Abstract
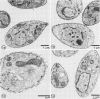
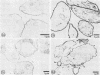
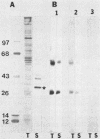
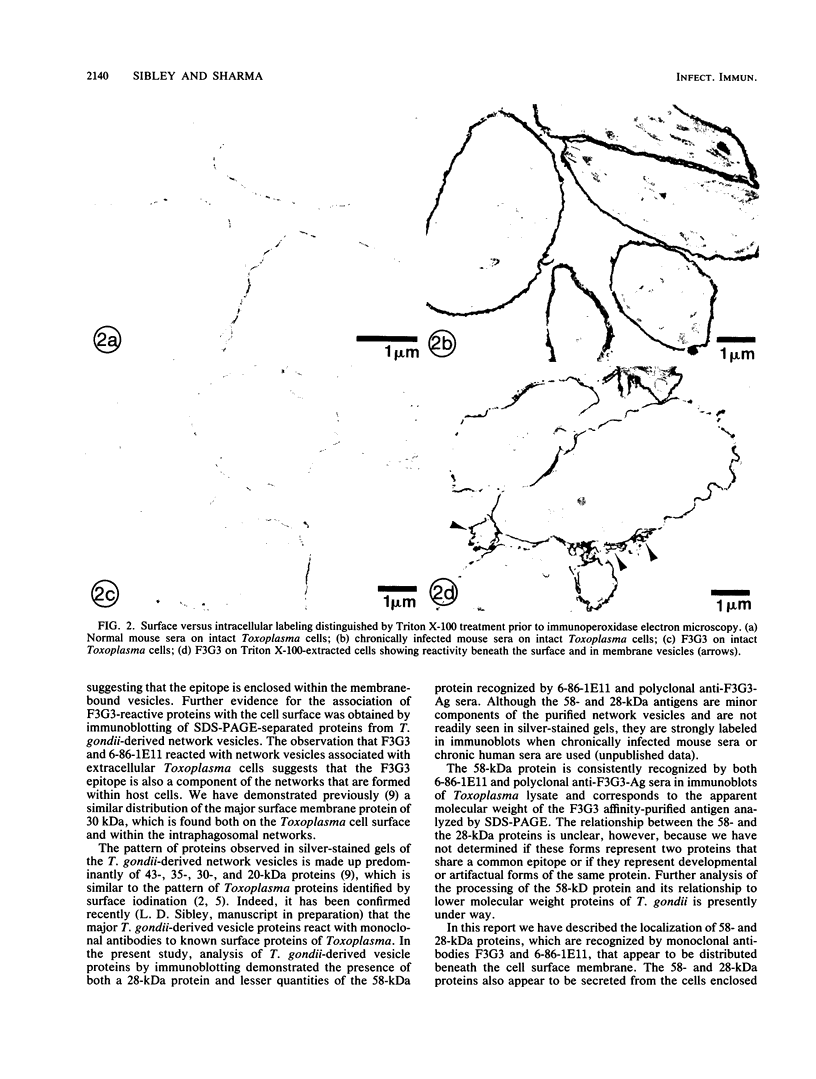
We report the ultrastructural localization of Toxoplasma antigens recognized by monoclonal antibody F3G3, which protects mice against lethal challenge. By using colloidal immunogold labeling, F3G3 failed to react with the surface of intact Toxoplasma cells, confirming previous observations that it recognizes an intracellular antigen. Immunoperoxidase labeling with F3G3 was obtained only when Toxoplasma cells were previously exposed to Triton X-100. A specific immunoperoxidase reaction was located beneath the surface membrane in the region of the pellicle and within the elaborate network of vesicles which are extruded from the surface of Toxoplasma cells during entry into host cells. Similar results were obtained with mouse polyclonal sera and a second monoclonal antibody, 6-86-1E11, both of which were produced against the F3G3 affinity-purified protein. The location of the epitope recognized by F3G3 was confirmed by purifying T. gondii-derived surface membrane vesicles, separating these proteins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and immunoblotting. Monoclonal antibody 6-86-1E11 and the analogous polyclonal sera reacted with the antigenically related proteins of 58 and 28 kilodaltons that were found both in the intact organisms and in the purified surface membrane vesicles. These results indicate that the epitope recognized by F3G3 is located beneath the Toxoplasma cell surface membrane and is contained within plasma membrane-derived vesicles.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. Partially purified antigen preparations of Toxoplasma gondii protect against lethal infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):122–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.122-126.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Goding J. W., Remington J. S. Detection and characterization of membrane antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2578–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Remington J. S. Serological and immunochemical characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):579–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., Haynes W. D., Leppard P. J., McDonald P. J., Neoh S. H. Ultrastructural and biochemical studies on the immunohistochemistry of Toxoplasma gondii antigens using monoclonal antibodies. Histochemistry. 1983;77(2):209–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00506564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., McDonald P. J., Neoh S. H. Monoclonal antibodies to Toxoplasma cell membrane surface antigens protect mice from toxoplasmosis. J Protozool. 1983 May;30(2):351–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1983.tb02929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. Use of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for detection of monoclonal antibodies: experience with antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. Toxoplasma antigen isolated by affinity chromatography with monoclonal antibody protects mice against lethal infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2818–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Krahenbuhl J. L., Adams G. M., Weidner E. Toxoplasma modifies macrophage phagosomes by secretion of a vesicular network rich in surface proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):867–874. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]