Abstract
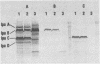
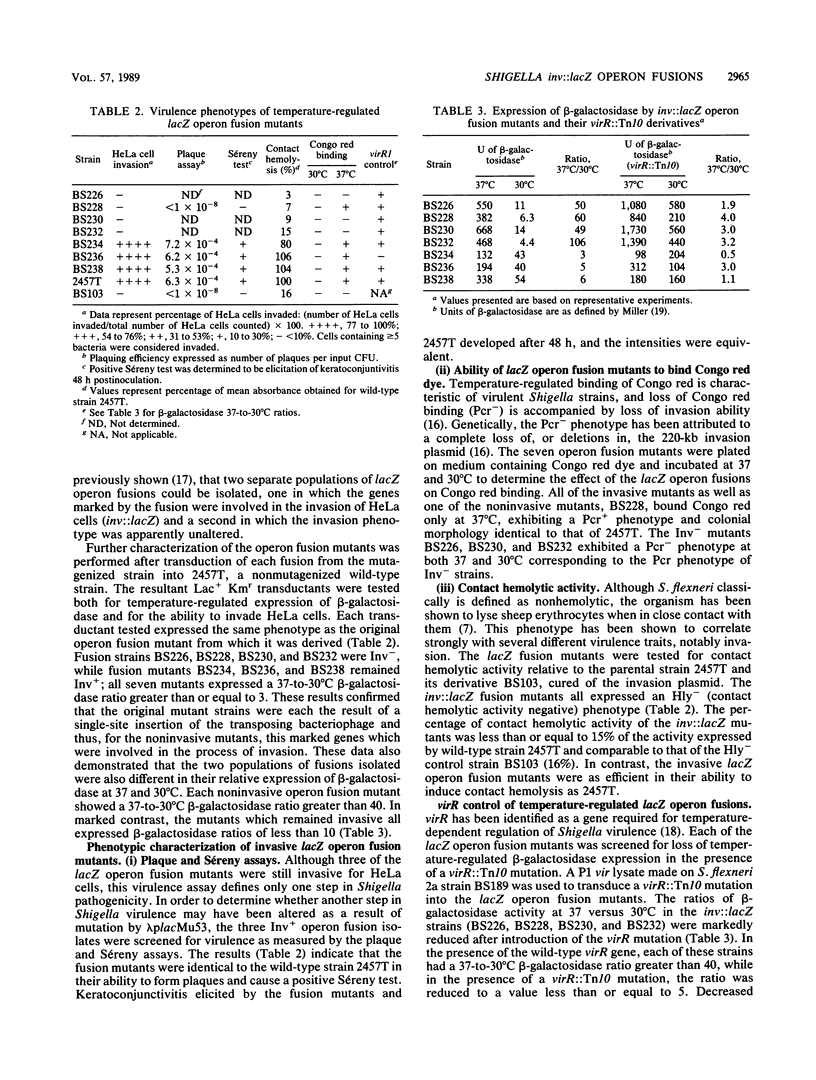
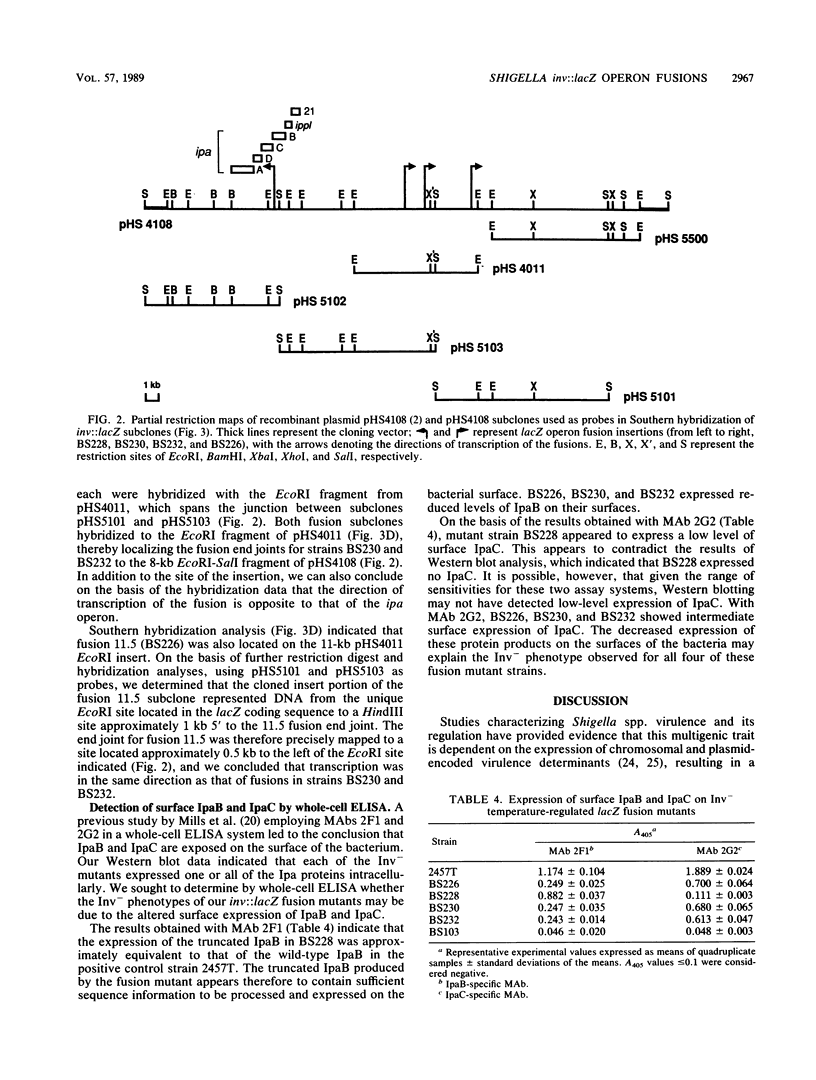
Penetration and multiplication within cells of the human colonic epithelium are hallmarks of Shigella spp. pathogenicity. Shigella spp. virulence is regulated by growth temperature. Strains phenotypically virulent when grown at 37 degrees C are phenotypically avirulent when grown at 30 degrees C. The number of genes involved in Shigella spp. pathogenicity and how many virulence genes are temperature regulated are unknown. To facilitate the study of temperature-regulated virulence in Shigella spp., we employed lacZ operon fusion technology to identify temperature-regulated invasion (inv) genes. Four inv::lacZ fusion mutants were identified and found to be unable to invade HeLa cells. The fusions were located in a region of the 220-kilobase invasion plasmid defined as the minimal amount of DNA required for invasion, and they were controlled by virR, the temperature-dependent virulence gene regulator. Western blot (immunoblot) and Southern hybridization analyses indicated that one of the fusions was located in a known inv gene, ipaB, which encodes one of the major immunogenic peptides of Shigella spp. This ipaB::lacZ operon fusion mutant synthesized a truncated IpaB protein recognized by IpaB-specific monoclonal antibodies. Three of the fusions were within novel genes mapping to regions previously identified as essential for a positive virulence phenotype. Analysis of bacterial surface proteins suggested that the genes marked by these fusions may play a role in the correct surface expression of the ipaB and ipaC gene products.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudry B., Kaczorek M., Sansonetti P. J. Nucleotide sequence of the invasion plasmid antigen B and C genes (ipaB and ipaC) of Shigella flexneri. Microb Pathog. 1988 May;4(5):345–357. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry B., Maurelli A. T., Clerc P., Sadoff J. C., Sansonetti P. J. Localization of plasmid loci necessary for the entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells, and characterization of one locus encoding four immunogenic polypeptides. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3403–3413. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer E., Silhavy T. J., Weinstock G. M. Transposable lambda placMu bacteriophages for creating lacZ operon fusions and kanamycin resistance insertions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1092–1099. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1092-1099.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Baudry B., Sansonetti P. J. Plasmid-mediated contact haemolytic activity in Shigella species: correlation with penetration into HeLa cells. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):267–278. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., DAMMIN G. J., LABREC E. H., SCHNEIDER H. Experimental Shigella infections: characteristics of a fatal infection produced in guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):604–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.604-610.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Protein synthesis in HeLa or Henle 407 cells infected with Shigella dysenteriae 1, Shigella flexneri 2a, or Salmonella typhimurium W118. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.137-144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Baudry B., d'Hauteville H., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Cloning of plasmid DNA sequences involved in invasion of HeLa cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.164-171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Loss of pigmentation in Shigella flexneri 2a is correlated with loss of virulence and virulence-associated plasmid. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.397-401.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in Shigella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.195-201.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Curtiss R., 3rd Bacteriophage Mu d1(Apr lac) generates vir-lac operon fusions in Shigella flexneri 2a. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):642–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.642-648.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of a chromosomal gene controlling temperature-regulated expression of Shigella virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2820–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. A., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens B and C: epitope location and characterization with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2933–2941. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2933-2941.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Serum immune response to Shigella protein antigens in rhesus monkeys and humans infected with Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.57-63.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Wingfield M. E., Formal S. B. Plaque formation by virulent Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.124-129.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M. Expression of four virulence antigens of Shigella flexneri is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by the 30 kiloDalton virF protein. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):589–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M. M., Buysse J. M., Kopecko D. J. Characterization of invasion plasmid antigen genes (ipaBCD) from Shigella flexneri. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9317–9321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]