Abstract
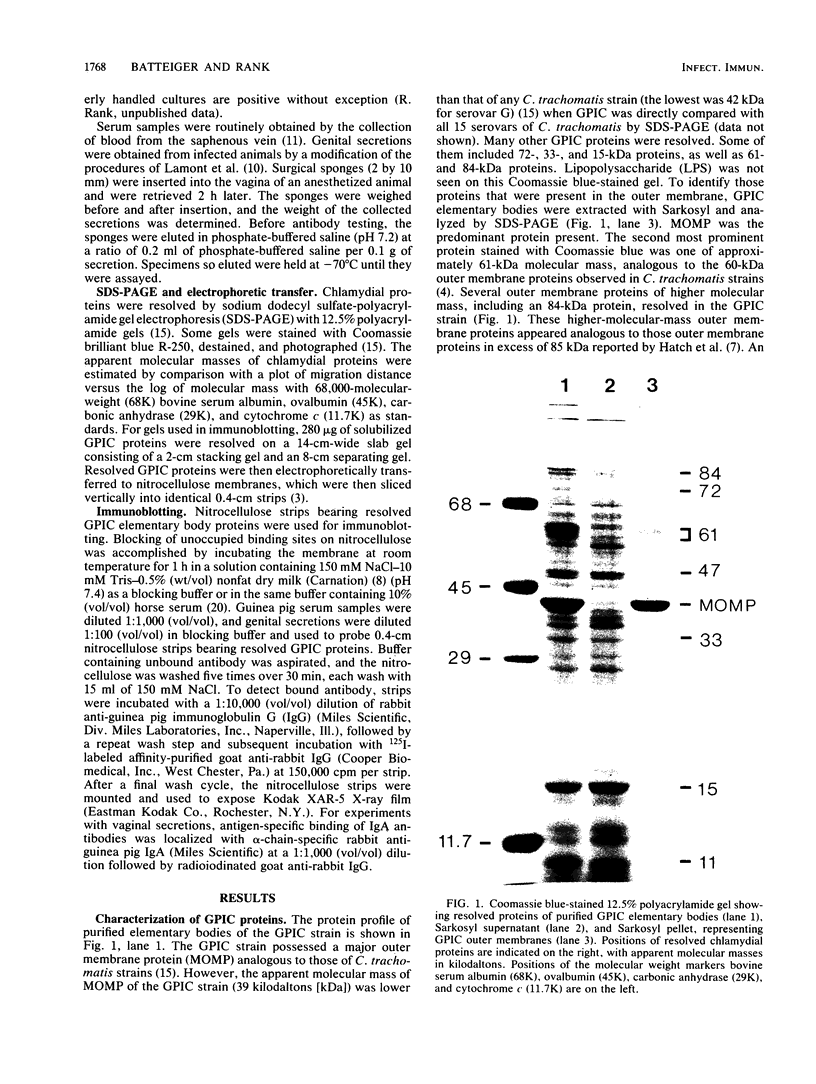
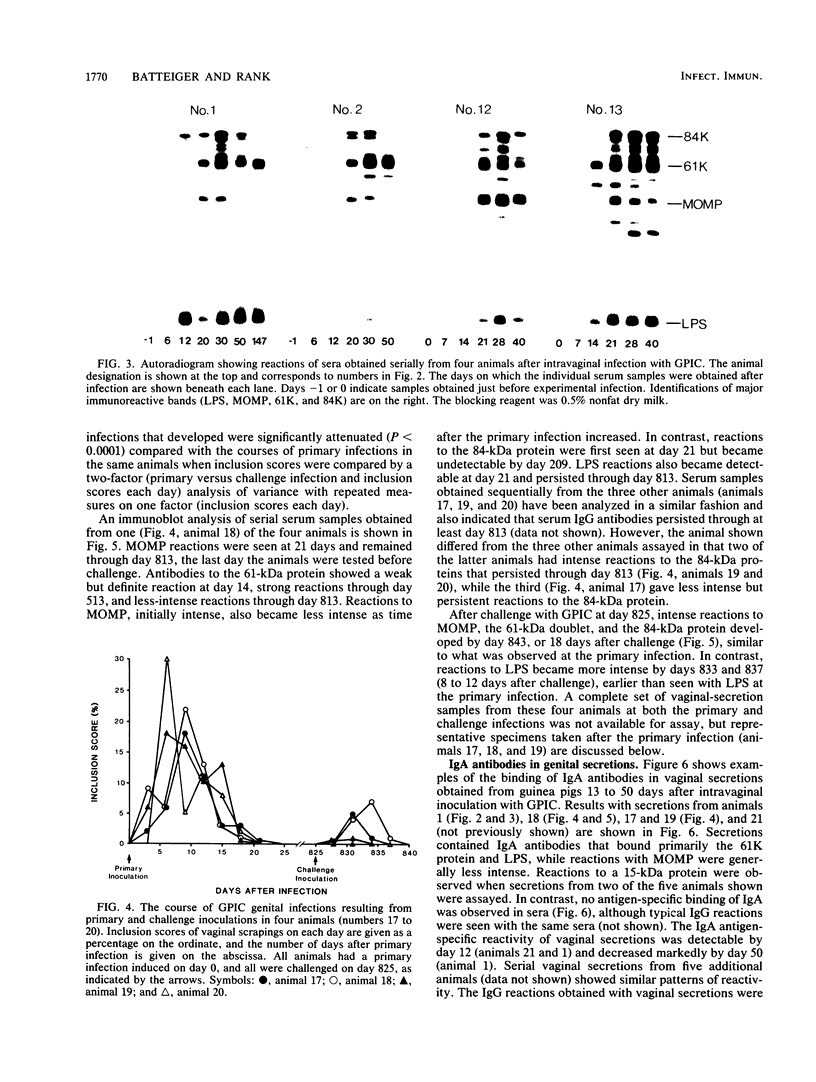
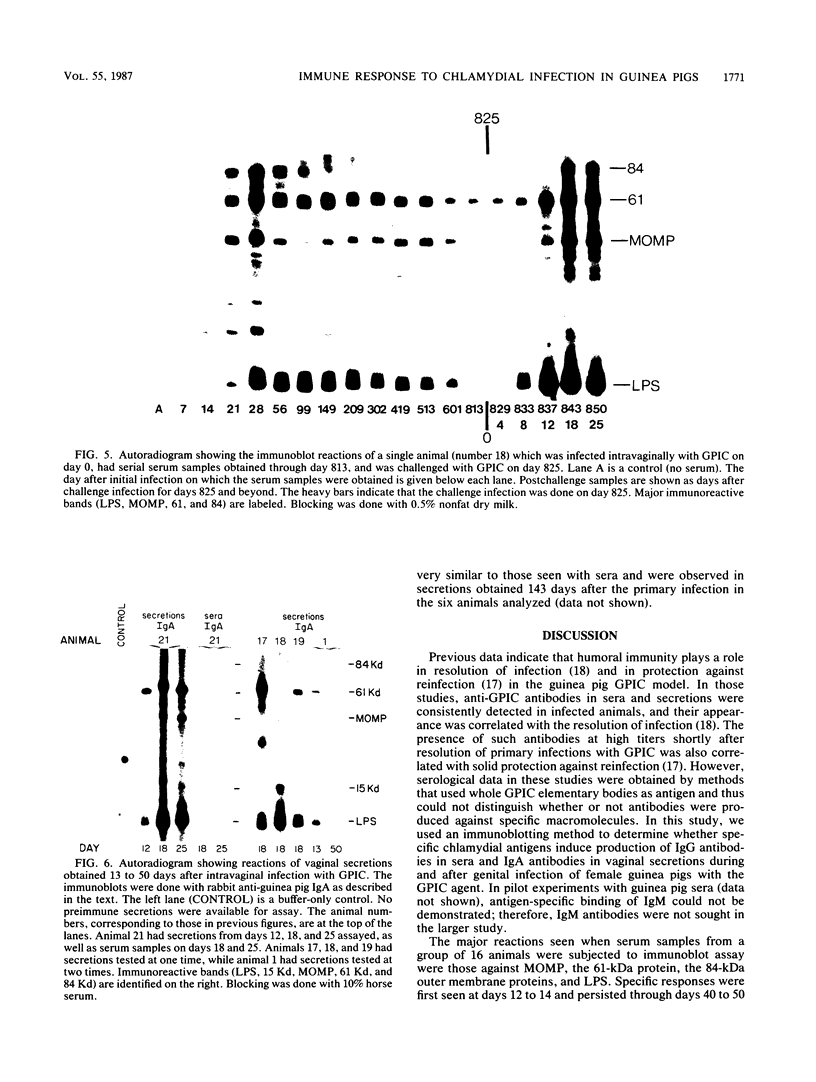
Studies using the guinea pig model of chlamydial genital infection with the Chlamydia psittaci agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis (GPIC) have shown that serum and local antibodies play a role both in the resolution of infection and in protection against reinfection. Thus, this model is suited for further exploration of immune mechanisms and for vaccine studies with chlamydial macromolecules. We have further characterized the model by assessing the antigen-specific antibody response to experimental genital infection by using immunoblotting to assay both genital secretions and serum. The GPIC agent was characterized by analysis of outer membrane proteins, which indicated that the GPIC agent possessed a major outer membrane protein (MOMP), with a molecular mass of 39 kilodaltons (kDa), and a 61-kDa protein, analogous to cysteine-rich 60-kDa proteins or doublets of Chlamydia trachomatis strains. As indicated by immunoblotting, most infected animals produced serum immunoglobulin G antibodies to MOMP, the 61-kDa proteins, an 84-kDa outer membrane protein, and lipopolysaccharide. Such serum antibodies persisted for at least 813 days after primary genital infection. Immunoglobulin A antibodies against the 61-kDa proteins, lipopolysaccharide, and MOMP, but not the 84-kDa protein, were detected in secretions. Animals challenged with GPIC 825 days after primary infection became infected again despite the presence of serum antibodies, but the period of chlamydial shedding was significantly shorter and less intense than in primary infections. Although the specific mechanism is not known, these data suggest that a long-lasting immune effect is capable of altering the course of infection late after primary infection. Correlation of the antigen-specific antibody response and other immune parameters with the duration and degree of protective immunity induced by infection or vaccination may be helpful in further understanding the nature of such protective immunity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barron A. L., White H. J., Rank R. G., Soloff B. L. Target tissues associated with genital infection of female guinea pigs by the chlamydial agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):60–68. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B. E., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. Differences in outer membrane proteins of the lymphogranuloma venereum and trachoma biovars of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):488–494. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.488-494.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Hitchcock P. J. Monoclonal antibody against a genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia species: location of the epitope on chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont H. C., Semine D. Z., Leveille C., Nichols R. L. Immunity to vaginal reinfection in female guinea pigs infected sexually with Chlamydia of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):807–813. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.807-813.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez H., Navia J. M. A technique for repeated collection of blood from the guinea pig. Lab Anim Sci. 1977 Aug;27(4):522–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnickendam M. A., Pearce J. H. Immune responses and chlamydial infections. Br Med Bull. 1983 Apr;39(2):187–193. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. T., Bigazzi P. E., Barron A. L. Experimental genital infection of male guinea pigs with the agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis and transmission to females. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):925–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.925-930.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. T., Bigazzi P. E., Barron A. L. Infection of genital tract and transmission of ocular infection to newborns by the agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):921–926. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.921-926.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Jones R. B. Disulfide-linked oligomers of the major outer membrane protein of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):998–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.998-1001.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Barron A. L. Humoral immune response in acquired immunity to chlamydial genital infection of female guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):463–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.463-465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., White H. J., Barron A. L. Humoral immunity in the resolution of genital infection in female guinea pigs infected with the agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):573–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.573-579.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., White H. J., Hough A. J., Jr, Pasley J. N., Barron A. L. Effect of estradiol on chlamydial genital infection of female guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):699–705. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.699-705.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. J., Rank R. G., Soloff B. L., Barron A. L. Experimental chlamydial salpingitis in immunosuppressed guinea pigs infected in the genital tract with the agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):728–735. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.728-735.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








