Abstract
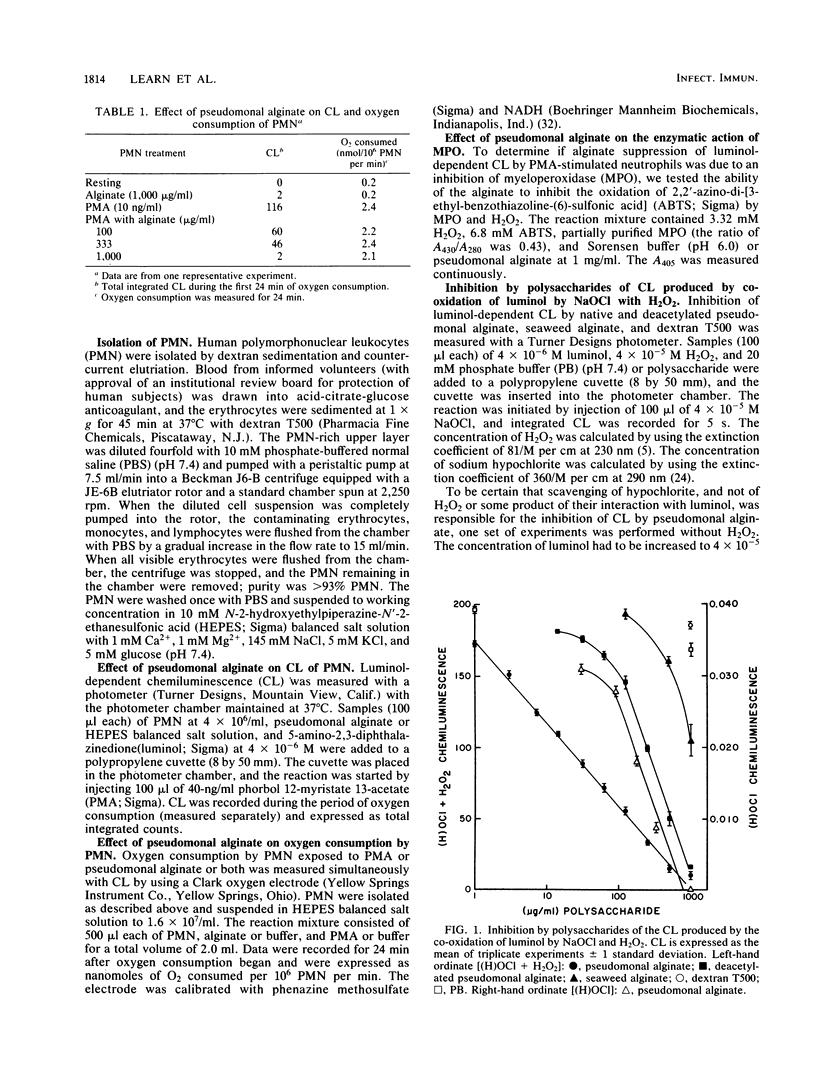
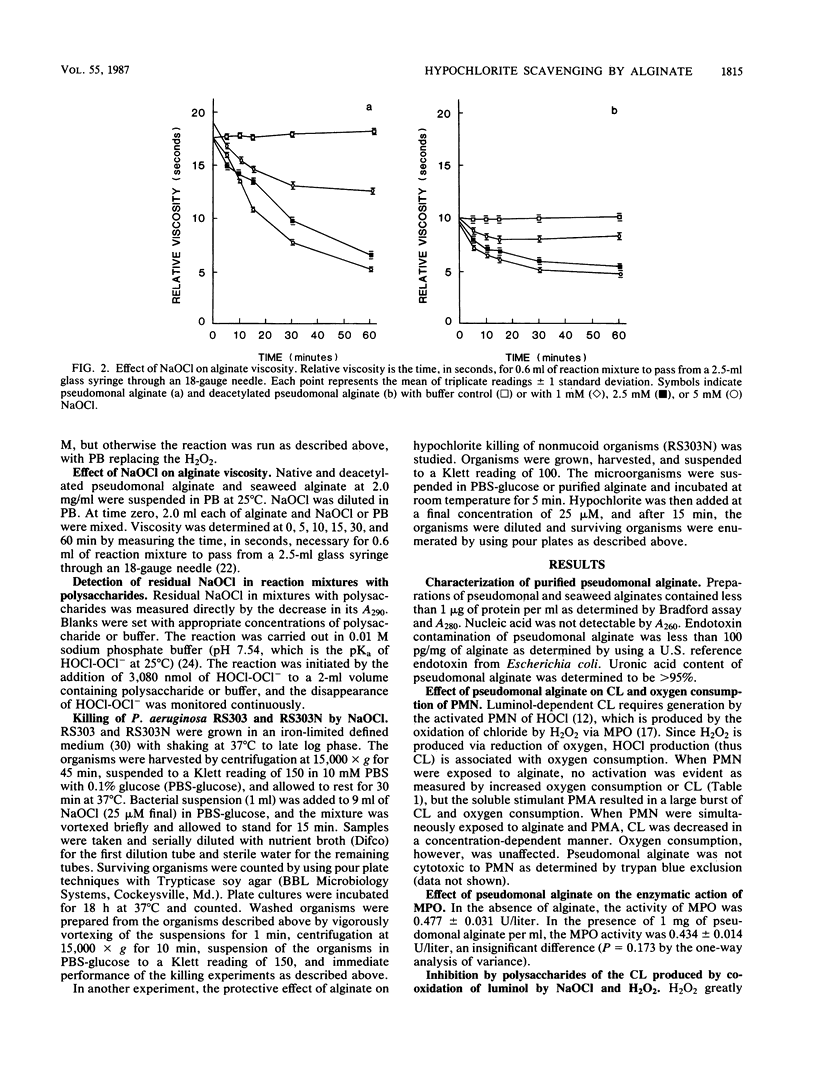
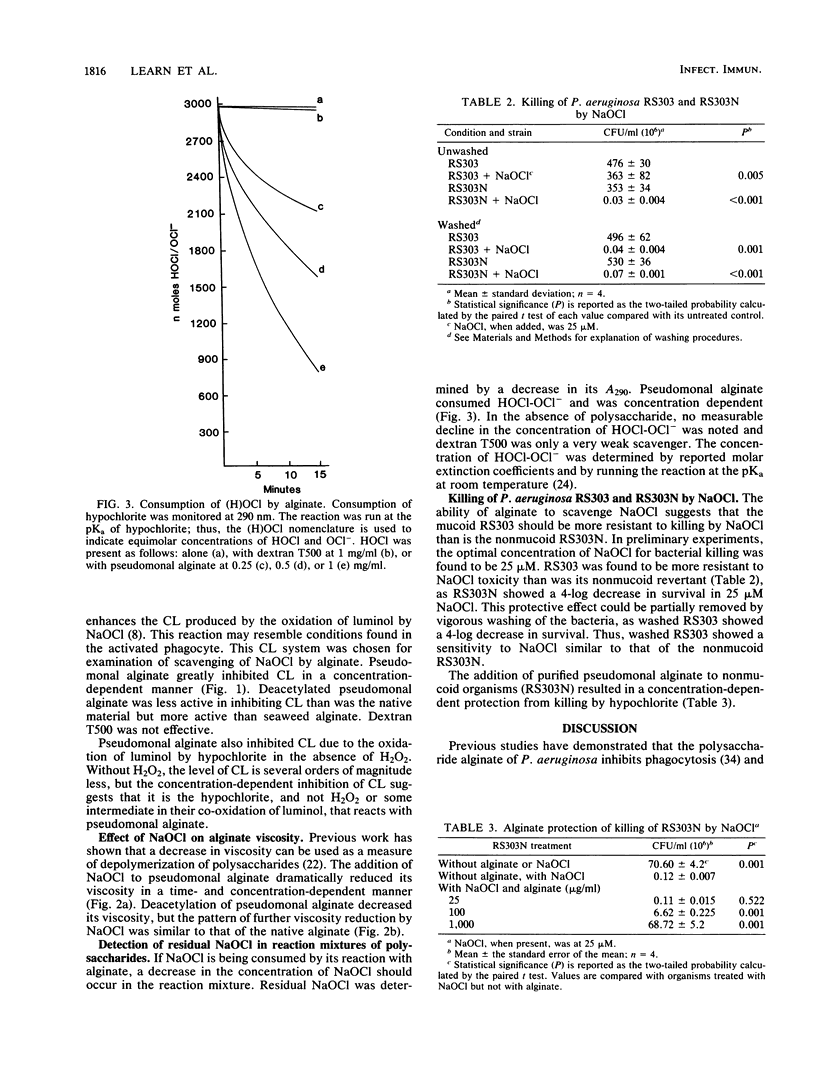
Alginic acid was purified from a mucoid clinical isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of phorbol myristate acetate-stimulated neutrophils was inhibited by this alginate, but oxygen consumption was unaffected. Further studies indicated that this effect was due to the ability of the pseudomonal alginate to scavenge hypochlorite. A seaweed alginate was less effective and dextran T500 was ineffective in hypochlorite scavenging. It appears that the uronic acid core and the O-acetyl groups of pseudomonal alginate are involved in its hypochlorite-scavenging ability. The relevance of this phenomenon was demonstrated by the greater resistance to killing by hypochlorite of mucoid P. aeruginosa compared with a nonmucoid revertant, and the addition of purified alginate to the nonmucoid revertant protected the organism from hypochlorite. Thus, this extracellular polysaccharide may enhance the virulence of P. aeruginosa by scavenging the phagocyte-generated oxidant HOCl. This enhanced virulence may be involved in disease processes in which mucoid organisms predominate, such as cystic fibrosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames P., DesJardins D., Pier G. B. Opsonophagocytic killing activity of rabbit antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):281–285. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.281-285.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anastassiou E. D., Mintzas A. C., Kounavis C., Dimitracopoulos G. Alginate production by clinical nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):656–659. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.656-659.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brestel E. P. Co-oxidation of luminol by hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide implications for neutrophil chemiluminescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):482–488. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90631-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brestel E. P., McClain E. J. A mechanism for inhibition of luminol-dependent neutrophil chemiluminescence by polyanions. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2515–2519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kureishi A., Rabin H. R. Detection of antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate extracellular polysaccharide in animals and cystic fibrosis patients by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):276–282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.276-282.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Long G. D., Shirley P. S., Bass D. A., Thomas M. J., Henderson F. W., Cohen M. S. Mechanism of the luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1589–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G. Incidence of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa from clinical sources. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):936–937. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.936-937.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. R., Linker A. Production and characterization of the slime polysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):915–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.915-924.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Schultz J. Studies on the chlorinating activity of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Flensborg E. W., Beck B., Friis B., Jacobsen S. V., Jacobsen L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa precipitins determined by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Respir Dis. 1977 Apr;58(2):65–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase-halide-hydrogen peroxide antibacterial system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2131-2138.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I. The pathogenesis and treatment of pulmonary infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80631-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Harding G. K., Ronald A. R., Dikkema J., Lam J., Hoban S., Costerton J. W. Influence of mucoidy on antibody coating of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):357–361. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. Free radicals and inflammation: protection of synovial fluid by superoxide dismutase. Science. 1974 Aug 9;185(4150):529–531. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4150.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian F. A., Jarman T. R., Righelato R. C. Biosynthesis of exopolysaccharide by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):418–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.418-422.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olitzki L. MUCIN AS A RESISTANCE-LOWERING SUBSTANCE. Bacteriol Rev. 1948 Jun;12(2):149–172. doi: 10.1128/br.12.2.149-172.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver A. M., Weir D. M. Inhibition of bacterial binding to mouse macrophages by Pseudomonas alginate. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1983 Apr;10(4):221–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul B., Sbarra A. J. The role of the phagocyte in host-parasite interactions. 13. The direct quantitative estimation of H2O2 in phagocytizing cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 1;156(1):168–178. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Matthews W. J., Jr, Eardley D. D. Immunochemical characterization of the mucoid exopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):494–503. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B. Pulmonary disease associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: current status of the host-bacterium interaction. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):575–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Pier G. B. Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide in adherence to tracheal cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Cooper J. M. Method of determining oxygen concentrations in biological media, suitable for calibration of the oxygen electrode. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):390–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. I. Metabolic changes during the ingestion of particles by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmann S., Boring J. R. Antiphagocytic Effect of Slime from a Mucoid Strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):762–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.762-767.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale T. W., Thirkill H., Tarpay M., Flux M., Rennert O. M. Serotypes and antibiotic susceptibilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from single sputa of cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.72-78.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Lawton D., Mutharia L. M. Antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide and to sodium alginate in cystic fibrosis serum. Pediatr Res. 1984 May;18(5):431–433. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198405000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, chloride antimicrobial system: nitrogen-chlorine derivatives of bacterial components in bactericidal action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.522-531.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Hill J. H. Detection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS): an improved method for isolation of the Limulus extract. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Dec;141(3):898–900. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Kao L., Victor M., Elsbach P. Oxygen-independent intracellular and oxygen-dependent extracellular killing of Escherichia coli S15 by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):206–212. doi: 10.1172/JCI111947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. D., Bowie J. U., Nelson R. D. Influence of yeast mannan on release of myeloperoxidase by human neutrophils: determination of structural features of mannan required for formation of myeloperoxidase-mannan-neutrophil complexes. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):467–471. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.467-471.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. D., Herron M. J., Gray G. R., Holmes B., Nelson R. D. Influence of yeast mannan on human neutrophil functions: inhibition of release of myeloperoxidase related to carbohydrate-binding property of the enzyme. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):731–738. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.731-738.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Sant'Agnese P. A., Davis P. B. Research in cystic fibrosis (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 9;295(11):597–602. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609092951105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


