Abstract
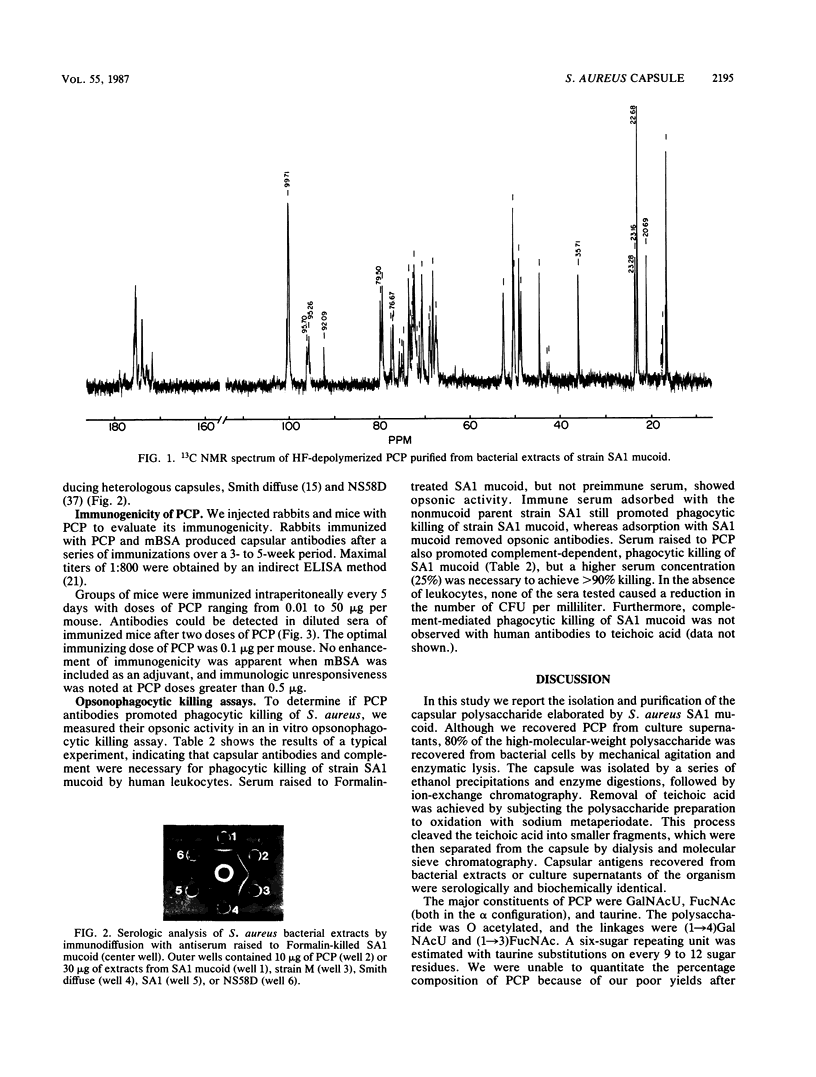
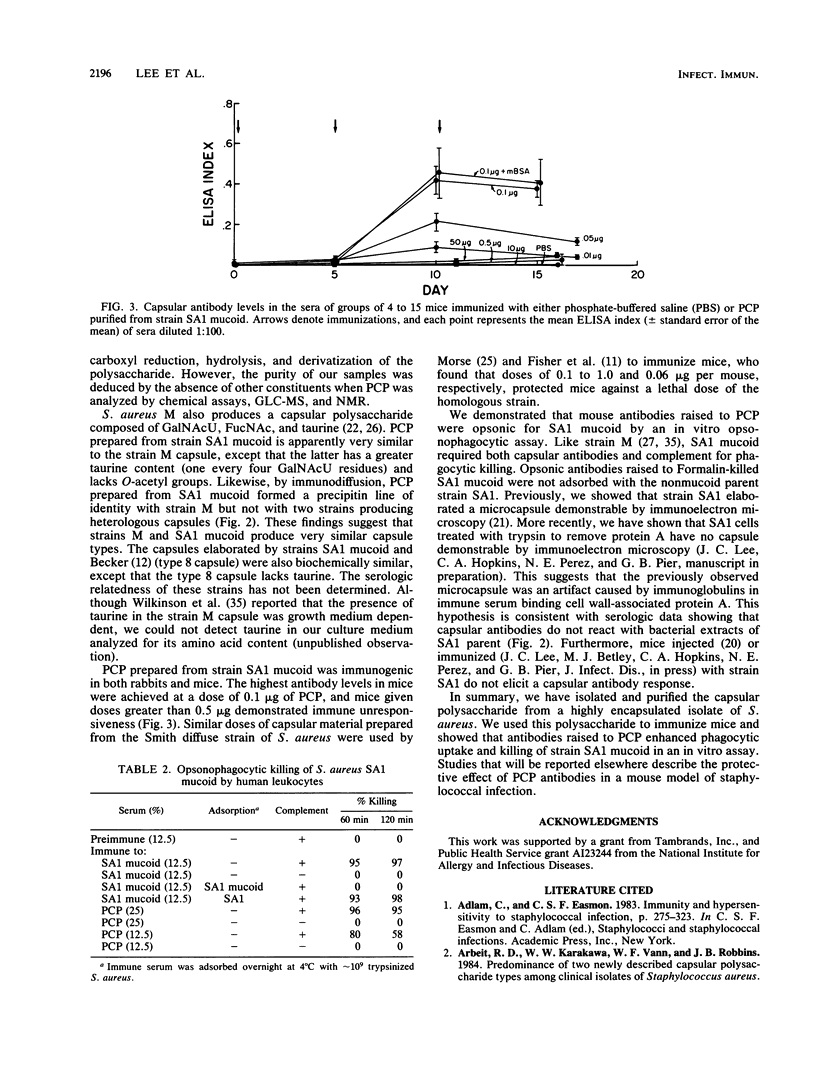
In this study we report the isolation and purification of the capsular polysaccharide elaborated by Staphylococcus aureus SA1 mucoid. The capsule was isolated from bacterial extracts and culture supernatants by a series of ethanol precipitations and enzyme digestions, followed by ion-exchange chromatography. Teichoic acid contamination was eliminated by oxidation with sodium metaperiodate, and the final product eluted in the void volume of a Sephacryl S-300 column. The purified capsular polysaccharide was analyzed by gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy, 13C and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance, amino acid analysis, immunelectrophoresis, and numerous biochemical assays. The major constituents of the capsule were 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-alpha-galacturonic acid (4-O linked), 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-alpha-fucose (3-O linked), and taurine. The polysaccharide also contained O-acetyl groups which were removed by mild alkaline hydrolysis. Serologically and biochemically, the capsule from strain SA1 mucoid appeared very similar to that produced by strain M. Purified capsular polysaccharide was immunogenic in both rabbits and mice. The optimal immunizing dose in mice was 0.1 microgram of purified capsular polysaccharide administered intraperitoneally. SA1 mucoid resisted opsonophagocytic killing by human leukocytes and complement. However, antibodies raised to the purified capsular polysaccharide neutralized the antiphagocytic effect of the capsule.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOWNESS J. M. 5-Formylfuroic acid and the carbazole reaction for uronic acids and acidic polysaccharides. Biochem J. 1958 Sep;70(1):107–110. doi: 10.1042/bj0700107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer F., Germanier R. Experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae burn wound sepsis: role of capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):440–441. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.440-441.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitriev B. A., Backinowsky L. V., Lvov V. L., Kochetkov N. K., Hofman I. L. Somatic antigen of Shigella dysenteriae type 3. Structural features of specific polysaccharide chain. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jan 15;50(3):539–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb09894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER M. W., DEVLIN H. B., ERLANDSON A. L. A NEW STAPHYLOCOCCAL ANTIGEN. ITS PREPARATION AND IMMUNIZING ACTIVITY AGAINST EXPERIMENTAL INFECTIONS. Nature. 1963 Sep 14;199:1074–1075. doi: 10.1038/1991074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER S. A heat stable protective staphylococcal antigen. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1960 Dec;38:479–485. doi: 10.1038/icb.1960.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier J. M., Vann W. F., Karakawa W. W. Purification and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus type 8 capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.87-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M. ELISA methodology for polysaccharide antigens: protein coupling of polysaccharides for adsorption to plastic tubes. J Immunol Methods. 1979;28(1-2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANESSIAN S., HASKELL T. H. STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON STAPHYLOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGEN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2758–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of microorganisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):104–123. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M. G., Melly M. A. The importance of surface antigens in staphylococcal virulence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):231–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käyhty H., Peltola H., Karanko V., Mäkelä P. H. The protective level of serum antibodies to the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;147(6):1100–1100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.6.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Structural analysis of the surface polysaccharide of Staphylococcus aureus M. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):194–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.194-200.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE S. I. Isolation and properties of a surface antigen of Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med. 1962 Feb 1;115:295–311. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S. V., Melly M. A., Harris T. M., Hellerqvist C. G., Hash J. H. The repeating sequence of the capsular polysaccharide of Staphylococcus aureus M. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Jun 16;117:113–123. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Influence of encapsulation on staphylococcal opsonization and phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):943–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.943-949.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger M. P., Lamport D. T. A microapparatus for liquid hydrogen fluoride solvolysis: sugar and amino sugar composition of Erysiphe graminis and Triticum aestivum cell walls. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jan;128(1):66–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Samra Z., Karakawa W. W., Vann W. F., Schneerson R., Malik Z. Encapsulation and capsular types in isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from different sources and relationship to phage types. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):828–834. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.828-834.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. L., Conrad H. E. Stoichiometric depolymerization of polyuronides and glycosaminoglycuronans to monosaccharides following reduction of their carbodiimide-activated carboxyl groups. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1383–1388. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Maverakis N. H. Capsule production and virulence among strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):221–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Cryptic peptidoglycan and the antiphagocytic effect of the Staphylococcus aureus capsule: model for the antiphagocytic effect of bacterial cell surface polymers. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):502–508. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.502-508.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Park J. T. Chemical characterization of a new surface antigenic polysaccharide from a mutant of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):874–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.874-884.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K. Demonstration of Serologically Different Capsular Types Among Strains of Staphylococcus aureus by the Serum-Soft Agar Technique. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.535-539.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ekstedt R. D. Relation of mucoid growth of Staphylococcus aureus to clumping factor reaction, morphology in serum-soft agar, and virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):902–908. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.902-908.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]