Abstract
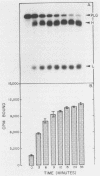
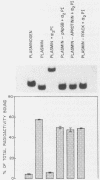
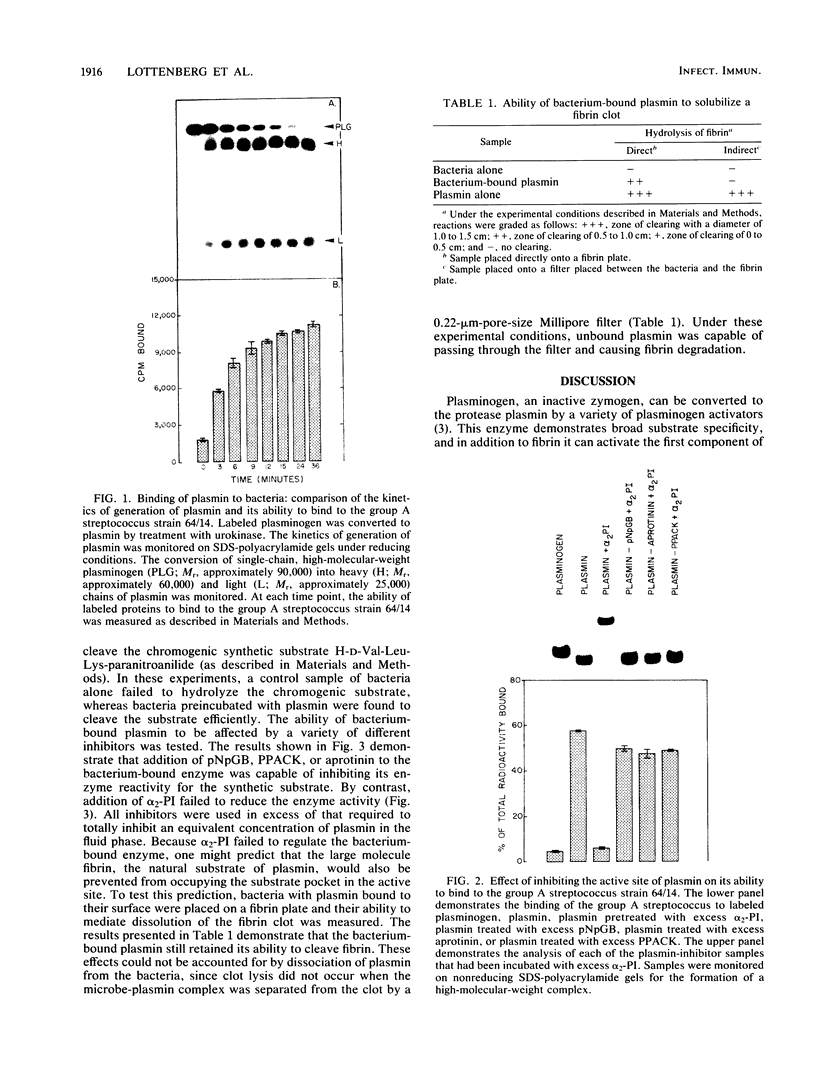
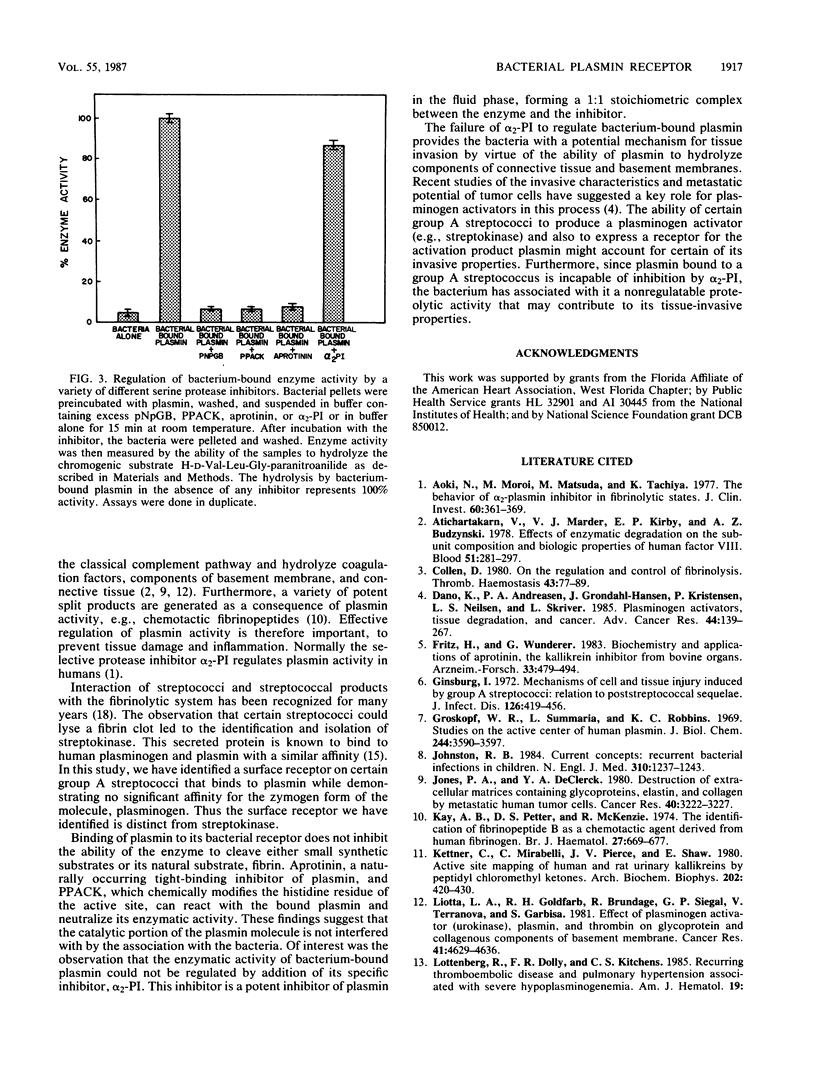
Certain group A streptococci demonstrate surface receptors that bind selectively to the key fibrinolytic enzyme, plasmin. These bacteria show no reactivity with the zymogen protein plasminogen or with other serine class proteases, such as trypsin or urokinase. Bacterium-bound plasmin retains its ability to cleave synthetic substrates and its ability to hydrolyze a fibrin clot. The bacterium-bound plasmin is not effectively regulated by its physiological regulator, alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor. This study is the first report of a bacterium-associated receptor for plasmin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Matsuda M., Tachiya K. The behavior of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor in fibrinolytic states. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):361–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI108784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atichartakarn V., Marder V. J., Kirby E. P., Budzynski A. Z. Effects of enzymatic degradation on the subunit composition and biologic properties of human factor VIII. Blood. 1978 Feb;51(2):281–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H., Wunderer G. Biochemistry and applications of aprotinin, the kallikrein inhibitor from bovine organs. Arzneimittelforschung. 1983;33(4):479–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I. Mechanisms of cell and tissue injury induced by group A streptococci: relation to poststreptococcal sequelae. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):419–456. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groskopf W. R., Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Studies on the active center of human plasmin. Partial amino acid sequence of a peptide containing the active center serine residue. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3590–3597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr Recurrent bacterial infections in children. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 10;310(19):1237–1243. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405103101907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., DeClerck Y. A. Destruction of extracellular matrices containing glycoproteins, elastin, and collagen by metastatic human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Sep;40(9):3222–3227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Pepper D. S., McKenzie R. The identification of fibrinopeptide B as a chemotactic agent derived from human fibrinogen. Br J Haematol. 1974 Aug;27(4):669–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Mirabelli C., Pierce J. V., Shaw E. Active site mapping of human and rat urinary kallikreins by peptidyl chloromethyl ketones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jul;202(2):420–430. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90446-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Goldfarb R. H., Brundage R., Siegal G. P., Terranova V., Garbisa S. Effect of plasminogen activator (urokinase), plasmin, and thrombin on glycoprotein and collagenous components of basement membrane. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4629–4636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. Isolation and characterization of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor from human plasma. A novel proteinase inhibitor which inhibits activator-induced clot lysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5956–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy K. N., Markus G. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen by streptokinase. Presence of active center in streptokinase-plasminogen complex. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1683–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis K. J., Ayoub E. M., Boyle M. D. Detection of receptors for the Fc region of IgG on streptococci. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Apr 15;59(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90148-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillett W. S., Sherry S. THE EFFECT IN PATIENTS OF STREPTOCOCCAL FIBRINOLYSIN (STREPTOKINASE) AND STREPTOCOCCAL DESOXYRIBONUCLEASE ON FIBRINOUS, PURULENT, AND SANGUINOUS PLEURAL EXUDATIONS. J Clin Invest. 1949 Jan;28(1):173–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI102046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Ayoub E. M., Boyle M. D. Analysis of surface receptor expression on bacteria isolated from patients with endocarditis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jul;132(7):2049–2052. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-7-2049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Boyle M. D. Isolation and characterization of type IIa and type IIb Fc receptors from a group A streptococcus. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Nov;24(5):549–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarnall M., Boyle M. D. Isolation and partial characterization of a type II Fc receptor from a group A streptococcus. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 Apr;70(1):57–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00233803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]