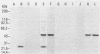
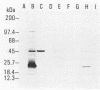
Abstract
A 46-kilodalton (kDa) polypeptide was immunoprecipitated from radiolabeled extracts of human cell lines infected with Mycoplasma hyorhinis by murine monoclonal antibodies PF/2A and ML77. Both of these antibodies also reacted in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with M. hyorhinis cells and with human and nonhuman cell lines infected with M. hyorhinis but failed to react with A7573 cells infected with any of 10 other species of the order Mycoplasmatales. PF/2A also reacted in the ELISA with certain human cell lines that were demonstrated to be free of mycoplasma infection. From extracts of these lines, a polypeptide antigen that appeared as a 24-kDa doublet on polyacrylamide gels was immunoprecipitated by PF/2A. When the PF/2A-reactive human cell lines were infected by M. hyorhinis, both the 46- and 24-kDa antigens were immunoprecipitated by PF/2A. ML77 did not react in the ELISA with any noninfected human cells tested and failed to immunoprecipitate a 24-kDa component from any human cells. In Western blotting analyses of extracts of M. hyorhinis cells, both PF/2A and ML77 stained a 46-kDa band. PF/2A also stained 24-kDa bands in Western blotting analyses of reactive human cells and M. hyorhinis cells, although a 24-kDa component was not precipitated from extracts of M. hyorhinis cells by PF/2A.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barden J. A., Decker J. L. Mycoplasma hyorhinis swine arthritis. I. Clinical and microbiologic features. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Mar-Apr;14(2):193–201. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. H., Jasper D. E. Mycoplasma alkalescens-induced arthritis in dairy calves. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):484–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G. Antibodies to brain and other tissues in cases of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Feb;8(2):319–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G. Autoimmune reactions associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1979 Oct;245(1-2):144–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler G. H., Stanbridge E. J. Infection of mouse lymphoblastoid cell lines with Mycoplasma hyorhinis: complex nature of mycoplasma-host cell interactions. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1136–1143. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1136-1143.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill J. F., Cole B. C., Wiley B. B., Ward J. R. Role of Biological Mimicry in the Pathogenesis of Rat Arthritis Induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):24–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.24-35.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Griffiths M. M., Eichwald E. J., Ward J. R. New models of chronic synovitis in rabbits induced by mycoplasmas: microbiological, histopathological, and immunological observations on rabbits injected with Mycoplasma arthritidis and Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):382–396. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.382-396.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R., Jones R. S., Cahill J. F. Chronic proliferative arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis. I. Induction of disease and histopathological characteristics. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):344–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.344-355.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale J. B., Beachey E. H. Epitopes of streptococcal M proteins shared with cardiac myosin. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):583–591. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S., Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Infection with vaccinia favors the selection of hybridomas synthesizing autoantibodies against intermediate filaments, one of them cross-reacting with the virus hemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1546–1553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. R., Ross R. F. Experimentally induced Mycoplasma hyorhinis arthritis of swine: pathologic response to 26th postinoculation week. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Mar;34(3):363–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis R. S., Dalgard D., Willerson J. T., Barden J. A., Decker J. L. Mycoplasma hyorhinis swine arthritis. II. Morphologic features. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Mar-Apr;14(2):202–211. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. Cold agglutinin titres, cold agglutinin structure and serum immunoglobulin levels in a variety of syndromes including mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Bibl Haematol. 1968;29:322–326. doi: 10.1159/000384628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. Cold agglutinins, the direct coombs' test and serum immunoglobulins in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):801–812. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernsten P. D., Pekny K. W., Reisfeld R. A., Walker L. E. Antigens associated with human squamous cell lung carcinoma defined by murine monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):2970–2977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Leinonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Antigenic similarities between brain components and bacteria causing meningitis. Implications for vaccine development and pathogenesis. Lancet. 1983 Aug 13;2(8346):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R., Sportsman R., Rhodes G., Luka J., Pearson G., Vaughan J. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane contains a 62,000-molecular-weight protein that shares an antigenic epitope with the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded associated nuclear antigen. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1539–1547. doi: 10.1172/JCI112469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Amino acid homology between the encephalitogenic site of myelin basic protein and virus: mechanism for autoimmunity. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1043–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.2414848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B., Wroblewska Z., Frankel M. E., Koprowski H. Molecular mimicry in virus infection: crossreaction of measles virus phosphoprotein or of herpes simplex virus protein with human intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2346–2350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami K. K., Morris R. J., Rastogi S. C., Lange L. S., Russell W. C. A neutralising monoclonal antibody against a paramyxovirus reacts with a brain antigen. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Jul;9(1-2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(85)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick H. J., Kalmanson G. M., Fox M. A., Guze L. B. Arthritis in mice due to infection with Mycoplasma pulmonis. I. Clinical and microbiologic features. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):533–540. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Lodge P. A. Coxsackievirus B-3 myocarditis in Balb/c mice. Evidence for autoimmunity to myocyte antigens. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jul;116(1):21–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C. Immunochemistry of groups A, B, and C meningococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan F. T. Mycoplasma-induced arthritis in poultry. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):622–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H. IMMUNOLOGIC RELATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL AND TISSUE ANTIGENS. I. PROPERTIES OF AN ANTIGEN IN CERTAIN STRAINS OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI EXHIBITING AN IMMUNOLOGIC CROSS-REACTION WITH HUMAN HEART TISSUE. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:595–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H., MEYESERIAN M. An immunological cross-reaction between group-A streptococcal cells and human heart tissue. Lancet. 1962 Apr 7;1(7232):706–710. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)91653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr K. M., Olson N. O. Pathology in chickens experimentally inoculated or contact-infected with mycoplasma gallisepticum. Avian Dis. 1967 Nov;11(4):559–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr K. M., Olson N. O. Pathology of chickens inoculated experimentally or contact-infected with Mycoplasma synoviae. Avian Dis. 1970 May;14(2):290–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhoff H., Heitmann J., Dubenkropp H., Schmidt R. Antigenic cross-reactions between Mycoplasma arthritidis and rat tissues. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Jul;9(3):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisher K., Cunningham M. W. Myosin: a link between streptococci and heart. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2578225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Kreofsky T., Pearson G. R., Hennessy K., Kieff E. Identification and characterization of a cellular protein that cross-reacts with the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):833–838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.833-838.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch B., Berg P. A., Kochsiek K. Autoantibodies and serum inhibition factors (sif) in patients with myocarditis. Klin Wochenschr. 1980 Mar 3;58(5):219–225. doi: 10.1007/BF01476967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H., Mäkelä H., Käyhty H., Jousimies H., Herva E., Hällström K., Sivonen A., Renkonen O. V., Pettay O., Karanko V. Clinical efficacy of meningococcus group A capsular polysaccharide vaccine in children three months to five years of age. N Engl J Med. 1977 Sep 29;297(13):686–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197709292971302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. F., Dale S. E., Duncan J. R. Experimentally induced Mycoplasma hyorhinis arthritis of swine: immune response to 26th postinoculation week. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Mar;34(3):367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. F., Duncan J. R. Mycoplasma hyosynoviae arthritis of swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1970 Dec 1;157(11):1515–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz G., Cheresh D. A., Varki N. M., Yu A., Staffileno L. K., Reisfeld R. A. Detection of ganglioside GD2 in tumor tissues and sera of neuroblastoma patients. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5914–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalheim O. H., Page L. A. Naturally occurring and experimentally induced mycoplasmal arthritis of cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Sep;2(3):165–168. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.3.165-168.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J. A reevaluation of the role of mycoplasmas in human disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:169–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefansson K., Dieperink M. E., Richman D. P., Gomez C. M., Marton L. S. Sharing of antigenic determinants between the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and proteins in Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Possible role in the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 24;312(4):221–225. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501243120407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. Mechanisms of pathogenesis in Mycoplasma infection. Harvey Lect. 1969;63:73–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD J. R., JONES R. S. The pathogenesis of mycoplasma (PPLO) arthritis in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1962 Apr;5:163–175. doi: 10.1002/art.1780050205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. R., Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Chronic arthritis of rabbits induced by mycoplasmas. II. Antibody response and the deposition of immune complexes. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jul;23(7):837–845. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Cassell G. H., Action R. T. Selective association of murine T lymphoblastoid cell surface alloantigens with Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4479–4483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Minion F. C., Cheung H. C. Translocation of Thy-1 antigen and a fluorescent lipid probe during lymphoblastoid cell interaction with Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4 (Suppl):S210–S218. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_1.s210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Watson R. K. Antigenic mimicry of mammalian intermediate filaments by mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):587–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.587-591.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Watson R. K. Monoclonal antibodies to Mycoplasma hyorhinis surface antigens: tools for analyzing mycoplasma-lymphoid cell interactions. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):623–629. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgram L. J., Beisel K. W., Rose N. R. Heart-specific autoantibodies following murine coxsackievirus B3 myocarditis. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1112–1121. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Hudson L., Jessell T. M., Yamamoto M. A monoclonal antibody defining antigenic determinants on subpopulations of mammalian neurones and Trypanosoma cruzi parasites. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):34–38. doi: 10.1038/296034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyle F. A., Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Tramont E. C., Kasper D. L., Altieri P. L., Berman S. L., Lowenthal J. P. Immunologic response of man to group B meningococcal polysaccharide vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):514–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B., Hsu K. C., Seegal B. C. Heart-reactive antibody associated with rheumatic fever: characterization and diagnostic significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):147–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]