Abstract
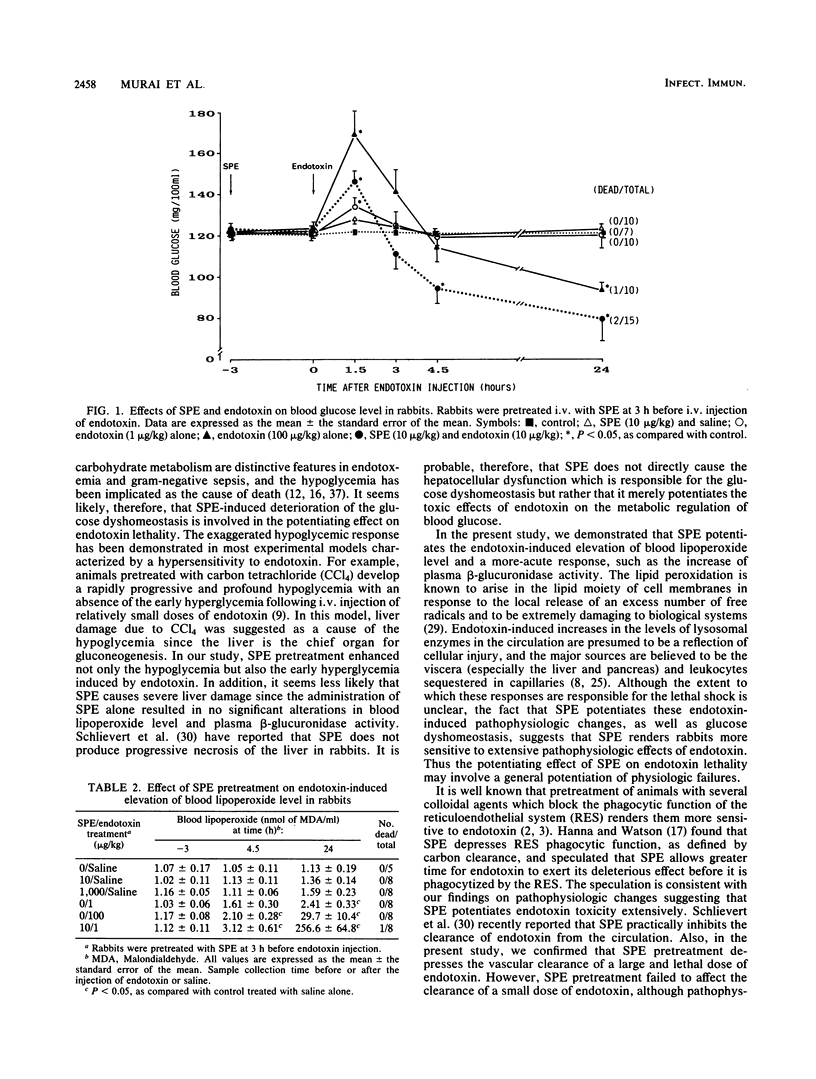
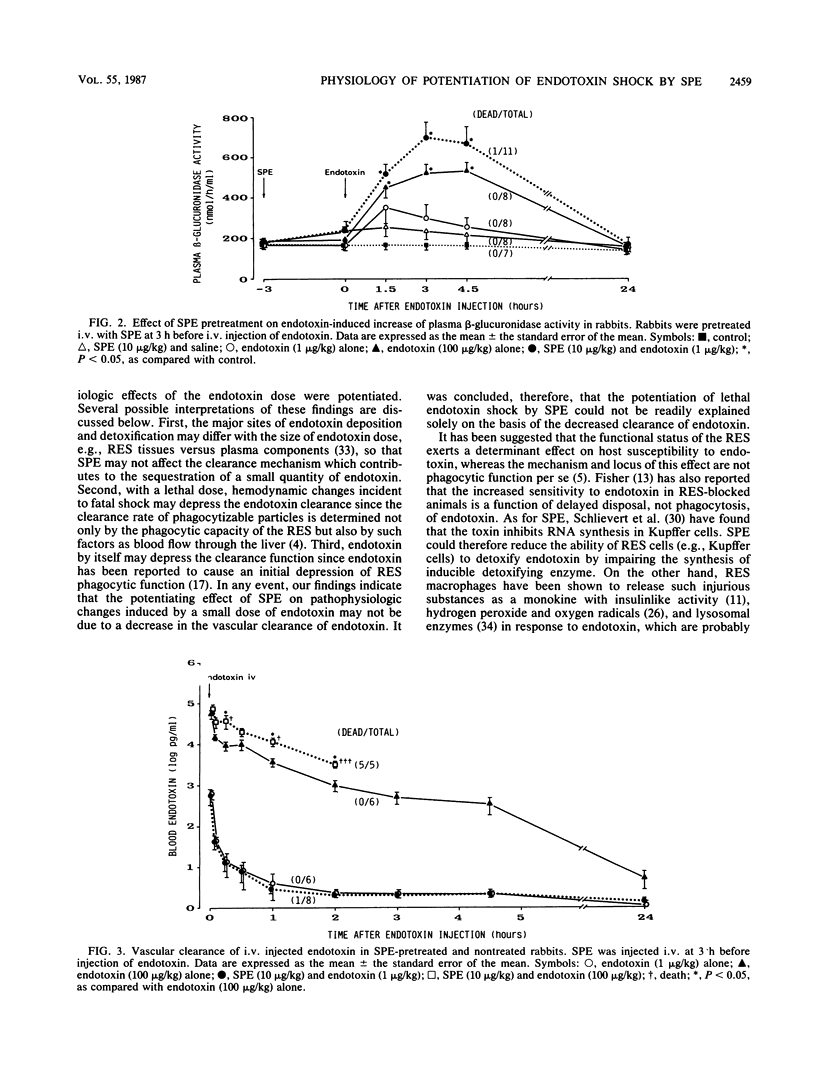
Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin (SPE) dramatically potentiates the lethal shock induced by gram-negative bacterial endotoxin. To provide further understanding of the mechanism underlying the potentiating effect, the physiological basis for the toxic synergism of the two toxins was investigated. Pretreatment of rabbits with an intravenous (i.v.) dose (10 micrograms/kg of body weight) of SPE greatly enhanced the endotoxin lethality and reduced the 50% lethal dose to less than 5 micrograms of endotoxin per kg. The SPE pretreatment dose caused severe pathophysiological changes in combination with a small i.v. dose of endotoxin (1 microgram/kg). These changes included transient hyperglycemia followed by profound hypoglycemia, elevation of the blood lipoperoxide level, and an acute increase in plasma beta-glucuronidase activity. These changes were comparable with those in animals given a large i.v. dose of endotoxin (100 micrograms/kg) alone. An injection of SPE alone did not alter any of the parameters described above. These results suggest that SPE renders rabbits more sensitive to extensive pathophysiologic effects of endotoxin, and the potentiating effect on endotoxin lethality may thus involve a general potentiation of physiologic failures. The SPE pretreatment depressed the vascular clearance of a large dose of endotoxin (100 micrograms/kg) but failed to affect that of a small dose of endotoxin (1 microgram/kg). The data suggest that the potentiating effect is not readily explained solely on the basis of the decreased clearance of endotoxin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M. M. Effect of bacterial endotoxins on the reticuloendothelial system. Fed Proc. 1957 Sep;16(3):860–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsumian E. L., Schlievert P. M., Watson D. W. Nonspecific and specific immunological mitogenicity by group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):681–688. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.681-688.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crafton C. G., Di LUZIO N. R. Relationship of reticuloendothelial functional activity to endotoxin lethality. Am J Physiol. 1969 Sep;217(3):736–742. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.3.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham C. M., Watson D. W. Alteration of clearance function by group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin and its relation to suppression of the antibody response. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.51-57.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham C. M., Watson D. W. Suppression of antibody response by group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin and characterization of the cells involved. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):470–476. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.470-476.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demling R. H., Proctor R., Grossman J., Duy N., Starling J. Lung injury and lung lysosomal enzyme release during endotoxemia. J Surg Res. 1981 Feb;30(2):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(81)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARRAR W. E., Jr, WATSON J. G. HYPOGLYCEMIA FOLLOWING ENDOTOXIN ADMINISTRATION IN ANIMALS WITH LIVER DAMAGE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:833–837. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P., Buchanan B. J. In vivo vs in vitro effects of endotoxin on glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and glucose utlization. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jun;155(2):216–218. doi: 10.3181/00379727-155-39776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P. Insulin-like activity (ILA) of a macrophage mediator on adipose tissue glucose oxidation. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Jun;25(6):591–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P. Phases of glucose dyshomeostasis in endotoxicosis. Circ Shock. 1978;5(4):347–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. Localization of radioiodinated endotoxin in organs of mice and rabbits: effect of thorotrast, trypan blue, endotoxin and carbon administered intravenously. Nature. 1967 Feb 4;213(5075):511–512. doi: 10.1038/213511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godin D. V., Tuchek J. M. Plasma acid phosphatase levels in endotoxaemia: modification by drugs and chemically detoxified endotoxins. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANNA E. E., WATSON D. W. HOST-PARASITE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI. 3. DEPRESSION OF RETICULOENDOTHELIAL FUNCTION BY STREPTOCOCCAL PYROGENIC EXOTOXINS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:154–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.154-158.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULTMAN E. Rapid specific method for determination of aldosaccharides in body fluids. Nature. 1959 Jan 10;183(4654):108–109. doi: 10.1038/183108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand M. S., Fettman M. J., Chandrasena L. G., Cleek J. L., Phillips R. W. Endotoxin dose. I. Hemodynamic, metabolic, and lethal consequences in Yucatan minipigs. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):E385–E398. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.4.E385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna E. E., Watson D. W. Enhanced immune response after immunosuppression by Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):1009–1011. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.1009-1011.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna E. E., Watson D. W. Host-parasite relationships among group A streptococci. IV. Suppression of antibody response by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):14–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.14-21.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston C. W., Ferretti J. J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of type A streptococcal exotoxin: kinetics and regulation during growth of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):862–869. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.862-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANOFF A., WEISSMANN G., ZWEIOFACH B. W., THOMAS L. Pathogenesis of experimental shock. IV. Studies on lysosomes in normal and tolerant animals subjected to lethal trauma and endotoxemia. J Exp Med. 1962 Oct 1;116:451–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.4.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. A purified group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Physiochemical and biological properties including the enhancement of susceptibility to endotoxin lethal shock. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):611–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefer A. M. The role of lysosomes in circulatory shock. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 15;19(12):1803–1809. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretion of oxygen intermediates: role in effector functions of activated macrophages. Fed Proc. 1982 Apr;41(6):2206–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T. Addition of perchloric acid to blood samples for colorimetric limulus test using chromogenic substrate: comparison with conventional procedures and clinical applications. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Sep;104(3):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Fairchild E. J., 2nd Evidence for lipid peroxidation in endotoxin-poisoned mice. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):613–616. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.613-616.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAB J. H., WATSON D. W., CROMARTIE W. J. Further studies of group A streptococcal factors with lethal and cardiotoxic properties. J Infect Dis. 1955 Jan-Feb;96(1):14–18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/96.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Bettin K. M., Watson D. W. Inhibition of ribonucleic acid synthesis by group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):542–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.542-548.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Watson D. W. Group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin: pyrogenicity, alteration of blood-brain barrier, and separation of sites for pyrogenicity and enhancement of lethal endotoxin shock. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):753–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.753-763.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. R., Keyhani A. H., Wright R. The influence of endotoxin in vitro on hepatic macrophage lysosomal enzyme release in different rat models of hepatic injury. Liver. 1983 Jun;3(3):151–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1983.tb00864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON D. W. Host-parasite factors in group A streptococcal infections. Pyrogenic and other effects of immunologic distinct exotoxins related to scarlet fever toxins. J Exp Med. 1960 Feb 1;111:255–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Elahi D., Spitzer J. J. Glucose kinetics in dogs following a lethal dose of endotoxin. Metabolism. 1977 Aug;26(8):847–850. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K. A simple fluorometric assay for lipoperoxide in blood plasma. Biochem Med. 1976 Apr;15(2):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(76)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


