Abstract
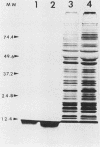
Analyses of chemical composition in whole cells of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi were performed and compared with those of the other rickettsiae and gram-negative bacteria. The results indicated that R. tsutsugamushi does not contain detectable amounts of 3-deoxy-D-mannooctulosonic acid, heptose, muramic acid, or glucosamine (less than 2, less than 2, less than 3, and less than 3 nmol/mg, respectively). The microorganism was found to contain four kinds of fatty acids (16:0, 18:0, 18:1, and 18:2), but not hydroxy fatty acids. Furthermore, in analysis by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by silver or Coomassie blue staining, lipopolysaccharide bands were not detected in preparations treated with proteinase K. It is concluded that R. tsutsugamushi has little or no peptidoglycan or lipopolysaccharide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Fukushi K. Chemical and ultrastructural differences in endotoxic glycolipids from Salmonella minnesota Re mutant extracted with various solvent systems. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(2):135–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Williams J. C. Chemical and immunological characterization of lipopolysaccharides from phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.994-1002.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Williams J. C., McCaul T. F., Peacock M. G. Biochemical and immunological properties of Coxiella burnetii cell wall and peptidoglycan-protein complex fractions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):982–988. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.982-988.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Some physiological and biochemical effects of a Coxiella burneti lipopolysaccharide preparation on guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):939–945. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.939-945.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Identification and partial characterization of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi major protein immunogens. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):603–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.603-609.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Yoshida Y., Osono M., Ohashi N., Oyanagi M., Urakami H., Tamura A., Nogami S., Tanaka H., Kawamura A., Jr Production and characterization of monoclonal strain-specific antibodies against prototype strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):599–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Brezina R., Kazár J. Some biological properties of an endotoxic lipopolysaccharide from the typhus group rickettsiae. Acta Virol. 1977 Sep;21(5):439–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Mayer H. Different sugar compositions of lipopolysaccharides isolated from phase I and pure phase II cells of Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):53–57. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.53-57.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr Comparative ultrastructural study on the cell envelopes of Rickettsia prowazekii, Rickettsia rickettsii, and Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1020–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1020-1023.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Ohashi N., Urakami H., Takahashi K., Oyanagi M. Analysis of polypeptide composition and antigenic components of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):671–675. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.671-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Urakami H., Tsuruhara T. Purification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(4):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzianabos T., Moss C. W., McDade J. E. Fatty acid composition of rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):603–605. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.603-605.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urakami H., Ohashi N., Tsuruhara T., Tamura A. Characterization of polypeptides in Rickettsia tsutsugamushi: effect of preparative conditions on migration of polypeptides in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):948–952. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.948-952.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urakami H., Tsuruhara T., Tamura A. Electron microscopic studies on intracellular multiplication of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in L cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(11):1191–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Silverman D. J., Waddell A., Brown D. T. Penicillin-induced unstable intracellular formation of spheroplasts by rickettsiae. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):147–158. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Walsh W. T. In vitro studies of the action of antibiotics on Rickettsia prowazeki by two basic methods of cell culture. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):564–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Kawabata N., Tamura A., Urakami H., Ohashi N., Murata M., Yoshida Y., Kawamura A., Jr Immunological properties of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, Kawasaki strain, isolated from a patient in Kyushu. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):611–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]