Abstract
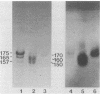
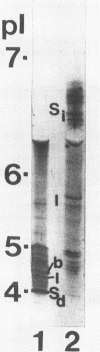
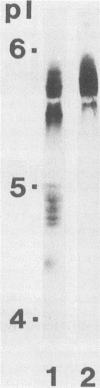
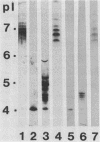
Murine monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) were raised against the glucosyltransferases (GTFs) of Streptococcus sobrinus 6715. The antibody panels included MAbs raised against the primer-independent, soluble product enzyme (GTF-Si) which did not cross-react with other GTFs, as well as MAbs raised against the primer-dependent, soluble product enzyme (GTF-Sd) which recognized both GTF-Si and GTF-Sd, thus indicating that these catalytically distinct enzymes share epitopes. MAbs raised against GTF-I recognized several forms of GTF-I and did not cross-react with the GTF-S enzymes. None of the MAbs recognized the major glucan-binding protein of S. sobrinus. Two MAbs inhibited glucan synthesis, one blocking primer synthesis by GTF-Si by 89% and the second inhibiting that by GTF-I by 92%.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardi J. E., Hageage G. J., Jr, Wittenberger C. L. Multicomponent nature of the glucosyltransferase system of Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1976 Apr;55(Spec No):C87–C96. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500330011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. L., Tanzer J. M. Dissociation of plaque formation from glucan-induced agglutination in mutants of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):189–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.189-196.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K., Fukui Y., Moriyama T. Purification and properties of dextransucrase and invertase from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.796-804.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., Nisizawa T., Chiba J., Hamada S. Production of monoclonal antibody against a glucosyltransferase of Streptococcus mutans 6715. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):872–875. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.872-875.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame D. A., Mayer R. M. The origin and composition of multiple forms of dextransucrase from Streptococcus sanguis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 27;786(1-2):42–48. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamelik R. M., McCabe M. M. An endodextranase inhibitor from batch cultures of streptococcus mutans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 15;106(3):875–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91792-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M., Hamelik R. M. An enzyme from Streptococcus mutans forms branches on dextran in the absence of sucrose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M., Hamelik R. M., Smith E. E. Purification of dextran-binding protein from cariogenic Streptococcus mutans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91250-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M. Purification and characterization of a primer-independent glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus mutans 6715-13 mutant 27. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):771–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.771-777.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M., Smith E. E. Origin of the cell-associated dextransucrase of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):829–838. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.829-838.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart M. P., Malamud D. Protein transfer from isoelectric focusing Gels: the native blot. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Glycosyltransferases of Streptococcus mutans strain Ingbritt. Microbios. 1978;23(93-94):136–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura A., Tsumori H., Mukasa H. Three kinds of extracellular glucosyltransferases from Streptococcus mutans 6715 (serotype g). FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Taubman M. A. Antigenic relatedness of glucosyltransferase enzymes from streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):91–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.91-103.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsumori H., Shimamura A., Mukasa H. Comparative study of Streptococcus mutans extracellular glycosyltransferases by isoelectric focusing. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3261–3269. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]