Abstract
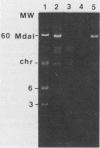
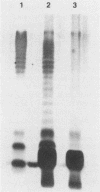
The role of a plasmid in the virulence activity of an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) strain belonging to serotype 0111:NM was examined. EPEC strain B171, which is resistant to chloramphenicol, streptomycin, sulfathiazole, and tetracycline, harbors a 54-megadalton plasmid, pYR111, and exhibits localized adherence (LA) with HeLa cells. Curing the plasmid yielded strain B171-4, which had lost the ability to exhibit LA, resistance to the antibiotics, and the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) O-antigenic polysaccharide. To confirm that these phenotypic characteristics were specified by pYR111, the plasmid was transferred by conjugation into a nalidixic acid-resistant strain of E. coli HB101. LA and antimicrobial resistance were expressed in most of the transconjugants examined. The O-polysaccharide side chains, antigenically reactive with O111-specific antiserum, were also expressed by the transconjugants. Although EPEC plasmids coding for both drug resistance and LA have been described, an EPEC plasmid encoding the expression of an LPS O antigen has not been previously reported. Similar findings described for some Shigella and Salmonella strains suggest that plasmid-encoded modification of the LPS in some enteric bacterial species may be more common than previously recognized and may contribute to the characteristic virulence activity of the organism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agbonlahor D. E., Odugbemi T. O. Enteropathogenic, enterotoxigenic and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli isolated from acute gastroenteritis patients in Lagos, Nigeria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(2):265–267. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M., Candy D. C., Moon H. W. Plasmid-mediated adhesion in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):534–538. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302030-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini M. M., Nataro J. P., Kaper J. B. Localization of a determinant for HEp-2 adherence by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.334-336.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury W. C., Mills S. D., Preston M. A., Barton L. J., Penner J. L. Detection of lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels by transfer to nitrocellulose followed by immunoautoradiography with antibody and 125I-protein A: "LPS blotting". Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C. R., Christie D. L. Chronic diarrhea in infants caused by adherent enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):358–361. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Wallace R. B., Whipp S. C., Olarte J. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and diarrheal disease in Mexican children. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):482–485. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edstrom R. D., Heath E. C. The biosynthesis of cell wall lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli. VII. Studies on the structure of the O-antigenic polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4125–4133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Guerry P., Seid R. C., Jr, Kapfer C., Wingfield M. E., Reaves C. B., Baron L. S., Formal S. B. Expression of lipopolysaccharide O antigen in Escherichia coli K-12 hybrids containing plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella dysenteriae 1. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.470-475.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J., Schad P. A., Austin S., Formal S. B. Characterization of virulence plasmids and plasmid-associated outer membrane proteins in Shigella flexneri, Shigella sonnei, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):340–350. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.340-350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izhar M., Nuchamowitz Y., Mirelman D. Adherence of Shigella flexneri to guinea pig intestinal cells is mediated by a mucosal adhesion. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1110–1118. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1110-1118.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S. I., Holzel A., Wolman B., Keen J. H., Miller V., Taylor J., Gross R. J. Outbreak of infantile gastro-enteritis caused by Escherichia coli O114. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Oct;45(243):656–663. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.243.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL G., MAGNUSSON J. H., FRISELL E., WERNER B. Epidemic infantile diarrhea and vomiting. Acta Paediatr. 1951 Jul;40(4):302–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1951.tb15797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Recombination mechanisms in bacteria. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1955 May;45(Suppl 2):75–107. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030450506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporta M. Z., Silva M. L., Scaletsky I. C., Trabulsi L. R. Plasmids coding for drug resistance and localized adherence to HeLa cells in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O55:H- and O55:H6. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):715–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.715-717.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Elimination of plasmids from several bacterial species by novobiocin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):423–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Evans D. J., Jr, Sack R. B., Sack D. A., Wadström T. Special Escherichia coli serotypes among enterotoxigenic strains from diarrhoea in adults and children. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1976 Jun 1;162(2):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF02121318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Jann B., Jann K. Immunoelectrophoretic patterns of extracts from all Escherichia coli O and K antigen test strains: correlation with pathogenicity. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(2):142–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb02141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulozzi L. J., Johnson K. E., Kamahele L. M., Clausen C. R., Riley L. W., Helgerson S. D. Diarrhea associated with adherent enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in an infant and toddler center, Seattle, Washington. Pediatrics. 1986 Mar;77(3):296–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M. Y., Le Minor L. Expression of antigenic factor O:54 is associated with the presence of a plasmid in Salmonella. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Sep-Oct;136B(2):169–179. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaletsky I. C., Silva M. L., Trabulsi L. R. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.534-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenderup J., Orskov F. The clonal nature of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1019–1024. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo M. R., Alvariza M. do C., Murahovschi J., Ramos S. R., Trabulsi L. R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serotypes and endemic diarrhea in infants. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):586–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.586-589.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Nakamura A., Timmis K. N. Small virulence plasmid of Shigella dysenteriae 1 strain W30864 encodes a 41,000-dalton protein involved in formation of specific lipopolysaccharide side chains of serotype 1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):55–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.55-63.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Timmis K. N. A small plasmid in Shigella dysenteriae 1 specifies one or more functions essential for O antigen production and bacterial virulence. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):391–396. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.391-396.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]