Abstract
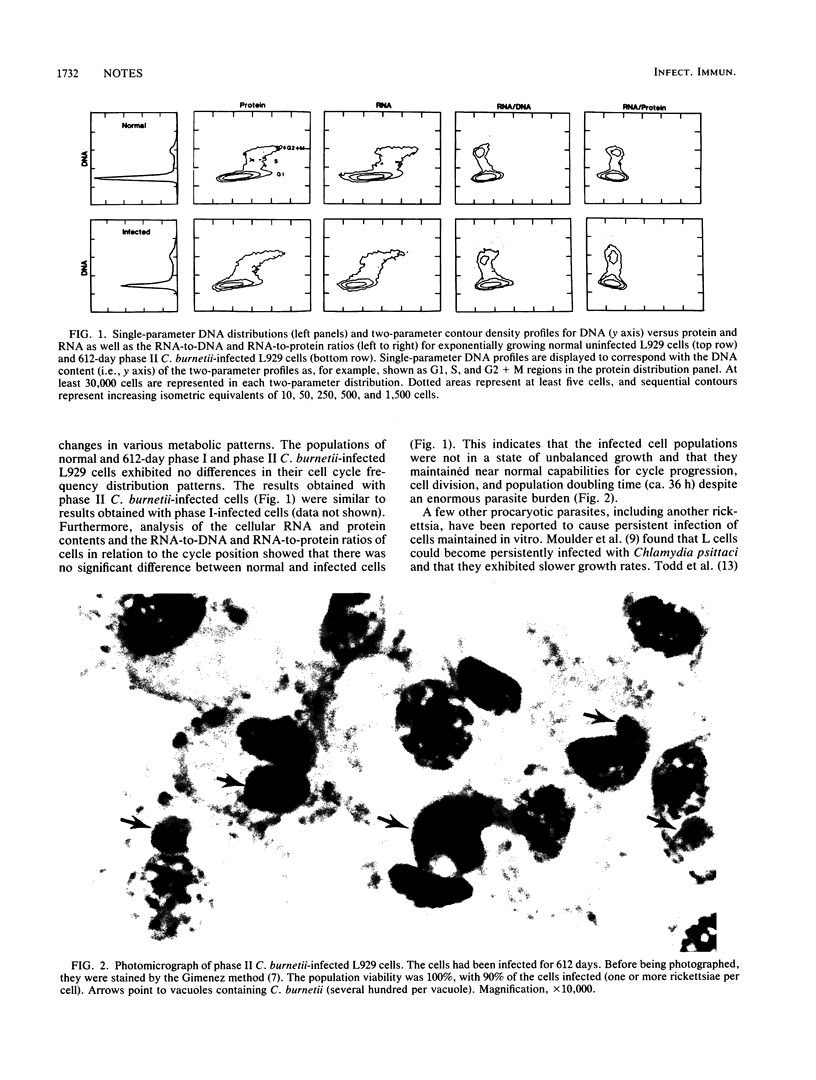
L929 cell populations persistently infected for more than 600 days exhibited cell cycle distributions and generation times similar to those of uninfected cells. The RNA and protein contents of these long-term-infected cells, as determined by flow cytometry and correlated with the cell cycle, were likewise approximately the same as those in normal uninfected cells. Also, the ratios of RNA to DNA and RNA to protein of infected cells were not significantly different from those of normal cells. Collectively, these data indicate that the long-term-infected cells remained in a state of balanced growth and maintained normal cycle progression and division capacity, allowing for growth and proliferation of host cells and thus ensuring the propagation and persistence of the parasite.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baca O. G., Akporiaye E. T., Aragon A. S., Martinez I. L., Robles M. V., Warner N. L. Fate of phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii in several macrophage-like tumor cell lines. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):258–266. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.258-266.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Q fever and Coxiella burnetii: a model for host-parasite interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):127–149. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.127-149.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Scott T. O., Akporiaye E. T., DeBlassie R., Crissman H. A. Cell cycle distribution patterns and generation times of L929 fibroblast cells persistently infected with Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):366–369. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.366-369.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Stueckemann J., Welsh R. M., Paretsky D. Some ultrastructural effects of persistent infections by the rickettsia Coxiella burnetii in mouse L cells and green monkey kidney (Vero) cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):556–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.556-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crissman H. A., Darzynkiewicz Z., Tobey R. A., Steinkamp J. A. Correlated measurements of DNA, RNA, and protein in individual cells by flow cytometry. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1321–1324. doi: 10.1126/science.2408339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crissman H. A., Darzynkiewicz Z., Tobey R. A., Steinkamp J. A. Normal and perturbed Chinese hamster ovary cells: correlation of DNA, RNA, and protein content by flow cytometry. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):141–147. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. C., 3rd, Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M., Rogers W. R., Bennetts R. W., Raaf J., Krause A., Gardner C. Q fever endocarditis in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):400–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Levy N. J., Schulman L. P. Persistent infection of mouse fibroblasts (L cells) with Chlamydia psittaci: evidence for a cryptic chlamydial form. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):874–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.874-883.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman M. J., Coriz P. D., Baca O. G. A proposed model to explain persistent infection of host cells with Coxiella burnetii. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 May;132(5):1415–1422. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-5-1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp J. A., Stewart C. C., Crissman H. A. Three-color fluorescence measurements on single cells excited at three laser wavelengths. Cytometry. 1982 Jan;2(4):226–231. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990020405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turck W. P., Howitt G., Turnberg L. A., Fox H., Longson M., Matthews M. B., Das Gupta R. Chronic Q fever. Q J Med. 1976 Apr;45(178):193–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]