Abstract
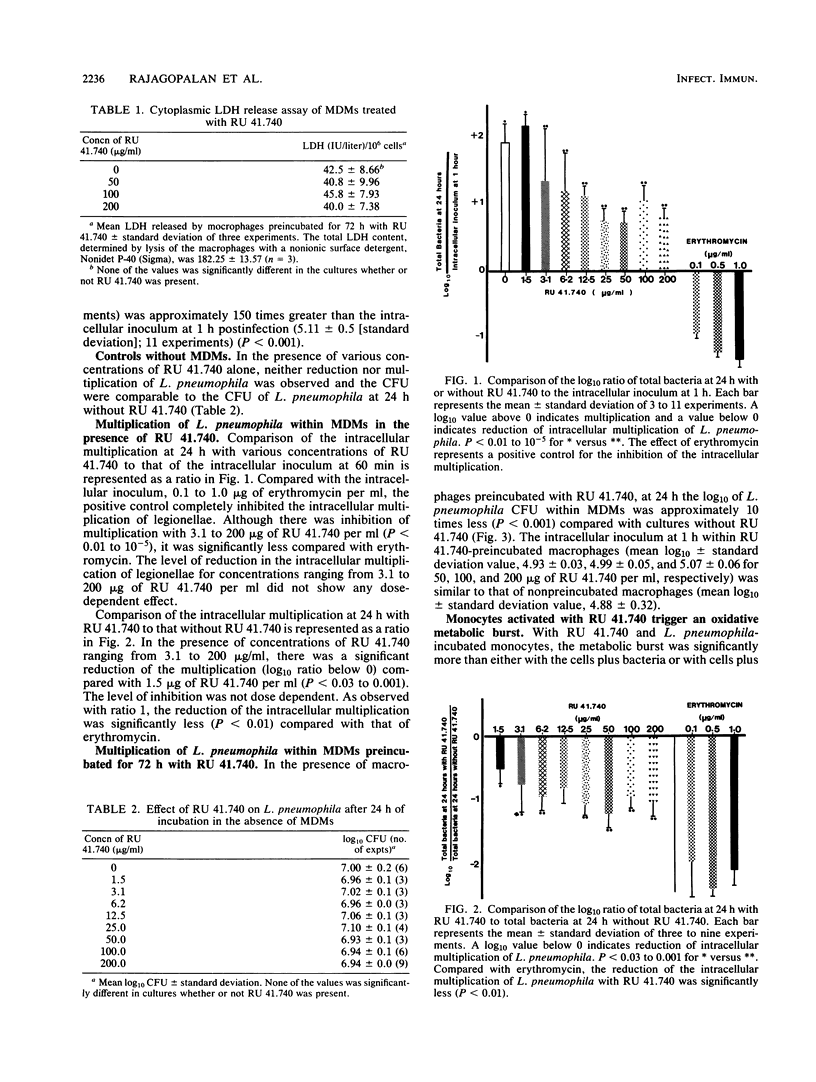
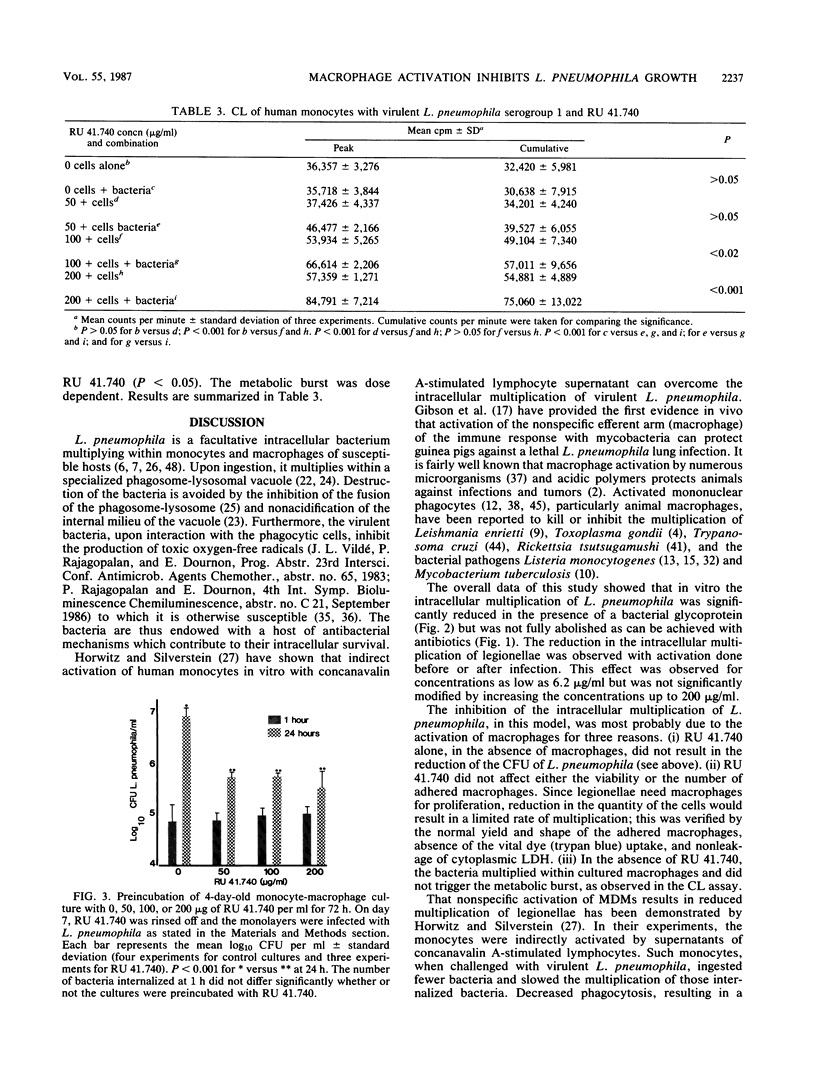
Intracellular multiplication of virulent Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 was inhibited by human monocyte-derived macrophages activated by a glycoprotein extract of Klebsiella pneumoniae, RU 41.740. Macrophage cultures were infected with L. pneumophila in the presence of immune antibodies on day 7 of culture. Extracellular bacteria were removed an hour after infection, and various concentrations of RU 41.740 or an antibiotic, erythromycin, were added. Intracellular multiplication in the presence of RU 41.740 was significantly slowed down compared with that of cultures without RU 41.740. The reduction was, however, significantly less than that effected by erythromycin, which was used as a positive control for inhibition of intracellular multiplication. Cultures incubated with RU 41.740 before infection also demonstrated a significant reduction in the intracellular multiplication of L. pneumophila. In addition, RU 41.740 increased superoxide anion production from human monocytes in suspension in the presence of L. pneumophila. These results show that direct nonspecific activation of macrophages by a bacterial glycoprotein inhibits the intracellular multiplication of L. pneumophila and may suggest a role for activated macrophages in host defense against intracellular pathogens.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C. Macrophage activation and nonspecific immunity. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1978;18:303–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Bautista S., Remington J. S. Induction of resistance to Toxoplasma gondii in human macrophages by soluble lymphocyte products. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskerville A., Dowsett A. B., Fitzgeorge R. B., Hambleton P., Broster M. Ultrastructure of pulmonary alveoli and macrophages in experimental Legionnaires' disease. J Pathol. 1983 Jun;140(2):77–90. doi: 10.1002/path.1711400202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskerville A., Fitzgeorge R. B., Broster M., Hambleton P., Dennis P. J. Experimental transmission of legionnaires' disease by exposure to aerosols of Legionella pneumophila. Lancet. 1981 Dec 19;2(8260-61):1389–1390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92803-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj N., Nash T. W., Horwitz M. A. Interferon-gamma-activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller Y., Mauel J. Studies on the mechanisms of macrophage activation. II. Parasite destruction in macrophages activated by supernates from concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):359–370. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahall D. L., Youmans G. P. Conditions for production, and some characteristics, of mycobacterial growth inhibitory factor produced by spleen cells from mice immunized with viable cells of the attenuated H37Ra strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):833–840. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.833-840.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheson B. D., Christensen R. L., Sperling R., Kohler B. E., Babior B. M. The origin of the chemiluminescence of phagocytosing granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):789–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI108530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. Activation of mononuclear phagocytes: fact, fancy, and future. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P. Activation of mouse peritoneal cells to kill Listeria monocytogenes by T-lymphocyte products. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.36-41.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dournon E., Rajagopalan P., Vilde J. L., Pocidalo J. J. Efficacy of pefloxacin in comparison with erythromycin in the treatment of experimental guinea pig legionellosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):41–48. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowles R. E., Fajardo I. M., Leibowitch J. L., David J. R. The enhancement of macrophage bacteriostasis by products of activated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):952–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Wachsmuth I., Bopp C., Feeley J. C., Tsai T. F. Antibiotic treatment of guinea-pigs infected with agent of Legionnaires' disease. Lancet. 1978 Jan 28;1(8057):175–178. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90611-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. H., Baskerville A., Ashworth L. A., Fitzgeorge R. B. Non-specific protection against pulmonary Legionella pneumophila infection in guinea-pigs immunized and challenged with mycobacteria. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Jun;66(3):333–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenounou M., Vacheron F., Nauciel C., Agneray J. Induction of interleukin 1 secretion by murine macrophages and human monocytes after stimulation by RU 41740, a bacterial immunomodulator. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(2):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(85)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenounou M., Vacheron F., Zalisz R., Smets P., Agneray J. Immunological activities of RU-41740, a glycoproteic extract from Klebsiella pneumoniae. I.--Activation of murine B cells and induction of interleukin-1 production by macrophages. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1984 Jul-Aug;135D(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(84)80155-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman J., Kew M. C., Rabson A. R. The effect of RU 41.740 (Biostim) on the production of interleukin-1 by monocytes and enriched large granular lymphocytes in normals and patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1986;21(1):26–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00199373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Formation of a novel phagosome by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Maxfield F. R. Legionella pneumophila inhibits acidification of its phagosome in human monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1936–1943. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) occurs by a novel mechanism: engulfment within a pseudopod coil. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1618–1635. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes is reversibly inhibited by erythromycin and rifampin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):15–26. doi: 10.1172/JCI110744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. The Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2108–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackett P. S., Aber V. R., Mitchison D. A., Lowrie D. B. The contribution of hydrogen peroxide resistance to virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis during the first six days after intravenous infection of normal and BCG-vaccinated guinea-pigs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Feb;62(1):34–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackett P. S., Andrew P. W., Aber V. R., Lowrie D. B. Hydrogen peroxide and superoxide release by alveolar macrophages from normal and BCG-vaccinated guinea-pigs after intravenous challenge with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Aug;62(4):419–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauregui H. O., Hayner N. T., Driscoll J. L., Williams-Holland R., Lipsky M. H., Galletti P. M. Trypan blue dye uptake and lactate dehydrogenase in adult rat hepatocytes--freshly isolated cells, cell suspensions, and primary monolayer cultures. In Vitro. 1981 Dec;17(12):1100–1110. doi: 10.1007/BF02618612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T., Youmans G. P. The in vitro inhibition of growth of intracellular Listeria monocytogenes by lymphocyte products. Cell Immunol. 1973 Dec;9(3):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L., Lazdins J. K. Biochemical criteria for activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochner J. E., Friedman R. L., Bigley R. H., Iglewski B. H. Effect of oxygen-dependent antimicrobial systems on Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):487–489. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.487-489.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Jacobs R. F., Wilson C. B., Weaver W. M., Klebanoff S. J. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to oxygen-dependent microbicidal systems. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2192–2197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Cellular immunity. Prog Allergy. 1967;11:89–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Maza O., Wood C. D., Britton S. Immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G secretion by human B cells exposed to RU 41.740, a glycoprotein extract from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Cell Immunol. 1985 Feb;90(2):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D. Legionella infections: a review of five years of research. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):258–278. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infection: macrophage activation in vitro for killing of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2544–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. A. Trypanosoma cruzi: in vitro induction of macrophage microbicidal activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):288–300. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The concept of the activated macrophage. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):806–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. B., Pierre R. V., Jordon R. E. Rapid identification of monocytes in a mixed mononuclear cell preparation. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vildé J. L., Dournon E., Rajagopalan P. Inhibition of Legionella pneumophila multiplication within human macrophages by antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):743–748. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. D., Möller G. Influence of RU 41.740, a glycoprotein extract from Klebsiella pneumoniae, on the murine immune system. I. T-independent polyclonal B cell activation. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):616–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. D., Möller G. Influence of RU 41.740, a glycoprotein extract from Klebsiella pneumoniae, on the murine system. II. RU 41.740 facilitates the response to Con A in otherwise unresponsive T-enriched cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


