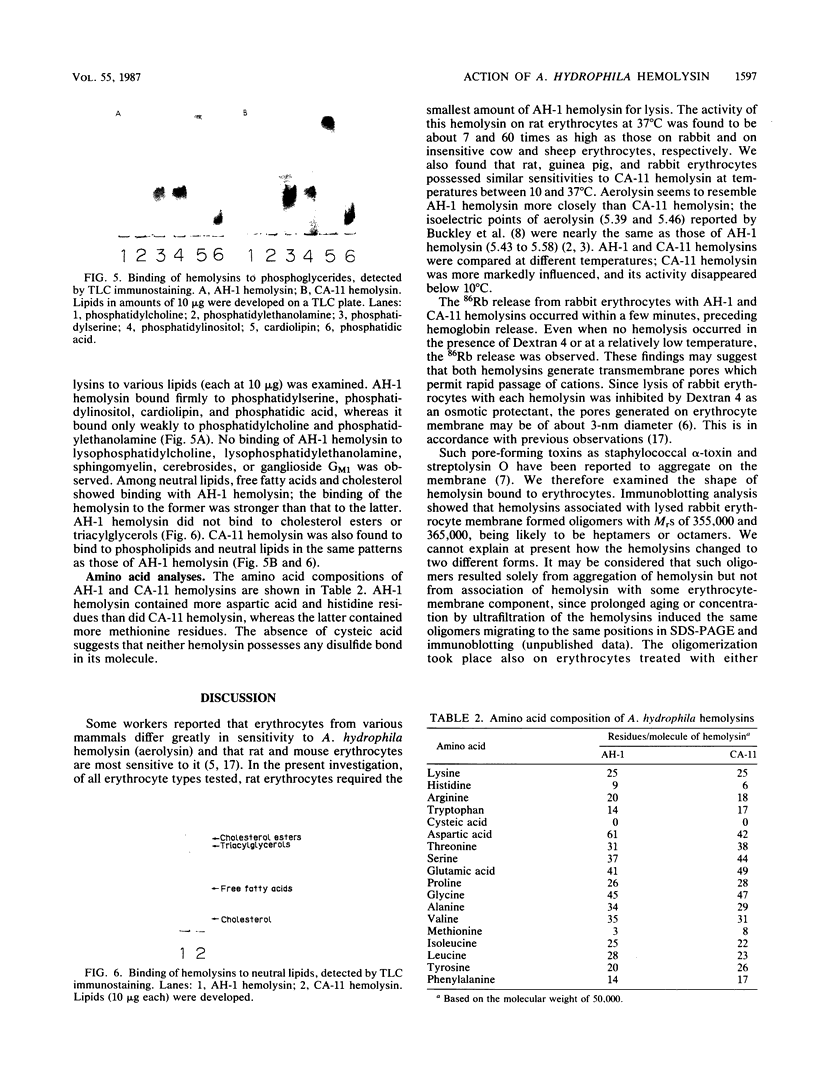
Abstract
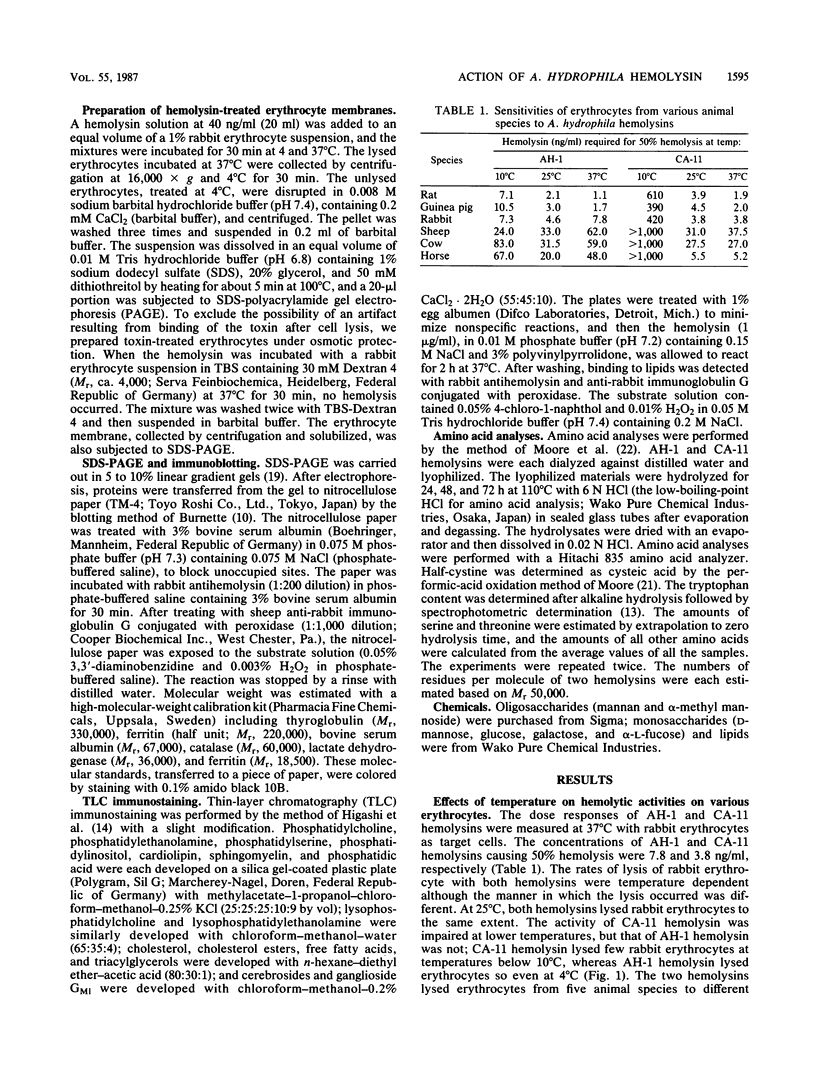
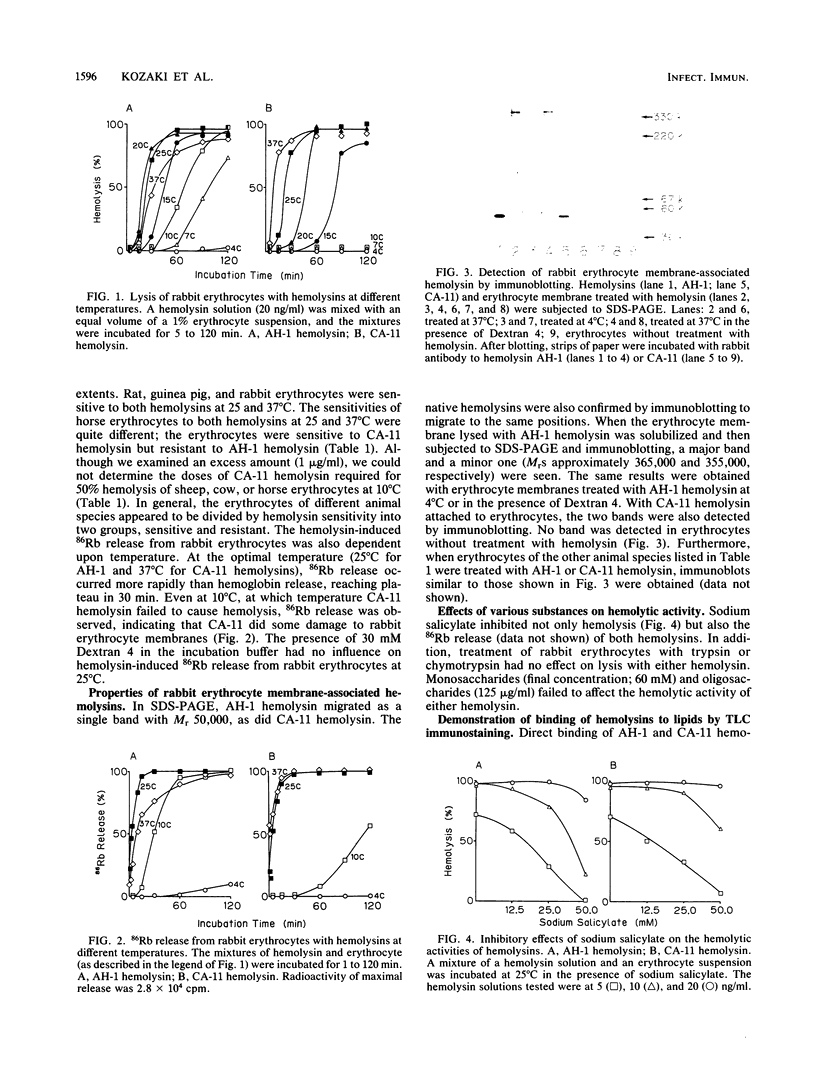
The activity of hemolysin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila CA-11, isolated from an environmental source, was more sensitive to temperature than that of hemolysin produced by strain AH-1, isolated from a diarrheal case. CA-11 hemolysin failed to elicit hemolysis below 10 degrees C. Immunoblotting analyses showed that both hemolysins formed into oligomers in rabbit erythrocyte membrane even when no hemolysis occurred. suggesting that the binding and the subsequent oligomerization are temperature independent. Sodium salicylate inhibited lysis of rabbit erythrocytes by both hemolysins, but selected monosaccharides and oligosaccharides did not. Thin-layer immunostaining indicated that both hemolysins bound to phosphoglycerides with net negative charge but weakly to the ones with no net negative charge. Neither sphingomyelin nor lysophosphoglyceride reacted with the hemolysins, whereas the hemolysins bound to free fatty acids. These results suggest that the binding of either hemolysin to the membrane component, probably phospholipid, requires both negative charge of the polar head group and suitable hydrophobicity of the nonpolar tails.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annapurna E., Sanyal S. C. Enterotoxicity of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Aug;10(3):317–323. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asao T., Kinoshita Y., Kozaki S., Uemura T., Sakaguchi G. Purification and some properties of Aeromonas hydrophila hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):122–127. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.122-127.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asao T., Kozaki S., Kato K., Kinoshita Y., Otsu K., Uemura T., Sakaguchi G. Purification and characterization of an Aeromonas hydrophila hemolysin. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):228–232. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.228-232.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S., Avigad G. Interactions between aerolysin, erythrocytes, and erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1312–1319. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1312-1319.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S. Partial characterization of aerolysin, a lytic exotoxin from Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1016–1021. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1016-1021.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. Escherichia coli hemolysin may damage target cell membranes by generating transmembrane pores. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Membrane damage by channel-forming proteins: staphylococcal alpha-toxin, streptolysin-O and the C5b-9 complement complex. Biochem Soc Symp. 1985;50:221–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley J. T., Halasa L. N., Lund K. D., MacIntyre S. Purification and some properties of the hemolytic toxin aerolysin. Can J Biochem. 1981 Jun;59(6):430–435. doi: 10.1139/o81-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Gracey M., Robinson J., Peck D., Beaman J., Bundell C. The microbiology of childhood gastroenteritis: Aeromonas species and other infective agents. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):68–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch N., Gurwith M. J., Langston C., Sack R. B., Brunton J. L. Cytotoxic enterotoxin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila: relationship of toxigenic isolates to diarrheal disease. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):829–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.829-837.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Nakata M. M., Thompson J., White M. L. Aeromonas-related diarrhea in adults. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Dec;145(12):2207–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Fukui Y., Ueda S., Kato S., Hirabayashi Y., Matsumoto M., Naiki M. Sensitive enzyme-immunostaining and densitometric determination on thin-layer chromatography of N-glycolylneuraminic acid-containing glycosphingolipids, Hanganutziu-Deicher antigens. J Biochem. 1984 May;95(5):1517–1520. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingson D. J., Massengill R. K., Mayer M. M. The kinetics of release of 86rubidium and hemoglobin from erythrocytes damaged by antibody and complement. Immunochemistry. 1969 Mar;6(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostacká A., Ciznár I., Korych B., Karolcek J. Toxic factors of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Sep;252(4):525–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Membrane glycoprotein receptor and hole-forming properties of a cytolytic protein toxin. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 30;21(7):1662–1667. doi: 10.1021/bi00536a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Aeromonas hydrophila: ecology and toxigenicity of isolates from an estuary. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;50(2):359–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. Salicylates and phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1973 May 25;243(5404):234–236. doi: 10.1038/243234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson G. J. Lipid composition of erythrocytes in various mammalian species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitarangsi C., Echeverria P., Whitmire R., Tirapat C., Formal S., Dammin G. J., Tingtalapong M. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides: prevalence among individuals with and without diarrhea in Thailand. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.666-673.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamizawa K., Iwamori M., Kozaki S., Sakaguchi G., Tanaka R., Takayama H., Nagai Y. TLC immunostaining characterization of Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin binding to gangliosides and free fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 9;201(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80614-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Van de Walle S., Koornhof H. J., Jeffery L., Bryant T. N. Enterotoxin production in relation to taxonomic grouping and source of isolation of Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.175-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]