Abstract
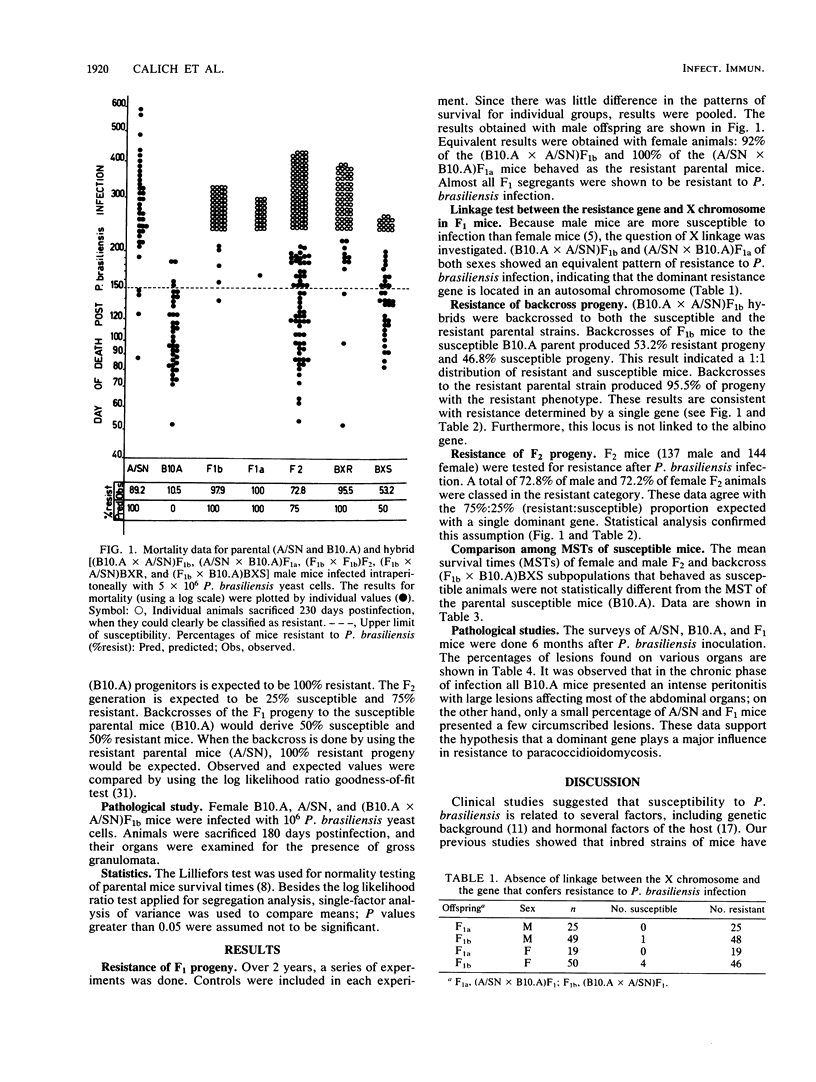
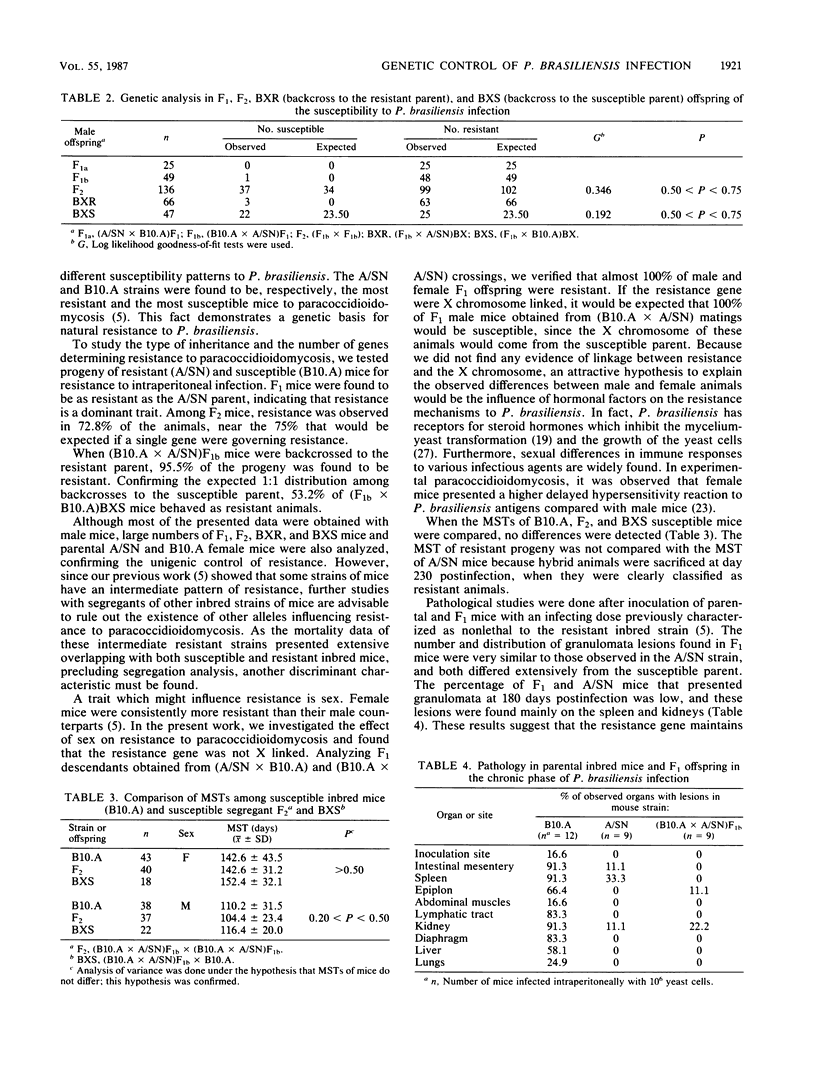
In a previous report it was shown that there are resistant, susceptible, and intermediate strains of mice to intraperitoneal Paracoccidioides brasiliensis infection. In the present work, we investigated the type of inheritance and the number of genes that determine resistance to paracoccidioidomycosis. Parental and hybrid mice were inoculated intraperitoneally with 5 X 10(6) P. brasiliensis yeast cells, and mortality was scored daily. Analysis of susceptible and resistant parental strains and of F1, F2, and backcross mice showed that the resistance to P. brasiliensis seems to be controlled genetically by a single dominant gene, which we designated the Pbr locus. The mean survival times of susceptible F2 and backcross hybrids were very similar to that of the susceptible parent. Examination of the pathological changes observed in parental and F1 mice, 6 months after infection, showed that F1 offspring presented a similar number and distribution of lesions to those of the resistant strains. The Pbr gene is not linked to H-2, Hc, and albino genes. Furthermore, resistance to paracoccidioidomycosis is controlled by an autosomal gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. W., Jr, Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental rickettsialpox: genetics of natural resistance to infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):132–136. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.132-136.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner M. D., Reca M. E. Vital staining of Histoplasma capsulatum with Janus Green B. Sabouraudia. 1966 Jun;5(1):26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. II. genetic control of acute susceptibility of mice to Leishmania donovani infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger E., Singer-Vermes L. M., Calich V. L. The role of C5 in experimental murine paracoccidioidomycosis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):425–425. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calich V. L., Singer-Vermes L. M., Siqueira A. M., Burger E. Susceptibility and resistance of inbred mice to Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Oct;66(5):585–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: genetics of listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.755-762.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick E. W., Roberts G. D. The varying susceptibility of different genetic strains of laboratory mice to Histoplasma capsulatum. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1974 Apr 30;52(3):251–253. doi: 10.1007/BF02198750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Acute systemic candidiasis in normal and congenitally thymic-deficient (nude) mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Feb;19(2):121–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DA LACAZ C. S. South America blastomycosis. An Fac Med Univ Sao Paulo. 1955 1956;29:1–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J. Host defense in cryptococcosis. II. Cryptococcosis in the nude mouse. Cell Immunol. 1978 Oct;40(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. Natural resistance to Salmonella typhimurium in different inbred mouse strains. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):311–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashino S. S., Calich V. L., Burger E., Singer-Vermes L. M. In vivo and in vitro characteristics of six Paracoccidioides brasiliensis strains. Mycopathologia. 1985 Dec;92(3):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00437630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland T. N., Fierer J. Genetic control of resistance to Coccidioides immitis: a single gene that is expressed in spleen cells determines resistance. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):548–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland T. N., Fierer J. Inbred mouse strains differ in resistance to lethal Coccidioides immitis infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):912–916. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.912-916.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. W., Balish E. Systemic candidosis in germfree, flora-defined and conventional nude and thymus-bearing mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Jan;29(1):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose D. S., Stover E. P., Restrepo A., Stevens D. A., Feldman D. Estradiol binds to a receptor-like cytosol binding protein and initiates a biological response in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7659–7663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis G., Montplaisir S., Pelletier M., Mousseau S., Auger P. Genetic resistance to murine cryptococcosis: increased susceptibility in the CBA/N XID mutant strain of mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):282–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.282-287.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis G., Montplaisir S., Pelletier M., Mousseau S., Auger P. Genetic resistance to murine cryptococcosis: the beige mutation (Chédiak-Higashi syndrome) in mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):288–293. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.288-293.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaji M., Nishimura K. Granuloma formation and killing functions of granuloma in congenitally athymic nude mice infected with Blastomyces dermatitidis and Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Mycopathologia. 1983 Jun 20;82(3):129–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00439218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoya F., Garcia-Moreno L. F. Effect of sex on delayed hypersensitivity responses in experimental mouse paracoccidioidomycosis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Nov;26(5):467–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi P. A., Brummer E., Stevens D. A. Strain differences in resistance to infection reversed by route of challenge: studies in blastomycosis. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):623–625. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.623-625.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi P. A., Halpern J. W., Stevens D. A. Susceptibility differences of inbred strains of mice to blastomycosis. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):160–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.160-168.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison W. I., Murray M. Trypanosoma congolense: inheritance of susceptibility to infection in inbred strains of mice. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Dec;48(3):364–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Netto C. F., Castro R. M., Gonçalves A. P., Dillon N. L. Ocorrência familiar da blastomicose sul-americana. A propósito de 14 casos. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1965 Nov-Dec;7(6):332–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C., Wicker L. S., Urba W. J. Genetic control of susceptibility to Cryptococcus neoformans in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):494–499. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.494-499.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. A., O'Brien A. D. Position on mouse chromosome 1 of a gene that controls resistance to Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1257–1260. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1257-1260.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Grumet F. C., Remington J. S. Genetic control of murine resistance to Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):416–420. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.416-420.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



