Abstract
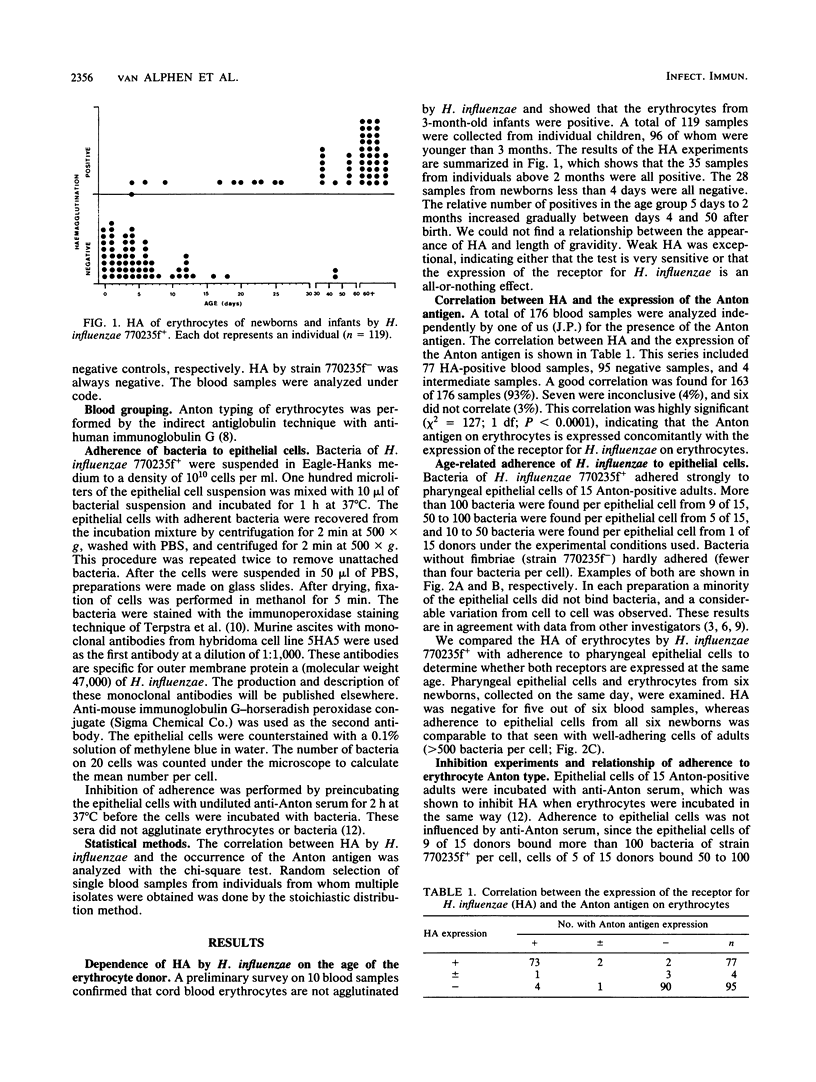
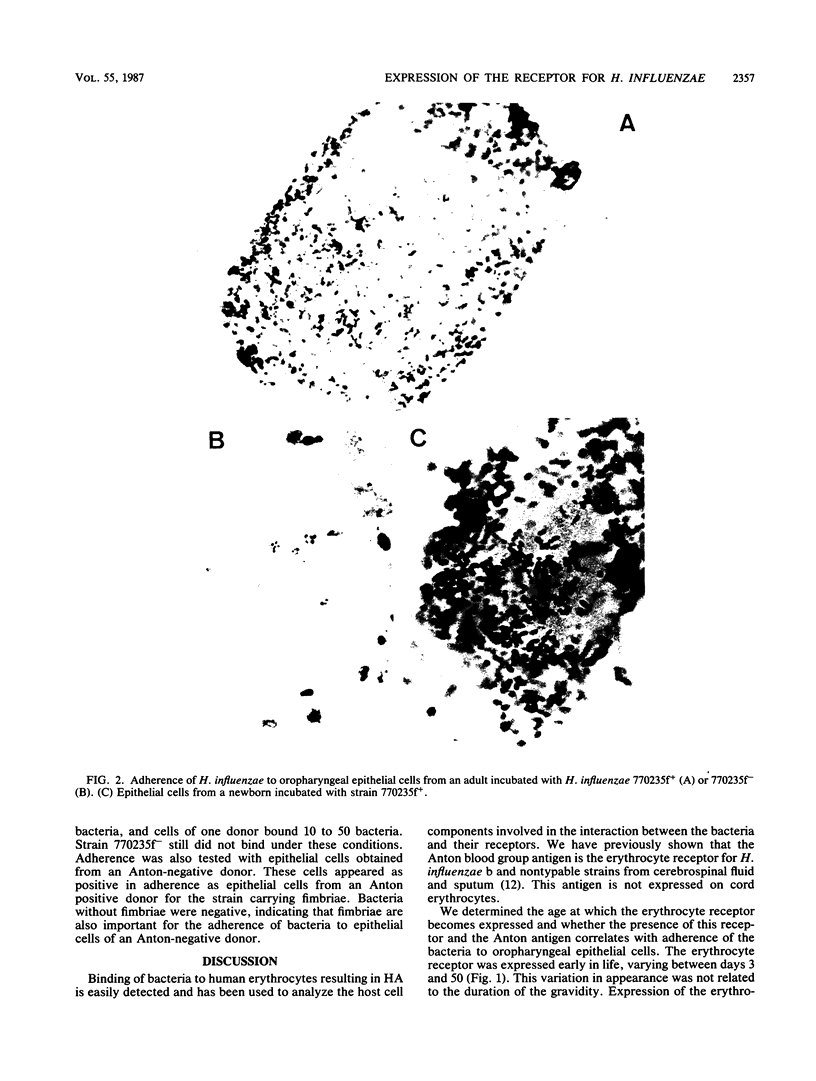
The Anton blood group antigen has been shown to be the erythrocyte receptor for Haemophilus influenzae. Cord erythrocytes, which lack the Anton antigen, were not agglutinated by H. influenzae (L. van Alphen, J. Poole, and M. Overbecke, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 37:69-71, 1986). Twenty-eight erythrocyte suspensions from newborns less than 4 days old were also not agglutinated, but 23 of 56 erythrocyte suspensions from 4- to 50-day-old newborns and 23 of 35 erythrocyte suspensions from older infants were agglutinated. Positive hemagglutination correlated with the presence of the Anton antigen on the erythrocytes for 163 of 173 (P less than 0.0001). Adherence of H. influenzae to buccal epithelial cells obtained from six newborns within 3 days after birth was as strong as that found with adult epithelial cells, whereas the erythrocytes from five of six of these newborns were not agglutinated by the bacteria. Adherence of H. influenzae to epithelial cells of 15 donors was not inhibited by anti-Anton serum. Moreover, H. influenzae carrying fimbriae adhered to epithelial cells of an Anton-negative donor. From these results we conclude that the age at which the erythrocyte receptor for H. influenzae is expressed is the same as for the Anton antigen, but that the receptor on the epithelial cells is already expressed at birth and is not identical to the Anton antigen.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Langermann S., Clegg H. W., Kessler T. W., Goldman D. A., Gilsdorf J. R. Adherence of piliated Haemophilus influenzae type b to human oropharyngeal cells. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):564–564. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler H., Svanborg-Edén C. Glycolipid receptors for uropathogenic Escherichia coli on human erythrocytes and uroepithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):920–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.920-929.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E. Adherence of Haemophilus influenzae to human buccal and pharyngeal epithelial cells: relationship to pilation. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):107–116. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E., Loeb M., Anderson, Smith D. H. Do pili play a role in pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type B? Lancet. 1982 Oct 30;2(8305):960–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole J., Giles C. M. Observations on the Anton antigen and antibody. Vox Sang. 1982;43(4):220–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1982.tb00015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sable N. S., Connor E. M., Hall C. B., Loeb M. R. Variable adherence of fimbriated Haemophilus influenzae type b to human cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):119–123. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.119-123.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra W. J., Jabboury-Postema J., Korver H. Immunoperoxidase staining of leptospires in blood and urine. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Jul;254(4):534–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk D. C. The pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):1–16. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Riemens T., Poolman J., Hopman C., Zanen H. C. Homogeneity of cell envelope protein subtypes, lipopolysaccharide serotypes, and biotypes among Haemophilus influenzae type b from patients with meningitis in The Netherlands. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):75–81. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Riemens T., Poolman J., Zanen H. C. Characteristics of major outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):878–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.878-885.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]