Abstract
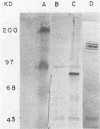
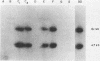
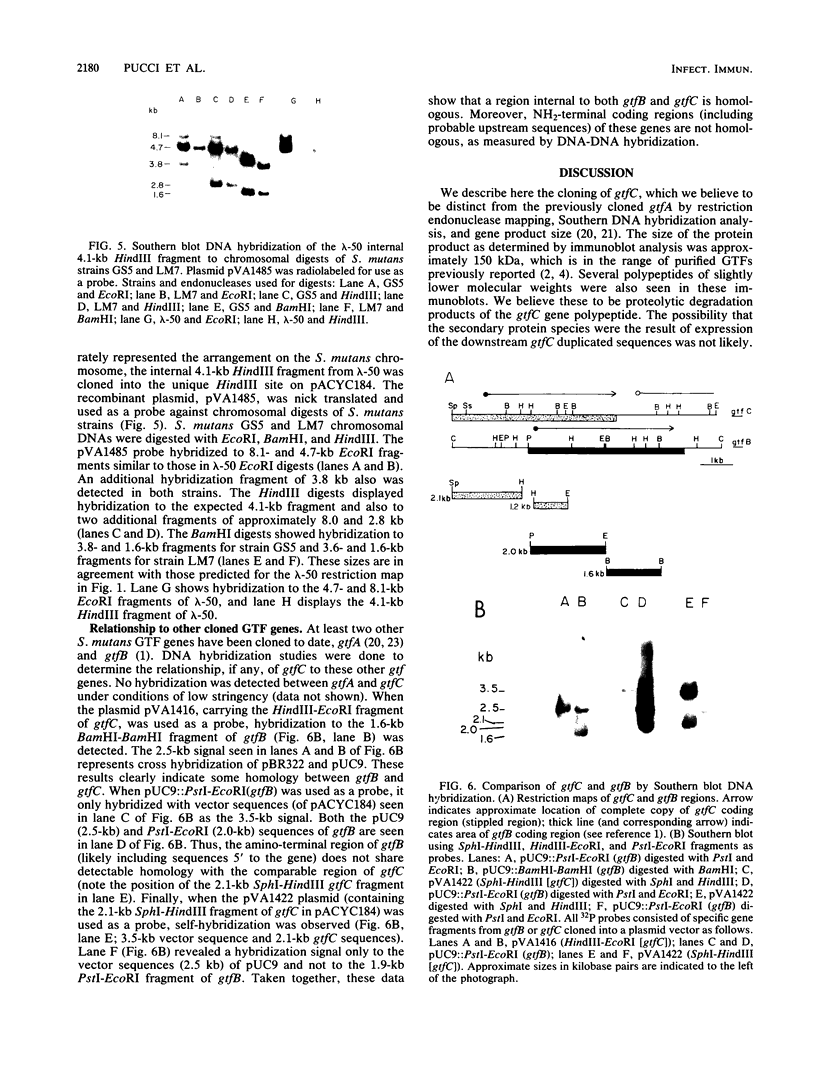
A glucosyltransferase (GTF) gene, designated gtfC, was cloned from Streptococcus mutans LM7. Its gene product was detected by screening a bacteriophage lambda library with rabbit antiserum raised against S. mutans LM7 extracellular proteins. DNA isolated from the immunopositive recombinant phage revealed two S. mutans chromosomal EcoRI fragment inserts, 8.1 and 4.7 kilobase pairs in size. Escherichia coli minicell analyses revealed the approximate position and direction of transcription of the gtfC gene. The gene product was determined to be a polypeptide of about 150 kilodaltons which synthesized a water-soluble glucan. Restriction endonuclease mapping and DNA hybridization indicated a repeated region of DNA corresponding to a portion of the coding region of gtfC immediately downstream from the intact gtfC locus on the chromosome. A 300-base-pair gtfC-specific probe showed that the gene and the putative duplicated sequence were present in S. mutans serotypes c, e, and f, but not in other related oral streptococci which had GTF activity. In addition, the gtfC determinant displayed homology to sequences corresponding to the carboxy-terminal coding region of a gene (gtfB) encoding a GTF activity that synthesized water-insoluble glucans. These data suggest that at least one class of GTF genes may be present in multiple copies in S. mutans and, further, that GTF genes may contain conserved sequences internal to their coding regions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki H., Shiroza T., Hayakawa M., Sato S., Kuramitsu H. K. Cloning of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene coding for insoluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.587-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asem K., Cornish-Bowden A. J., Cole J. A. A comparative study of the extracellular glucosyl- and fructosyltransferases from cariogenic and non-cariogenic Streptococcus mutans strains of two different serotypes. Microbios. 1986;47(190):53–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd Genetic analysis of Streptococcus mutans virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:253–277. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSSON B. E., QUENSEL C. E., LANKE L. S., LUNDQVIST C., GRAHNEN H., BONOW B. E., KRASSE B. The Vipeholm dental caries study; the effect of different levels of carbohydrate intake on caries activity in 436 individuals observed for five years. Acta Odontol Scand. 1954 Sep;11(3-4):232–264. doi: 10.3109/00016355308993925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germaine G. R., Schachtele C. F., Chludzinski A. M. Rapid filter paper assay for the dextransucrase activity from Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1974 Nov-Dec;53(6):1355–1360. doi: 10.1177/00220345740530061101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Dental caries. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:121–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Tobian J. A., Jones K. R., Evans R. P., Clewell D. B. A cloning vector able to replicate in Escherichia coli and Streptococcus sanguis. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucci M. J., Macrina F. L. Cloned gtfA gene of Streptococcus mutans LM7 alters glucan synthesis in Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):704–712. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.704-712.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucci M. J., Macrina F. L. Molecular organization and expression of the gtfA gene of Streptococcus mutans LM7. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):77–84. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.77-84.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucci M. J., Tew J. G., Macrina F. L. Human serum antibody response against Streptococcus mutans antigens. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):600–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.600-606.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robeson J. P., Barletta R. G., Curtiss R., 3rd Expression of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.211-221.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M. Essential dependence of smooth surface caries on, and augmentation of fissure caries by, sucrose and Streptococcus mutans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.526-531.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Freedman M. L., Fitzgerald R. J., Larson R. H. Diminished virulence of glucan synthesis-defective mutants of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.197-203.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., Gold L. Overproduction of bacteriophage Q beta maturation (A2) protein leads to cell lysis. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]