Abstract
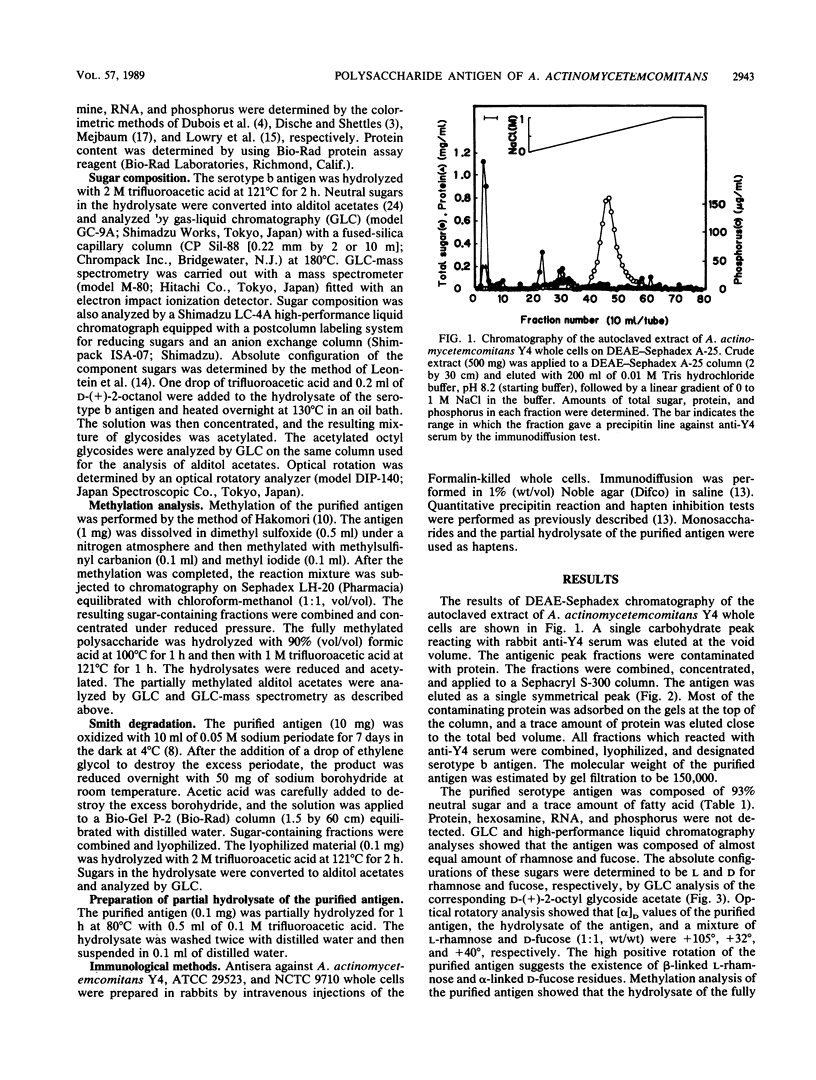
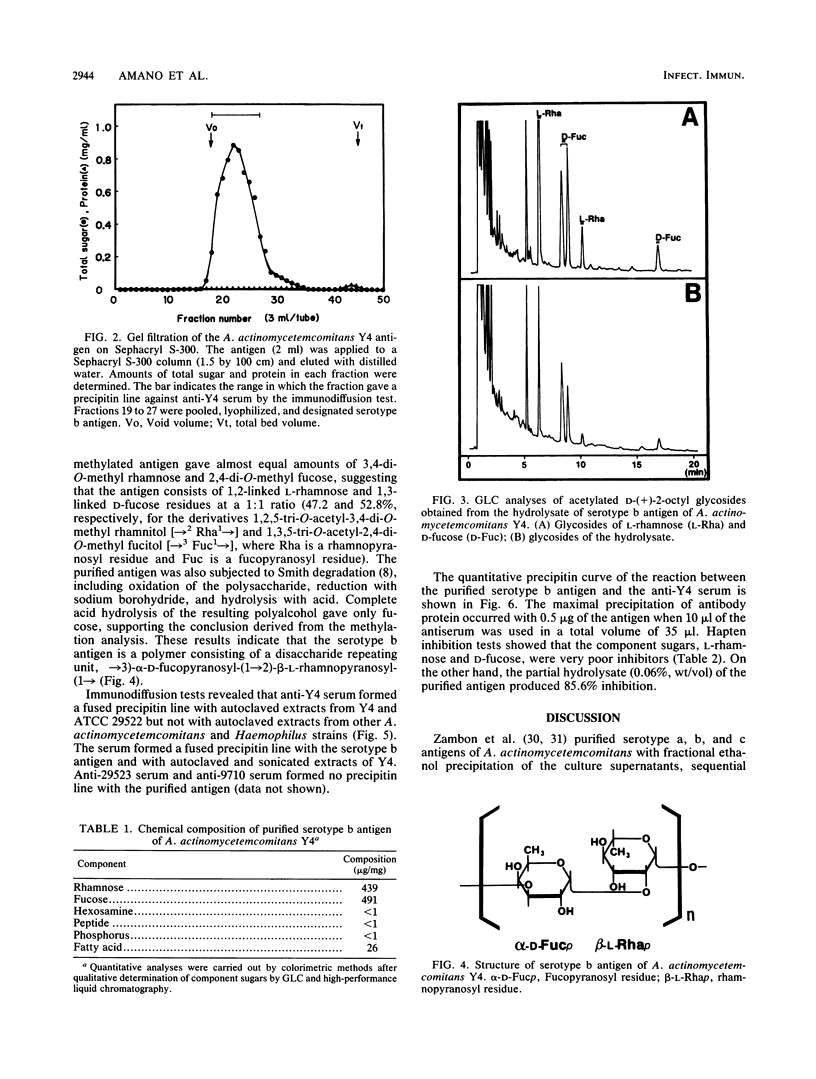
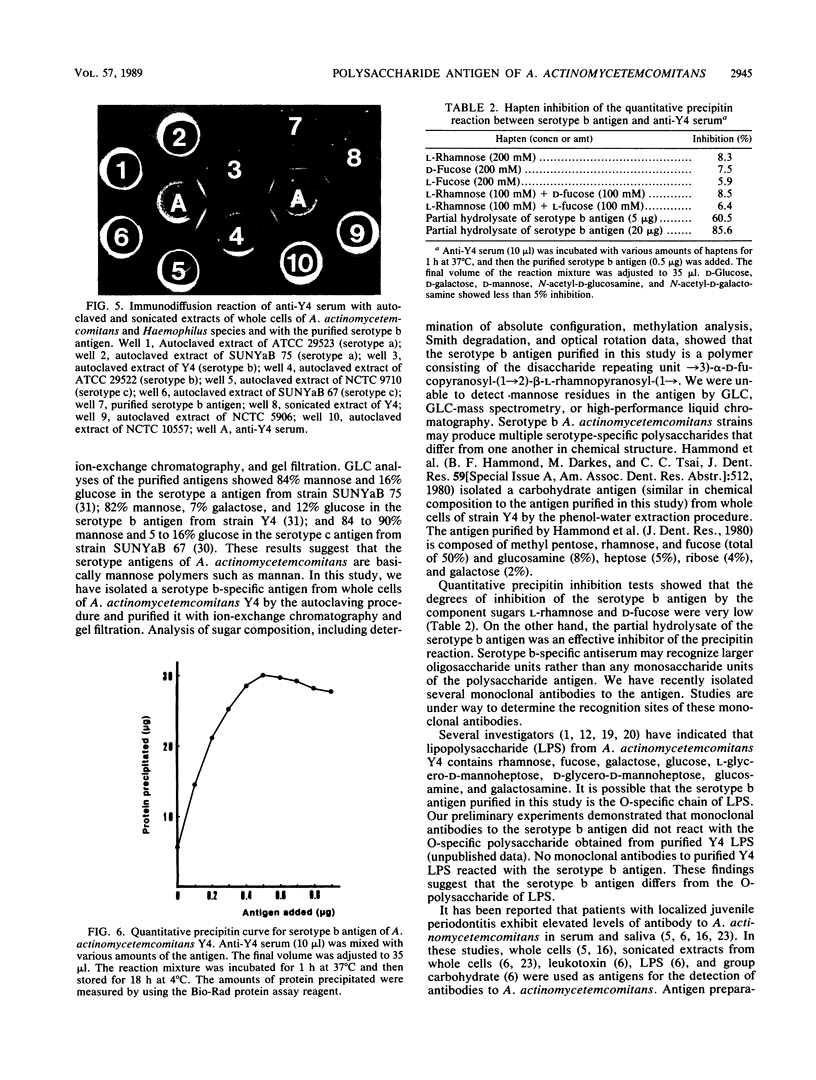
A serotype-specific polysaccharide antigen of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Y4 (serotype b) was extracted from whole cells by autoclaving. The extract was purified by chromatography on DEAE-Sephadex A-25 and Sephacryl S-300 columns. The purified polysaccharide antigen formed a single precipitin line with anti-type b serum but not with anti-type a serum and anti-type c serum. The antigen was composed of 43.9% L-rhamnose, 49.1% D-fucose, and a trace amount of fatty acid. Methylation analysis, Smith degradation, and optical rotation data showed that the antigen was a polymer consisting of a disaccharide repeating unit, ----3)-alpha-D-fucopyranosyl-(1----2)-beta-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1----. In quantitative precipitin inhibition tests, D-fucose and L-rhamnose showed very low inhibition, but the partial hydrolysate of the purified antigen was an effective inhibitor, suggesting that the serotype b specific antiserum recognizes the larger oligosaccharide units.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brondz I., Olsen I. Differentiation between Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Haemophilus aphrophilus based on carbohydrates in lipopolysaccharide. J Chromatogr. 1984 Oct 12;310(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(84)80091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgher L. W., Loomis G. W., Ware F. Systemic infection due to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Sep;60(3):412–415. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.3.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J., Genco R. J., Frey D. E. Human immune responses to oral micro-organisms. I. Association of localized juvenile periodontitis (LJP) with serum antibody responses to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jan;47(1):43–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J., Hammond B. F., Frey D. E. Human immune responses to oral microorganisms. II. Serum antibody responses to antigens from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and the correlation with localized juvenile periodontitis. J Clin Immunol. 1983 Oct;3(4):321–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00915793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner J. J., Rosenthal M. S., Lerner P. I., McHenry M. C. Infective endocarditis caused by slow-growing, fastidious, Gram-negative bacteria. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Mar;58(2):145–158. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197903000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace C. J., Levitz R. E., Katz-Pollak H., Brettman L. R. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans prosthetic valve endocarditis. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):922–929. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz E. A., Pugsley M. P., Turbes P. G., Clark R. B. Pericarditis caused by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):152–153. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley P., Holt S. C. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Y4 and N27. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):862–873. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.862-873.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Okahashi N., Yamamoto T., Mizuno J., Inoue M., Hamada S. Purification and immunochemical characterization of Streptococcus sanguis ATCC 10557 serotype II carbohydrate antigen. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):696–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.696-700.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell R. L., Ebersole J. L., Socransky S. S. Clinical immunologic and microbiologic features of active disease sites in juvenile periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 1987 Oct;14(9):534–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1987.tb00996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhle I., Rau J., Ruskin J. Vertebral osteomyelitis due to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. JAMA. 1979 Apr 27;241(17):1824–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara T., Fujiwara T., Koga T., Hamada S. Chemical composition and immunobiological properties of lipopolysaccharide and lipid-associated proteoglycan from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Periodontal Res. 1986 Sep;21(5):521–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1986.tb01488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara T., Koga T., Hamada S. Extracellular proteinaceous substances from Haemophilus actinomycetemcomitans induce mitogenic responses in murine lymphocytes. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1987 Mar;2(1):48–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1987.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara T., Koga T., Hamada S. Suppression of murine macrophage interleukin-1 release by the polysaccharide portion of Haemophilus actinomycetemcomitans lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):619–625. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.619-625.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandholm L., Tolo K., Olsen I. Salivary IgG, a parameter of periodontal disease activity? High responders to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Y4 in juvenile and adult periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 1987 May;14(5):289–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1987.tb01535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides species, Capnocytophaga species, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: virulence factors in colonization, survival, and tissue destruction. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):412–421. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630031101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Listgarten M. A. Bacteroides gingivalis, Bacteroides intermedius and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol. 1988 Feb;15(2):85–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1988.tb00999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Zambon J. J., Rosling B. G., Reynolds H. S., Christersson L. A., Genco R. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease. Association, serology, leukotoxicity, and treatment. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Sep;17(5):447–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb02022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1985 Jan;12(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1985.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Slots J., Genco R. J. Serology of oral Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and serotype distribution in human periodontal disease. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):19–27. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.19-27.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Slots J., Miyasaki K., Linzer R., Cohen R., Levine M., Genco R. J. Purification and characterization of the serotype c antigen from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):22–27. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.22-27.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Umemoto T., De Nardin E., Nakazawa F., Christersson L. A., Genco R. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in the pathogenesis of human periodontal disease. Adv Dent Res. 1988 Nov;2(2):269–274. doi: 10.1177/08959374880020021101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




