Abstract
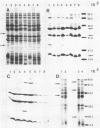
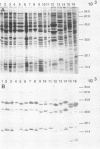
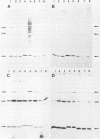
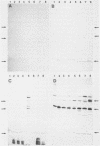
Outer membrane protein (OMP)-enriched extracts and whole-cell protein preparations of Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae and related organisms were examined by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. Both the OMP-enriched and whole-cell protein profiles of Actinobacillus suis, A. pleuropneumoniae (NAD-independent biovar), A. lignieresii, and Pasteurella haemolytica were very similar to those of H. pleuropneumoniae serotypes 1 to 8. Antisera prepared against H. pleuropneumoniae typically recognized three major OMP antigens with approximate molecular weights of 17,000 (17K), 32K, and 42K in immunoblots of H. pleuropneumoniae serotypes 1 to 8, Actinobacillus spp., and P. haemolytica. Antisera prepared against Actinobacillus spp. and Haemophilus sp. "minor group" also recognized these 17K, 32K, and 42K antigens. Using absorbed sera, we demonstrated that the 17K antigen had an epitope (or epitopes) common to all the gram-negative organisms examined, including Escherichia coli. The 32K and 42K antigens had epitopes common to members of the family Pasteurellaceae but, in the case of the 32K antigen, also contained unique epitopes. These results provide a basis for understanding the lack of specificity of serodiagnostic tests for H. pleuropneumoniae infection and provide another line of evidence for the association of H. pleuropneumoniae with the genus Actinobacillus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbride K. A., Rosendal S. Evaluation of a selective medium for isolation of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Oct;47(4):445–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A. Evaluation of different antigens in the complement-fixation test for diagnosis of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae (parahaemolyticus) infections in swine. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Nov;40(11):1564–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R. Identification of concanavalin A-binding proteins after sodium dodecyl sulfate--gel electrophoresis and protein blotting. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jun;123(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Larivière S., Mittal K. R., Martineau G. P., Rousseau P., Cameron J. Evaluation of a Killed Vaccine Against Porcine Pleuropneumonia Due to Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can Vet J. 1985 Feb;26(2):86–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K., Nakai T., Sawata A. Isolation of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae from the nasal cavities of healthy pigs. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1984 Oct;46(5):641–647. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.46.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombin L. H., Rosendal S., Mitchell W. R. Evaluation of the complement fixation test for the diagnosis of pleuropneumonia of swine caused by Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Apr;46(2):109–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Larivière S., Leblanc D. A 2-mercaptoethanol tube agglutination test for diagnosis of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Apr;45(4):715–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J., Paroz P., Krawinkler M., Baumgartner A. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, using an EDTA-extracted antigen for the serology of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Dec;42(12):2139–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae (Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae). Serotypes 8, 3 and 6. Serological response and cross immunity in pigs. Nord Vet Med. 1985 Jul-Aug;37(4):217–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotypes--cross protection experiments. Nord Vet Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;36(7-8):221–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Pleuropneumonia of swine caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Studies on the protection obtained by vaccination. Nord Vet Med. 1976 Jul-Aug;28(7-8):337–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Serological and immunological studies of pleuropneumonia of swine caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Acta Vet Scand. 1974;15(1):80–89. doi: 10.1186/BF03547495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., Thomsen A. D., Vesterlund S. D. Pleuropneumonia caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. An attempt to control the disease at two progeny testing stations by serological blood testing followed by removal of the seropositive animals and their litter mates. Nord Vet Med. 1976 Jul-Aug;28(7-8):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly T., Niven D. F. Tryptone-yeast extract broth as a culture medium for Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae and Haemophilus parasuis to be used as challenge inocula. Can J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;50(3):441–443. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp V. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Ross R. F. Outer membrane protein profiles of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):414–420. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.414-420.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp V. J., Ross R. F. Antibody response of swine to outer membrane components of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae during infection. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.751-760.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp V. J., Ross R. F., Young T. F. Characterization of Haemophilus spp. isolated from healthy swine and evaluation of cross-reactivity of complement-fixing antibodies to Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae and Haemophilus taxon "minor group". J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):945–950. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.945-950.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Boyd D. A. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):840–843. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.840-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Lombin L., DeMoor J. Serotyping and detection of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae by indirect fluorescent antibody technique. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Jul;45(3):271–274. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Mitchell W. R. Epidemiology of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in pigs: a survey of Ontario Pork Producers, 1981. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Jan;47(1):1–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Mittal K. R. Serological cross-reactivity between a porcine Actinobacillus strain and Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Apr;49(2):164–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOPE R. E. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. I. EXPERIMENTAL TRANSMISSION, ETIOLOGY, AND PATHOLOGY. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:357–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teige J., Jr, Larsen H. J., Tollersrud S. Swine dysentery: the influence of dietary selenium on clinical and pathological effects of Treponema hyodysenteriae infection. Acta Vet Scand. 1984;25(1):1–9. doi: 10.1186/BF03547273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]