCC, orange box: HCV-cirrosis from patients with HCC (non tumor tissues), Blue box: HCV-HCC.
Figure-1A illustrates the number of significant probe sets for the three pairwise comparisons including HCV-HCC vs. normal liver (N=768 with 594 probe sets being unique for this comparison); HCV-HCC vs. HCV cirrhosis from patients with HCC (N=224, with 17 probe sets being unique for this comparison); HCV-HCC vs. HCV cirrhosis without HCC (N=1,206 with 878 probe sets being unique for this comparison). From the analysis of the 17 unique probe sets (N=16 genes) differentially expressed in HCV-HCC samples when compared to HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients with HCC (Supplemental Table II), genes involved in regulation of transcription (TAF10) and DNA repair (APEX2) were up-regulated in HCV-HCC samples while coagulation factors (F5, TFPI) and apoptosis genes (BAG5) were down regulated.
We identified 878 probe sets (N=867 genes) differentially expressed in HCV-HCC samples when compared with HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients without HCC (after eliminating overlapping probe sets). From the analysis of the resulting 878 probe sets (Figure-1A) we identified genes related to cell division (i.e., CDC2L6, CDKN1C, CDCA4), cell adhesion (i.e., CDH22, CDH4, CDH6), apoptosis (i.e.,TNFAIP3, TNFRSF21, MCL1, BNIP1, BAK1) being differentially expressed in HCV-HCC tissue samples when compared with HCV cirrhotic tissues.
Figure-1B illustrates the number of significant probe sets for the three pairwise comparisons including HCV-HCC vs. HCV cirrhosis from patients with HCC (N=224 probe sets); HCV cirrhosis from patients with HCC vs. HCV cirrhosis (N=12 probe sets); HCV cirrhosis from patients with HCC vs. normal liver (N=771 probe sets). Also, overlapping of probe sets among the different analysis is showed. In this analysis, only 10 probe sets were identified as differentially expressed when HCV cirrhosis from patients with and without HCC were compared. TNFSF12, CD97, TMEM109 were the more relevant genes in this list. The protein encoded by TNFSF12 gene is a cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. This protein is a ligand for the FN14/TWEAKR receptor. This cytokine can induce apoptosis via multiple pathways of cell death in a cell type-specific manner. This cytokine is also found to promote proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, and thus acts as a regulator of angiogenesis. However, when this analysis was evaluated with HCV-HCC vs. cirrhotic tissues from patients without HCC and tissues from patients without HCC vs. normal liver, these probe sets (N=10) were shared with the other comparisons leaving no unique probe sets differentially expressed when HCV cirrhosis from patients with and without HCC were compared (Figure-1C).
Also, we were able to identify 149 unique probe sets statistically differentially expressed in HCV-HCC samples when compared with HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients with HCC (Figure-1B). The down regulated genes in HCV-HCC samples were principally associated with apoptosis. Also, coagulation factor genes were down regulated in HCV-HCC. The expression of oncogenes as FYN and RAS was affected also in HCV-HCC samples when compared with HCV cirrhosis from patients with HCC.
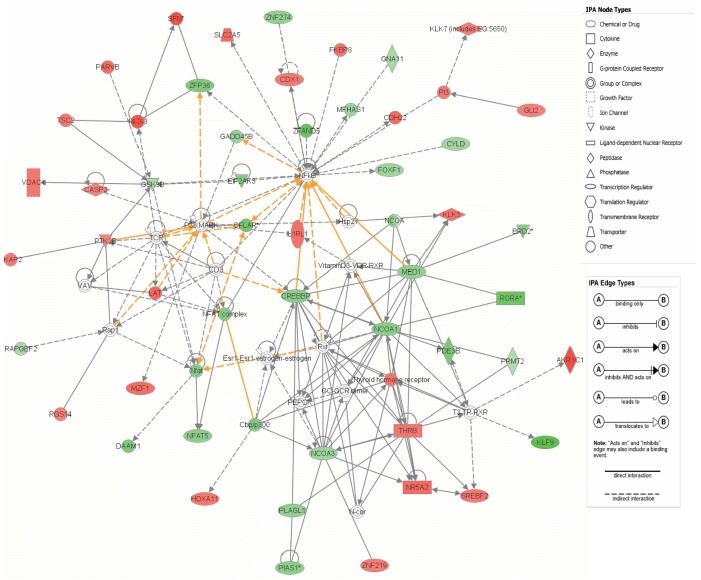
Figure-1C illustrates the number of significant probe sets for the three pairwise comparisons including HCV cirrhosis from patients with HCC vs. HCV cirrhosis from patients without HCC (N=12 probe sets); HCV-HCC vs. HCV cirrhosis (N=1206 probe sets); HCV cirrhosis from patients with HCC vs. normal liver (N=771 probe sets). From this analysis, we were able to identify the unique statistically differentially probe sets (N=542) in HCV-HCC when compared with HCV cirrhosis from patients without HCC. From this analysis, genes related to immune response, apoptosis, and growth factors were up-regulated in HCV cirrhosis when compared to HCV-HCC. Cell division and cell cycle genes were up regulated in HCV-HCC samples. Core analysis was performed to interpret the data set in the context of biological processes, pathways and molecular networks. Twenty one networks were identified with a score 15 (including at least 13 molecules). Two of the top scored networks were merged as it is showed in the Figure-2. The top molecular and cellular functions in the networks were classified as cell morphology, development and cancer (score=41) and gene expression, viral function and cancer (score=32).
Figure 2. The 2 top-scoring networks of interactions among the differentially expressed genes between HCV-HCC vs. HCV-cirrhotic tissues.
Core analysis was performed to interpret the data set in the context of biological processes, pathways and molecular networks for the 542 probe sets differentially expressed only in the HCV-HCC vs. HCV cirrhosis comparison. The top molecular and cellular functions in the networks were classified as cell morphology, development and cancer (score=41) and gene expression, viral function and cancer (score=32). Interconnections of significant functional networks in HCV cirrhosis are indicated. Spatial location of nodes into their corresponding subcellular locations is also indicated. The meaning of the node shapes and interaction edges is also indicated.
Finally, the Figure-1D illustrates the number of significant probe sets for the three pairwise comparisons including HCV-HCC vs. normal liver (N=768 probe sets); HCV cirrhosis with HCC vs. normal liver (N=771 probe sets); HCV cirrhosis without HCC vs. normal liver (N=1586 probe sets).
Gene signatures involved in HCV-induced HCC
In testing whether gene expression significantly increased or decreased across the tissue types from normal (N=19), to HCV cirrhosis (N=43), to early HCV-HCC (N=26), to advanced HCV-HCC (N=20), there were 1997 probe sets (1598 genes) with a significant decreasing trend and 56 probe sets (50 genes) with a significant increasing trend in expression values.
From this analysis we observed that an important number of the down regulated genes from normal to advanced HCV-HCC were genes associated with normal liver function including for example coagulation factors as TFPI, C8A, C1RL, F9, among others. Also, genes related to immune response (i.e., IL18R, IL33, IL4R, ILF3, among others) and interferon inducible genes and interferon receptors (i.e., IFITM2, ISG20L2, IFNAR1, IFNAR2) presented a negative trend among tissues. Interesting, many genes of the RAS family (i.e., RASB27A, RAB14, RAB1A, KRAS, RAB2A, among others) as well as growth factors and receptors were present in the negative trend list. From the analysis of the more important molecular and cellular functions associated with these genes, gene expression (p=1.4E-07-9.0E-03), cell death (p=2.7E-06-9.9E-03), RNA post transcriptional modifications (p=5.6E-06-2.1E-03), molecular transport (p=8.1E-6-7.4E-3), and protein trafficking (p=8.0E-6-7.4E-3) were the more relevant. Acute phase response signaling (p=2E-10) and JAK/STAT signaling (6.7E-05) represented the more important canonical pathways.
From the analysis of the probe sets with positive trend from normal liver, to HCV cirrhosis, to HCV-HCC, we observed that the list included MHC class I receptor activity (i.e., HLA-G, F, and B), DNA damage checkpoint (i.e., CHECK1), cell division (i.e., BIRC5, KNTC1), and ubiquitin cycle (i.e., FBXO41, FBXL7, UBD) genes.
The associated network functions cancer, cell cycle, cell death (score=44) and inflammatory disease, cancer, cellular growth and proliferation (score=32) were the top scored networks. The top canonical pathways included cell cycle (p=1.3E-05), p53 signaling (p=4.2E-03), antigen presentation pathway (p=5.2E-03), and protein ubiquitination pathway (p=1.4E-2).
Differential gene expression patterns between HCV-cirrhotic liver tissue from patients with and without HCC
When examining only 58 HCV cirrhotic tissues, the comparison between cirrhotic tissues with (N=17) and without (N=41) HCC yielded 863 probe sets differentially expressed. The 17 cirrhotic tissues were collected from explanted livers to ensure the absence of HCC. From this analysis we observed that genes related to apoptosis (i.e., BCL7, TNFRSF1A, TNF5F13, TRAADD, LITAF), angiogenesis (i.e., TNFAIP2, TNFSF12) were down regulated in HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients with HCC while genes related to immune response (i.e., IL1R, IL9R, IL8R) and response to stress (i.e., TP53I11, TP53TG3) were down regulated when compared to HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients without HCC. To redefine the significance of the altered genes, we next investigated the biological interactions using the IPA tool and found the genes to map to genetic networks with functional relationships. Five networks with high scores (>15) were found associated to HCV cirrhosis without HCC. These networks had between 10–17 genes affected, being related to cellular death, cell-to-cell signaling, cancer and DNA replication, recombination, and repair. We also performed gene ontology analysis using the IPA tool. Twenty functions were identified as having high scores. The functions with the highest P values were related to cell cycle (P= 1.6E-06-1.1E-02 (25 molecules)) and cell death (P= 3.0E-05-1.1E-02 (12 molecules)). The top canonical pathways associated with HCV cirrhosis included p53 signaling (P=0.0012), acute phase response signaling (P=0.0016), xenobiotic metabolism signaling (P=0.008), IL-6 signaling (P=0.01), and NFR2-mediated oxidative stress response (P=0.013).
Classifier to predict whether the tissue type was associated with HCC
It was of interest to derive a classifier to predict whether the HCV cirrhotic tissue was from a patient without HCC vs. cirrhotic tissue with HCC. The 58 CEL files representing the cirrhotic tissues were read into the R programming environment and normalized together using quantile normalization, and RMA expression summaries were obtained. Prior to deriving a classifer, all Affymetrix control probe sets were removed. Afterward, the random forest algorithm was used to predict tissue type using the 22,215 RMA probe set expression summaries as covariates; due to memory limitations, three random forests were separately derived using roughly 1/3 of the probe sets. Thereafter, for the three independent random forests, all probe sets with a Gini importance measure exceeding the μGini+3SEGini were retained and a subsequent random forest predicting tissue type using only these important probe sets was derived. All random forests consisted of 5,000 trees. This entire process was repeated three times to examine the stability of the probe sets with the highest variable importance values. Since the random forest uses bootstrap samples in deriving each classification tree, there is a natural test set, those observations not in the bootstrap sample that are as a natural test set in order to provide an unbiased estimate of classification error. The random forest had an unbiased error rate of 8.93% estimated using the observations not in the bootstrap re-samples (Supplemental Figure-1).
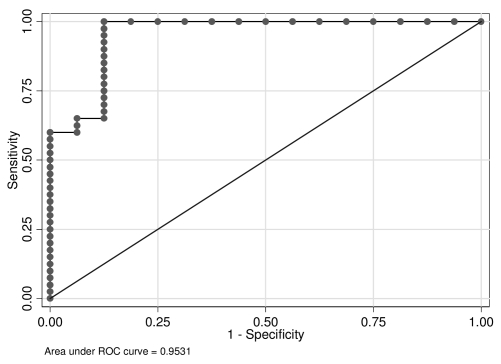
Fifteen probe sets were consistently identified among the random forest classifiers as being important both with respect to the mean decrease in accuracy and the mean decrease in the Gini index (Table I). A pairwise scatterplot for these 15 probe sets revealed that all probe sets were correlated, with the cirrhotic tissues with HCC having lower expression values (red) than the cirrhotic tissues without HCC (blue) (Supplemental Figure-2). Due to the correlation among these 15 probe sets, a multivariable logistic regression model was derived using a forward variable selection strategy to obtain a more parsimonious set of genes predictive of tissue of origin. First, all univariable logistic regression models were fit and that model with the smallest log-likelihood was selected as the most important probe set. Thereafter, all possible two-variable models containing this probe set and one other were fit and that probe set having the most significant decrease in the log-likelihood was retained. This process was repeated until there was no significant decrease in the log-likelihood. The probe sets in the final multivariate logistic regression model were 201362_at and 218059_at (Table I). Moreover, other bivariable models using these 15 probe sets will yield similar performance so that there is a multiplicity of models that could be used to predict tissue source. After the final model was determined, the Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test was performed which indicated no departure from goodness-of-fit (P= 0.4238). The model was then used in calculating the predicted probabilities p̂i for patients i=1,…,56. If p̂i ³ 0.5 the patient was predicted to have HCC, and no HCC otherwise. These classifications cross-tabulated against the true class (Table II (A)) were then used in estimating sensitivity, specificity, positive predicted value, negative predicted value, and accuracy (Table II (B)). The ROC curve was also plotted (Figure-3).
Table 1.
Fifteen probe sets consistently identified among the random forest classifiers as being important both with respect to the mean decrease in accuracy and the mean decrease in the Gini index.
| AffyID | Symbol | Gene Name | HCV-Cirrhosis from patients with HCC | HCV-Cirrhosis only | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 218062_x_at | CDC42EP 4 | CDC42 effector protein (Rho GTPase binding) 4 | 7.73 | 8.34 | 1.52 |
| 201362_at* | IVNS1AB P | influenza virus NS1A binding protein | 6.83 | 7.27 | 1.36 |
| 221270_s_at | QTRT1 | queuine tRNA-ribosyltransferas e 1 (tRNA-guanine transglycosylase) | 7.08 | 7.89 | 1.75 |
| 221217_s_at | A2BP1 | ataxin 2-binding protein 1 | 5.5 | 5.85 | 1.27 |
| 209059_s_at | EDF1 | endothelial differentiation-related factor 1 | 9.57 | 9.99 | 1.34 |
| 211241_at | ANXA2P3 | annexin A2 pseudogene 3 | 8.23 | 8.7 | 1.38 |
| 218059_at* | ZNF706 | zinc finger protein 706 | 5.57 | 5.91 | 1.26 |
| 201332_s_at | STAT6 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 6, interleukin-4 induced | 7.9 | 8.31 | 1.32 |
| 213183_s_at | CDKN1C | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (p57, Kip2) | 4.71 | 5.21 | 1.42 |
| 208891_at | DUSP6 | dual specificity phosphatase 6 | 7.58 | 8.31 | 1.66 |
| 200827_at | PLOD1 | procollagen-lysine 1, 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1 | 9.38 | 9.99 | 1.53 |
| 213042_s_at | ATP2A3 | ATPase, Ca++ transporting, ubiquitous | 7.47 | 7.99 | 1.43 |
| 45749_at | FAM65A | family with sequence similarity 65, member A | 6.06 | 6.53 | 1.39 |
| 204164_at | SIPA1 | signal-induced proliferation-associated gene 1 | 5.23 | 6.03 | 1.73 |
| 203315_at | NCK2 | NCK adaptor protein 2 | 6.29 | 6.62 | 1.26 |
201362_at and 218059_at were the probe sets in the final multivariate logistic regression model
Table 2.
| A) Cross-tabulation of true and predicted class where the predicted class was determined from the multivariable logistic regression model using p̂i ³ 0.5. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| True class | Total | ||
| Classified | No HCC | HCC | |
| No HCC | 40 | 2 | 42 |
| HCC | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| Total | 40 | 16 | 56 |
| B) Sensitivity, specificity, positive predicted value, negative predicted value, and accuracy of the predicted class was determined from the multivariable logistic regression model using p̂i ³ 0.5. | |
|---|---|
| Using p̂i ³ 0.5 | % |
| Sensitivity | 100.0% |
| Specificity | 87.5% |
| Positive predictive value | 95.2% |
| Negative predictive value | 100.0% |
| Accuracy | 96.4% |
Figure 3.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Gene expression profiles among early, advanced, and very advanced HCV-HCCs
After applying the Jonckheere-Terpstra test for trend to assess which probe sets have a significant increasing trend and again to assess which probe sets have a significant decreasing trend, the q-values were estimated as a means of assessing the false discovery rate. The increasing trend analysis yielded 189 probe sets and the decreasing trend analysis yielded only 3 probe sets. Angiopoietin 1 gene was affected by the positive trend. Angiopoietins are proteins with important roles in vascular development and angiogenesis. All angiopoietins bind with similar affinity to an endothelial cell-specific tyrosine-protein kinase receptor. The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted glycoprotein that activates the receptor by inducing its tyrosine phosphorylation. It plays a critical role in mediating reciprocal interactions between the endothelium and surrounding matrix and mesenchyme. Genes involved in DNA repair were also present in the positive trend results (RAD51, RAD17, PML, FANCI).
Gene expression quantitation using QPCR
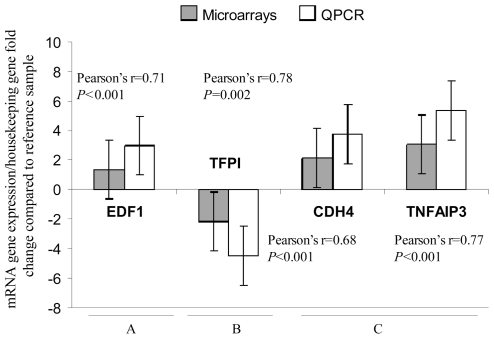
Expression levels of the EDF1, TFPI, CDH4, and TNFAIP3 mRNAs were further confirmed using QPCR. These genes were identified as significant differentially expressed between different tissues types and/or as a part of classifier to predict whether the tissue type was associated with HCC. The results from the microarray were reproduced by QPCR (r=0.71, P<0.001; r=0.78, p=0.002; r=0.68, P<0.001; and r=0.77, P<0.001, respectively) (Figure-4).
Figure 4. Validation of microarray results for expression levels of EDF1, TFPI, CDH4, and TNFAIP3 genes using QPCR.
Total RNA from the same RNAs samples that were subjected to microarray study were used in the QPCR validation reactions. Values were expressed as mRNA gene expression level (for each specific gene)/housekeeping gene fold change expression compared to the reference sample. The gene expression of the study genes was identified as significant differentially expressed when comparing different group of tissues samples. Specifically, EDF1 was identified as differentially expressed when HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients with HCC (non-tumor samples) (N=17) were compared with HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients without HCC (N=41) (A). TFPI was differentially expressed in HCV-HCC samples (N=47) when compared with HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients with HCC (N=17) (B). CDH4 and TNFAIP3 were identified as differentially expressed when HCV-HCC samples (N=47) were compared with HCV cirrhotic tissues (N=41) (C).
Discussion
HCC due to HCV may be an indirect result of enhanced hepatocyte turnover that occurs in an effort to replace infected cells that have been immunologically attacked. Chronic inflammation, immune mediated hepatocellular destruction, and liver regeneration underlie cirrhosis, and are thought to play central roles in primary carcinogenesis (18–23). Viral functions may also play a more direct role in mediating oncogenesis.
In the present study, we aimed to identify the genes implicated in the origin and progression of HCV-HCC. We studied the molecular biology of HCV-HCC including the study of HCV-cirrhotic liver, HCV-cirrhotic livers from patients with HCC, and HCC at different stages.
For elucidating the genes and molecular pathways involved in the HCV-induced HCC progression, different analyses were performed. Among probe sets identified as differentially expressed via the F test, all possible six pairwise were performed. This analysis allowed us to identify the unique probe sets characterizing every tissue type/condition when overlapping genes from another comparison were eliminated. As expected, the gene expression patterns were found to vary significantly among the HCC and normal liver samples. In concordance with previous publications (41, 42), genes associated with cell proliferation and mitosis were found to have increased expression in HCC samples. In contrast, most genes that were expressed at lower levels in HCC than in normal liver tissues comprised genes specifically expressed in differentiated hepatocytes. These observations suggest that accelerated cell proliferation accomplished by the up regulation of proliferation and mitotic-associated genes are generally involved in hepatocarcinogenesis. However, the down regulation of liver-specific genes is possibly associated with dedifferentiation of cancer cells during tumor progression.
Cell adhesion, cell division, and apoptosis were the more important cellular and molecular functions when HCV-HCC samples were compared with HCV cirrhotic tissues. A lower number of differentially expressed genes were observed when HCV-HCC samples were compared with HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients with HCC (non-tumor samples). Cirrhosis is a recognized, established risk factor for HCC and this finding might represent a molecular compromise already present in these tissues even when non histological evidence of tumor was present.
To examine the molecular mechanisms during the process of liver carcinogenesis, it is considered reasonable to investigate the non cancerous portion of the liver tissue because multicentric occurrence of HCC is mainly associated with underlying chronic liver damage rather than adverse tumor factors. For this reason, we evaluated HCV cirrhotic tissues from patients with HCC as an independent sample group. When examining only 58 cirrhotic tissues, the comparison between cirrhotic tissues with and without HCC yielded 863 probe sets differentially expressed. The top canonical pathways associated with HCV cirrhosis in patients with HCC included p53 signaling, acute phase response signaling, xenobiotic metabolism signaling, IL-6 signaling, and NFR2-mediated oxidative stress response. These results might have important impact in the early and accurate diagnosis of HCV-HCC in cirrhotic patients.
It was of interest to derive a classifier to predict whether the studied HCV cirrhotic tissue was from a patient without HCC (from explanted livers) versus cirrhotic tissue with HCC. It can be of great importance to identify markers that can indicate the presence of HCC in cirrhotic tissues even when non-tumor cells are present in the study sample. Fifteen probe sets were consistently identified among the random forest classifiers. Moreover, when cross-tabulation of true and predicted class where the predicted class was determined, very good values were obtained for sensitivity, specificity, positive predicted value, negative predicted value, and accuracy. These findings might have an important value in diagnosis of HCC in HCV-cirrhotic patients.
In testing whether gene expression significantly increased or decreased across the tissue types from normal liver, to HCV-cirrhosis, to early HCV-HCC, to advanced HCV-HCC, trend analysis was performed. A high number of genes related with normal liver function were present in the negative trend gene list. Acute phase response signaling and JAK/STAT signaling represented the more important down regulated canonical pathways. Cell cycle, p53 signaling, antigen presentation pathway, and protein ubiquitination pathway were the top canonical pathway in positive trend analysis.
In conclusion, we identified gene signatures that distinguish the pathological stages of HCC and potential molecular markers for early HCC diagnosis in high risk cirrhotic HCV patients. These findings provide a comprehensive molecular portrait of genomic changes in progressive HCV-related HCC.
Supplemental Data
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by a National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) grant, RO1DK069859.
This work has been presented in part at the American Transplant Congress meeting, Toronto, 2008.
The following individuals were instrumental in the planning, conduct and/or care of patients enrolled in this study at each of the Adult to Adult Living Donor Liver Transplant Cohort Study (A2ALL; NIDDK 1U01DK62531) participating institutions as follows:
Northwestern University, Chicago, IL (DK62467): PI: Michael M.I. Abecassis, MD, MBA; Co-PI: Andreas Blei, MD; Study Coordinator: Patrice Al-Saden, RN, CTCC
University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia, PA (DK62494): PI: Abraham Shaked, MD, PhD; Co-PI: Kim M. Olthoff, MD; Study Coordinators: Mary Kaminski, PA-C; Mary Shaw, RN, BBA
University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA (DK62496): PI: Rafik Mark Ghobrial, MD, PhD; Co-PI: Ronald W. Busuttil, MD, PhD; Study Coordinator: Lucy Artinian, RN, MN
University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA (DK62444): PI: Chris E. Freise, MD, FACS; Co-PI: Norah A. Terrault, MD; Study Coordinator: Dulce MacLeod, RN
University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, MI (DK62498): PI: Robert M. Merion, MD; DCC Staff: Anna S.F. Lok, MD; Akinlolu O. Ojo, MD, PhD; Brenda W. Gillespie, PhD; Douglas R. Armstrong, RN, MS; Margaret Hill-Callahan, BS, LSW; Terese Howell, BS; Lan Tong, MS; Tempie H. Shearon, MS; Karen A. Wisniewski, MPH; Monique Lowe, BS
University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC (DK62505): PI: Jeffrey H. Fair, MD; Study Coordinator: Carrie A. Nielsen, MA
Medical College of Virginia Hospitals, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA (DK62531): PI: Robert A. Fisher, MD, FACS; Co-PI: Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD; Study Coordinators: Ede Fenick, RN; April Ashworth, RN
Footnotes
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:153–156. doi: 10.1002/ijc.1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tagger A, Donato F, Ribero ML, et al. Case-control study on hepatitis C virus (HCV) as a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma: the role of HCV genotypes and the synergism with hepatitis B virus and alcohol. Brescia HCC Study. Int J Cancer. 1999;81:695–699. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19990531)81:5<695::aid-ijc4>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tsukuma H, Hiyama T, Tanaka S, Nakao M, Yabuuchi T, Kitamura T, Nakanishi K, et al. Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1797–1801. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199306243282501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.El-Serag HB, Mason AC. Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:745–750. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199903113401001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Marsh JW, Dvorchik I. Liver organ allocation for hepatocellular carcinoma: are we sure? Liver Transpl. 2003;9:693–696. doi: 10.1053/jlts.2003.50086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fisher RA, Maluf DG, Wolfe L, et al. Is hepatic transplantation justified for primary liver cancer? J Surg Oncol. 2007;95:674–679. doi: 10.1002/jso.20617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Barnett CC, Jr, Curley SA. Ablative techniques for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 2001;28:487–496. doi: 10.1053/sonc.2001.26951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Figueras J, Jaurrieta E, Valls C, et al. Resection or transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: outcomes based on indicated treatment strategy. J Am Coll Surg. 2000;190:580–587. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(00)00251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Iwatsuki S, Dvorchik I, Marsh JW, Madariaga JR, Carr B, Fung JJ, Starzl TE. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a proposal of a prognostic scoring system. J Am Coll Surg. 2000;191:389–394. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(00)00688-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marsh JW, Finkelstein SD, Demetris AJ, et al. Genotyping of hepatocellular carcinoma in liver transplant recipients adds predictive power for determining recurrence-free survival. Liver Transpl. 2003;7:664–671. doi: 10.1053/jlts.2003.50144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nam SW, Park JY, Ramasamy A, et al. Molecular changes from dysplastic nodule to hepatocellular carcinoma through gene expression profiling. Hepatology. 2005;42:809–818. doi: 10.1002/hep.20878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Iizuka N, Oka M, Yamada-Okabe H, et al. Oligonucleotide microarray for prediction of early intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Lancet. 2003;361:923–929. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12775-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mas VR, Maluf DG, Archer KJ, Yanek K, Williams B, Fisher RA. Genes associated with progression and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C patients waiting and undergoing liver transplantation: preliminary results. Transplantation. 2007;83:973–981. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000258643.05294.0b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mas VR, Maluf DG, Archer KJ, Yanek K, Williams B, Fisher RA. Differentially expressed genes between early and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as a potential tool for selecting liver transplant recipients. Mol Med. 2006;12:97–104. doi: 10.2119/2006-00032.Mas. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Moinzadeh P, Breuhahn K, Stutzer H, Schirmacher P. Chromosome alterations in human hepatocellular carcinomas correlate with aetiology and histological grade - results of an explorative CGH meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:935–941. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schafer DF, Sorrell MF. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 1999;353:1253–1257. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)09148-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis C in the United States. Hepatology. 2002;36:S74–83. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.36807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guan XY, Fang Y, Sham JS, et al. Recurrent chromosome alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma detected by comparative genomic hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2000;29:110–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Marchio A, Terris B, Meddeb M, et al. Chromosomal abnormalities in liver cell dysplasia detected by comparative genomic hybridization. Mol Pathol. 2001;54:270–274. doi: 10.1136/mp.54.4.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wong N, Lam WC, Lai PB, Pang E, Lau WY, Johnson PJ. Hypomethylation of chromosome 1 heterochromatin DNA correlates with q-arm copy gain in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 2001;159:465–471. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61718-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nishida N, Nishimura T, Ito T, Komeda T, Fukuda Y, Nakao K. Chromosomal instability and human hepatocarcinogenesis. Histol Histopathol. 2003;18:897–909. doi: 10.14670/HH-18.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Buendia MA. Genetic alterations in hepatoblastoma and hepatocellular carcinoma: common and distinctive aspects. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2002;39:530–535. doi: 10.1002/mpo.10180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Taniguchi K, Roberts LR, Aderca IN, et al. Mutational spectrum of beta-catenin, AXIN1, and AXIN2 in hepatocellular carcinomas and hepatoblastomas. Oncogene. 2002;21:4863–4871. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Al-Sukhun S, Hussain M. Current understanding of the biology of advanced bladder cancer. Cancer. 2003;97:2064–2075. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Theodorescu D. Molecular pathogenesis of urothelial bladder cancer. Histol Histopathol. 2003;18:259–274. doi: 10.14670/HH-18.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Iizuka N, Oka M, Yamada-Okabe H, et al. Comparison of gene expression profiles between hepatitis B virus- and hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocellular carcinoma by oligonucleotide microarray data on the basis of a supervised learning method. Cancer Res. 2002;62:3939–3944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Okabe H, Satoh S, Kato T, et al. Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in human hepatocellular carcinomas using cDNA microarray: identification of genes involved in viral carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2129–2137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shirota Y, Kaneko S, Honda M, Kawai HF, Kobayashi K. Identification of differentially expressed genes in hepatocellular carcinoma with cDNA microarrays. Hepatology. 2001;33:832–840. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.23003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.American Liver Tumor Study Group. Investigators Booklet and protocol 1998. United Network for Organ Sharing; A randomized prospective multi-institutional trial of orthotopic liver transplantation or partial hepatic resection with or without adjuvant chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Policy 3.6.4.4.1998. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC, et al. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis. Hepatology. 1981;1:431–435. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, et al. Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004;5:R80. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r80. 81-R80-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; Vienna, Austria: 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA. affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:307–315. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Huber W, Gentleman R. matchprobes: a Bioconductor package for the sequence-matching of microarray probe elements. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:1651–1652. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U, Speed TP. Exploration, Normalization, and Summaries of High Density Oligonucletide Array Probe Level Data. Biostatistics. 2003;4:249–264. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/4.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope LM, Hobbs B, Speed TP. Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data. Nucleic Acids Research. 2003;31:e15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gng015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Smyth GK. Limma: linear models for microarray data. In: Gentleman R, Carey VJ, Dudoit S, Irizarry R, Huber W, editors. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions using R and Bioconductor. New York: Springer; 2005. pp. 397–420. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–1917. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14964-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gao Q, Wang XY, Fan J, et al. Selection of reference genes for real-time PCR in human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008;134:979–86. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0369-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Waxman S, Wurmbach E. De-regulation of common housekeeping genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:243. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chen X, Cheung ST, So S, et al. Gene expression patterns in human liver cancers. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13:1929–1939. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-02-0023.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Delpuech O, Trabut JB, Carnot F, Feuillard J, Brechot C, Kremsdorf D. Identification, using cDNA macroarray analysis, of distinct gene expression profiles associated with pathological and virological features of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2002;21:2926–2937. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.