Abstract
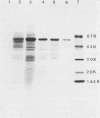
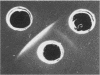
We purified and characterized an extracellular hemolysin produced by Listeria monocytogenes. Hemolysin production was greatly enhanced by growing bacteria in resin (Chelex)-treated medium. This hemolysin was separated as a homogeneous protein of 60,000 daltons by using thiol-disulfide exchange affinity chromatography. This protein was a sulfhydryl-activated toxin, termed listeriolysin O, which shared the classical properties of other bacterial sulfhydryl-activated toxins: inhibition by very low amounts of cholesterol; activation by reducing agents and suppression of the lytic activity by oxidation; antigenic cross-reactivity with streptolysin O. However, listeriolysin O differed remarkably from the other sulfhydryl-activated toxins in that its cytolytic activity towards erythrocytes from various animal species was maximum at low pH (approximately 5.5) and was undetectable at pH 7.0. This suggests that the lytic activity of the toxin in host tissues might be better expressed in the acidic microenvironment, including macrophage phagosomes where bacteria presumably replicate. Listeriolysin O was lethal to mice (50% lethal dose of ca. 0.8 microgram) and induced a rapid inflammatory reaction when injected intradermally. These results favor the view that listeriolysin O might play a major role during intracellular replication of L. monocytogenes, ultimately promoting death of infected macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E. Streptococcal toxins (streptolysin O, streptolysin S, erythrogenic toxin). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(3):661–717. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alouf J. E., Viette M., Corvazier R., Raynaud M. Préparation et propriétés de sérums de chevaux antistreptolysine O. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Apr;108(4):476–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong B. A., Sword C. P. Electron microscopy of Listeria monocytogenes-infected mouse spleen. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1346–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1346-1355.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berche P., Gaillard J. L., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes as a prerequisite for in vivo induction of T cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2266–2271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Roth M., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J. Isolation and identification of two hemolytic forms of streptolysin-O. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):394–400. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.394-400.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., Brom H. J., Alouf J. E., König W., Spur B., Crea A., Peters W. Generation of leukotrienes from human granulocytes by alveolysin from Bacillus alvei. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):188–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.188-193.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., König W., Pfeiffer P., Rauschen I., Theobald K., Thelestam M., Alouf J. E. Effect of thiol-activated toxins (streptolysin O, alveolysin, and theta toxin) on the generation of leukotrienes and leukotriene-inducing and -metabolizing enzymes from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):844–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.844-851.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1127–1138. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowart R. E., Foster B. G. Differential effects of iron on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes: minimum requirements and mechanism of acquisition. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):721–730. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD K. F., SBARRA A. J., BARDAWIL W. A. Serology of Listeria monocytogenes. I. Characteristics of the soluble hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:349–355. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.349-355.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Alouf J. E. Selective purification by thiol-disulfide interchange chromatography of alveolysin, a sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Bacillus alvei. Toxin properties and interaction with cholesterol and liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9968–9972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves R. D., Welshimer H. J. Separation of pathogenic from apathogenic Listeria monocytogenes by three in vitro reactions. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):559–563. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.559-563.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI A. N., ADAMS E. W. PURIFICATION OF THE SOLUBLE HEMOLYSINS OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:418–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.418-424.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins E. M., Watson B. B. Extracellular Antigens from Listeria monocytogenes I. Purification and Resolution of Hemolytic and Lipolytic Antigens from Culture Filtrates of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):589–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.589-594.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. A., Seaman T. A., Woodbine M. Listeria monocytogenes-haemolysin: lecithinase. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Oct;225(1):66–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon G. C., Sword C. P. Biochemical and Immunological Effects of Listeria monocytogenes Hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):363–372. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.363-372.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon G. C., Sword C. P. Cardiotoxic and Lethal Effects of Listeria monocytogenes Hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):373–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.373-379.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon G. C., Sword C. P. Effects of Listeria monocytogenes Hemolysin on Phagocytic Cells and Lysosomes. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):356–362. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.356-362.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NJOKU-OBI A. N., JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI J. C., ADAMS J., COVINGTON V. PRODUCTION AND NATURE OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES HEMOLYSINS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:1–8. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.1-8.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Laveck G. D. Immunochemical and cytotoxic activities of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (shiga) and shiga-like toxins. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1151–1154. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1151-1154.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrisius J., Bhakdi S., Roth M., Tranum-Jensen J., Goebel W., Seeliger H. P. Production of listeriolysin by beta-hemolytic strains of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):314–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.314-319.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent D., Alouf J. E. Interaction of steptolysin O with sterols. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 16;443(2):288–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90511-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent D., Geoffroy C., Alouf J. E. Purification de la streptolysine O par chromatographie covalente sur gel de thiol-agarose. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1978 Oct 23;287(10):951–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocourt J., Schrettenbrunner A., Seeliger H. P. Différenciation biochimique des groupes génomiques de Listeria monocytogenes (sensu lato). Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Jan-Feb;134A(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique I. H., Cooper G. W., Jr Hemodynamic effect of listerial hemolysin in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jun;216(6):1399–1403. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.6.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique I. H., Lin I. F., Chung R. A. Purification and characterization of hemolysin produced by Listeria monocytogenes. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Feb;35(2):289–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka B., Smola J., Elischerová K. Routine test for in vitro differentiation of pathogenic and apathogenic Listeria monocytogenes strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):503–507. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.503-507.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sword C. P. Mechanisms of pathogenesis in Listeria monocytogenes infection. I. Influence of iron. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):536–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.536-542.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson B. B., Lavizzo J. C. Extracellular antigens from Listeria monocytogenes. II. Cytotoxicity of hemolytic and lipolytic antigens of Listeria for cultured mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):753–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.753-758.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]