Abstract
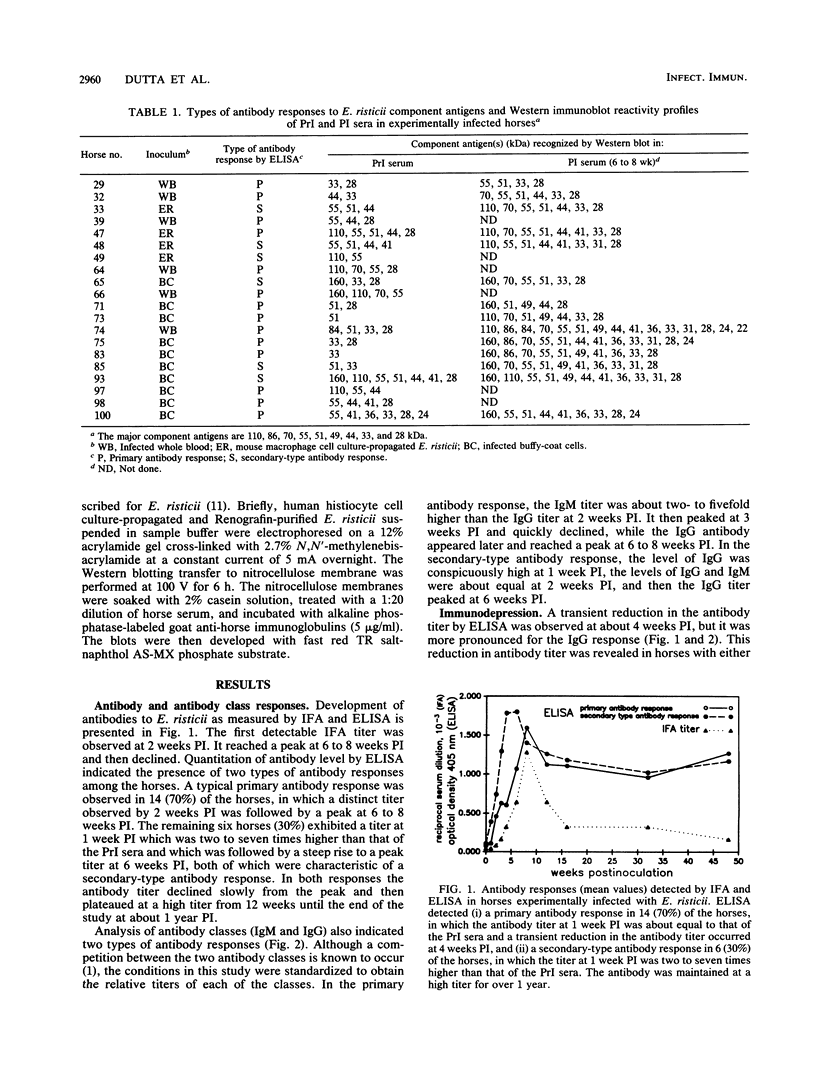
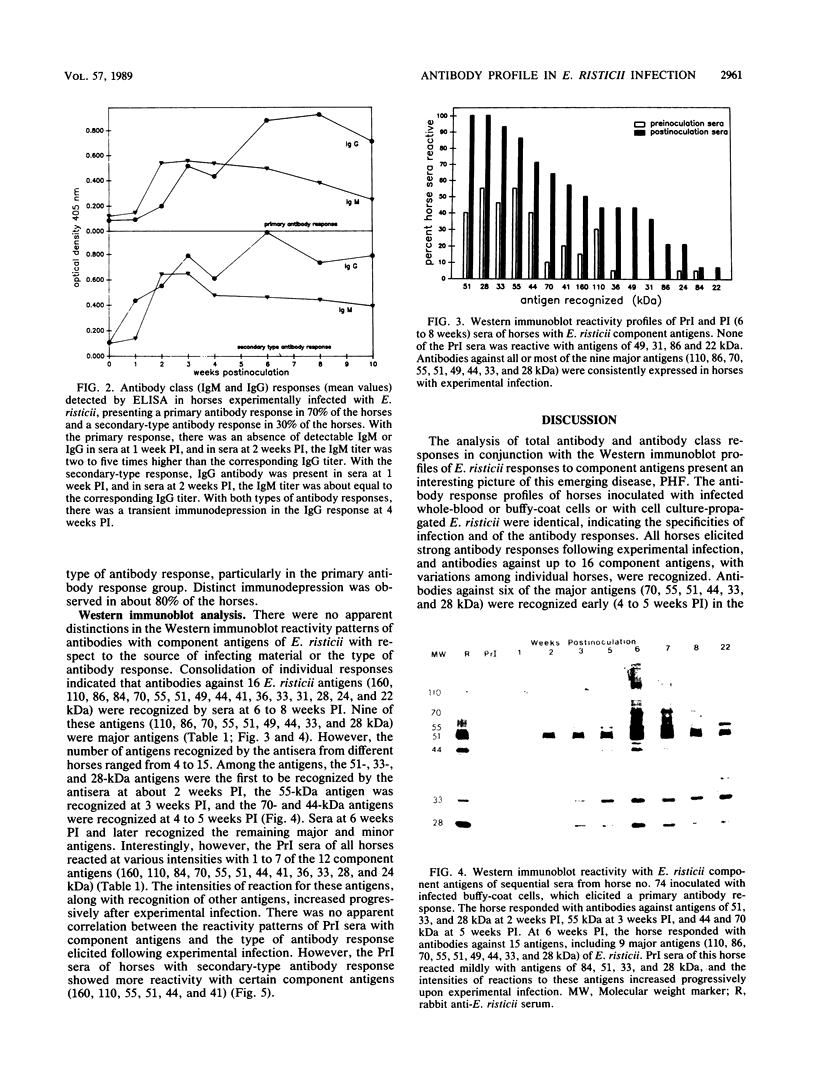
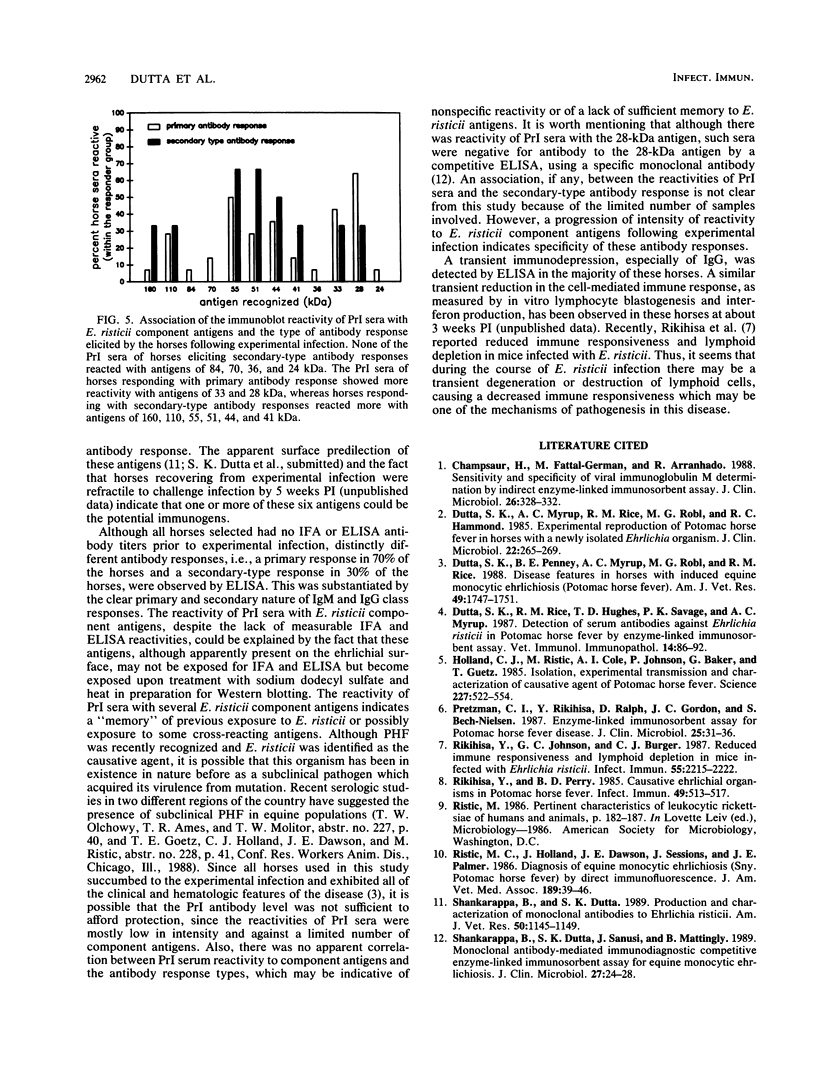
The antibody response and the antibody reactivity to component antigens of Ehrlichia risticii were studied in horses with induced Potomac horse fever. These horses had no detectable antibodies to E. risticii in their preinoculation (PrI) sera by indirect fluorescent-antibody assay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). All the horses exhibited typical disease features following experimental infection and responded with specific antibodies, as measured by ELISA and indirect fluorescent-antibody assay. A primary antibody response was detected in 70% of the horses, while a secondary-type antibody response was detected in 30% of the horses by ELISA. In the primary antibody response, a distinct titer was observed at 2 weeks postinoculation (PI), when the immunoglobulin M (IgM)/IgG ratio was 2 to 5, and the overall antibody titer peaked at 6 to 8 weeks PI. The secondary-type antibody response exhibited a characteristic titer at 1 week PI, the IgM and IgG titers were about equal at 2 weeks PI, and the overall antibody titer peaked at 6 weeks PI. A transient depression in the IgG response at 4 weeks PI was observed in both response types. The antibody was maintained at a high titer for over a year in all horses. Western immunoblot reactivity showed that the antisera collected from these infected horses at 4 to 5 weeks PI recognized some or all of the six major E. risticii component antigens (70, 55, 51, 44, 33, and 28 kilodaltons), all of which were apparent surface components. The 6- to 8-week PI antisera recognized up to 16 component antigens, including 9 major antigens (110, 86, 70, 55, 51, 49, 44, 33, and 28 kilodaltons). However, the PrI sera of these horses showed reactivity at various intensities with one to seven of the component antigens. There was no apparent correlation between this reactivity pattern and the subsequent antibody response types.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Champsaur H., Fattal-German M., Arranhado R. Sensitivity and specificity of viral immunoglobulin M determination by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.328-332.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta S. K., Myrup A. C., Rice R. M., Robl M. G., Hammond R. C. Experimental reproduction of Potomac horse fever in horses with a newly isolated Ehrlichia organism. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):265–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.265-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta S. K., Penney B. E., Myrup A. C., Robl M. G., Rice R. M. Disease features in horses with induced equine monocytic ehrlichiosis (Potomac horse fever). Am J Vet Res. 1988 Oct;49(10):1747–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta S. K., Rice R. M., Hughes T. D., Savage P. K., Myrup A. C. Detection of serum antibodies against Ehrlichia risticii in Potomac horse fever by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Jan;14(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(87)90077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. J., Ristic M., Cole A. I., Johnson P., Baker G., Goetz T. Isolation, experimental transmission, and characterization of causative agent of Potomac horse fever. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.3880925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretzman C. I., Rikihisa Y., Ralph D., Gordon J. C., Bech-Nielsen S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Potomac horse fever disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):31–36. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.31-36.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y., Johnson G. C., Burger C. J. Reduced immune responsiveness and lymphoid depletion in mice infected with Ehrlichia risticii. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2215–2222. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2215-2222.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y., Perry B. D. Causative ehrlichial organisms in Potomac horse fever. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):513–517. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.513-517.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristic M., Holland C. J., Dawson J. E., Sessions J., Palmer J. Diagnosis of equine monocytic ehrlichiosis (Potomac horse fever) by indirect immunofluorescence. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1986 Jul 1;189(1):39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankarappa B., Dutta S. K. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Ehrlichia risticii. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jul;50(7):1145–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankarappa B., Dutta S. K., Sanusi J., Mattingly B. L. Monoclonal antibody-mediated, immunodiagnostic competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for equine monocytic ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.24-28.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]