Abstract
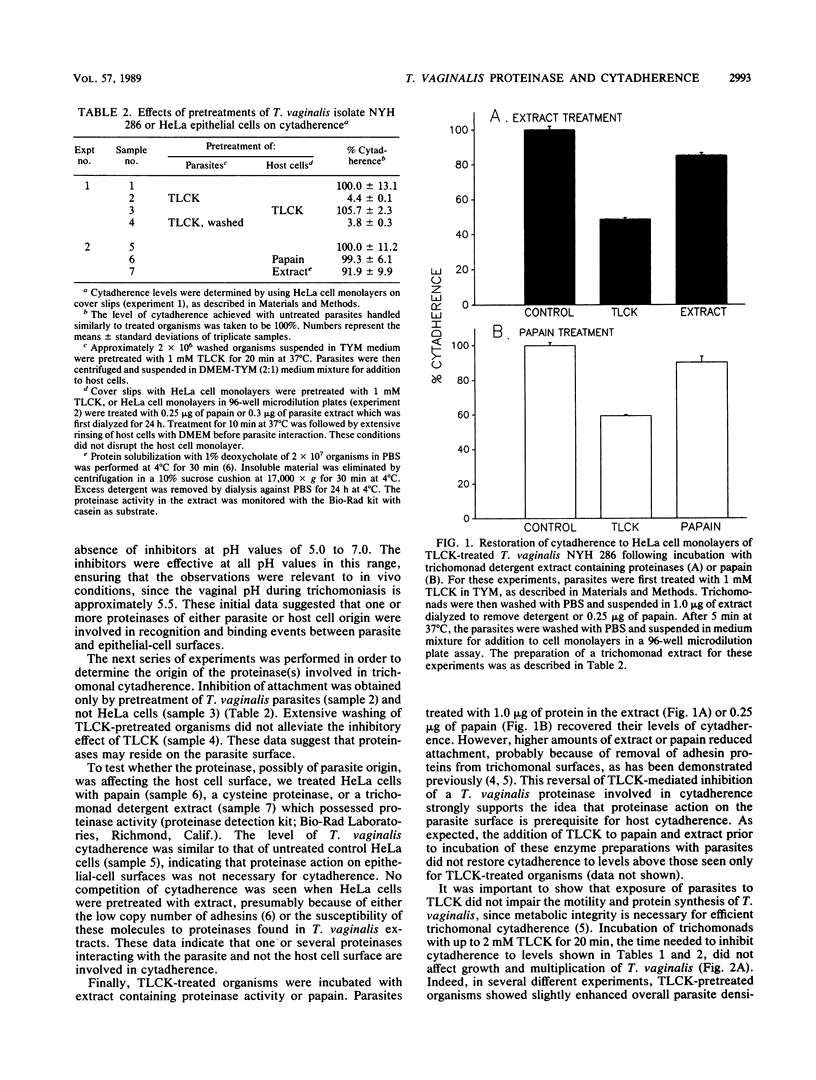
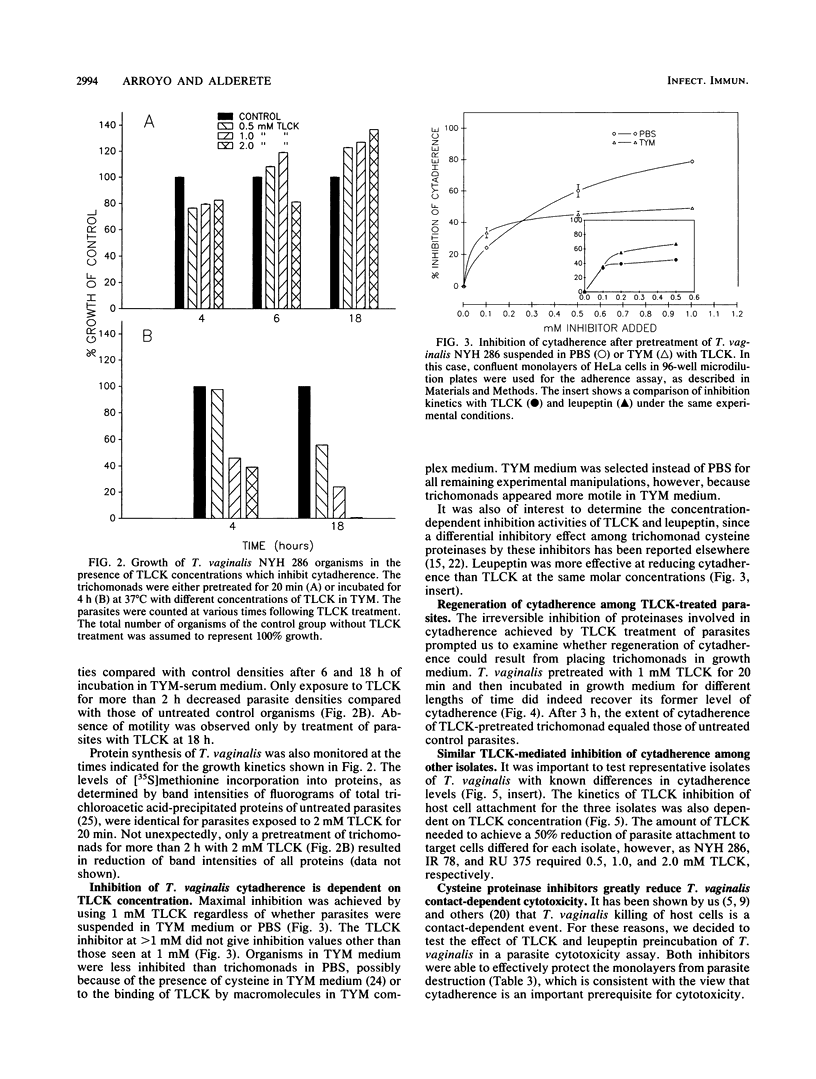
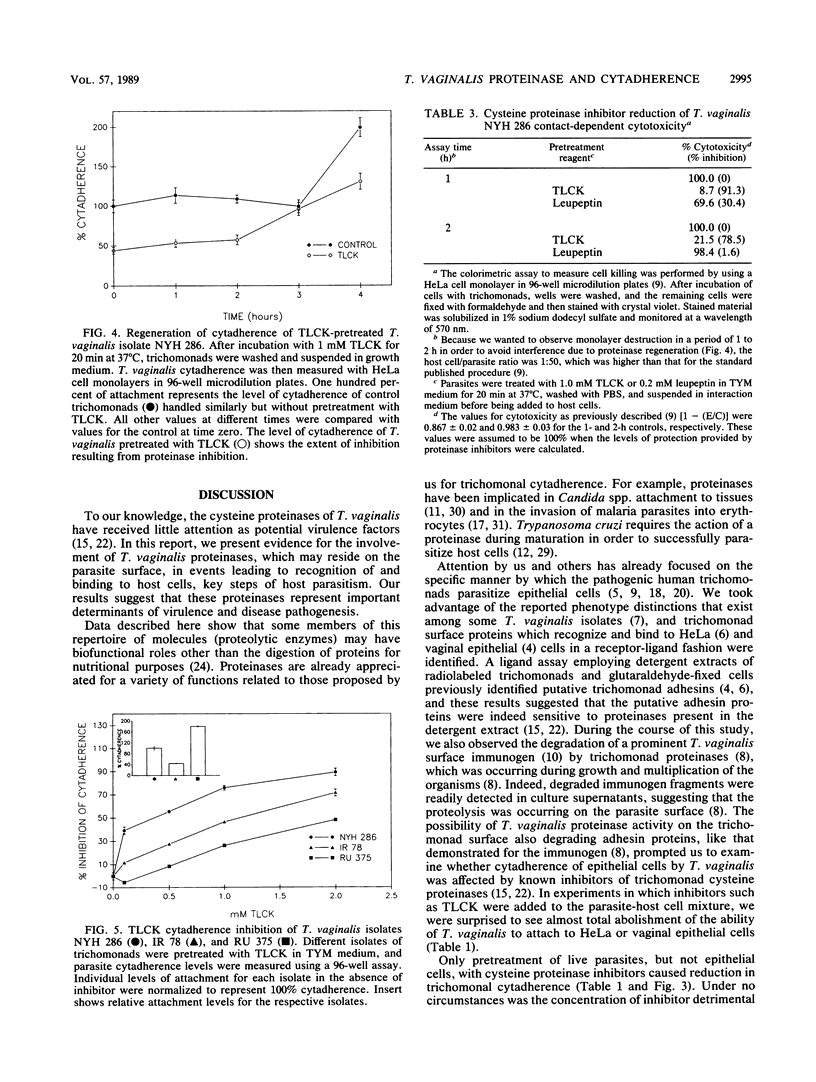
The role of cysteine proteinases in adherence of Trichomonas vaginalis NYH 286 to HeLa and human vaginal epithelial cells was evaluated. Only pretreatment of trichomonads, but not epithelial cells, with N-alpha-p-tosyl-L-lysine chloromethyl ketone (TLCK), an inhibitor of trichomonad cysteine proteinases, greatly diminished the ability of T. vaginalis to recognize and bind to epithelial cells. Leupeptin and L-1-tosylamide-2-phenylethyl chloromethyl ketone, other cysteine proteinase inhibitors, also decreased T. vaginalis cytadherence. Parasites incubated with TLCK and washed extensively still did not adhere to cells at levels equal to those seen for control trichomonads treated with phosphate-buffered saline or culture medium alone. Exposure of TLCK-treated organisms with other cysteine proteinases restored cytadherence levels, indicating that proteinase action on the parasite surface is prerequisite for host cell attachment. Concentrations of TLCK which inhibited cytadherence did not alter the metabolism of T. vaginalis, as determined by metabolic labeling of trichomonad proteins; the protein patterns of T. vaginalis in the presence and absence of TLCK were identical. Kinetics of TLCK-mediated inhibition of cytadherence of other T. vaginalis isolates with different levels of epithelial-cell parasitism were similar to the concentration-dependent inhibition seen for isolate NYH 286. Incubation of TLCK-treated, washed organisms in growth medium resulted in regeneration of adherence. Finally, treatment of T. vaginalis organisms with proteinase inhibitors for abrogation of cytadherence effectively rendered the trichomonads unable to kill host cells, which is consistent with the contact-dependent nature of host cytotoxicity. These data show for the first time the involvement of T. vaginalis cysteine proteinases in parasite attachment to human epithelial cells. These results have implications for future pharmacologic intervention at a key step in infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F. Antigen analysis of several pathogenic strains of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1041–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1041-1047.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Demeś P., Gombosova A., Valent M., Fabusová M., Jánoska A., Stefanovic J., Arroyo R. Specific parasitism of purified vaginal epithelial cells by Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2558–2562. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2558-2562.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G. E. Identification and properties of Trichomonas vaginalis proteins involved in cytadherence. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.28-33.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G. E. Specific nature of Trichomonas vaginalis parasitism of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):701–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.701-708.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F. Identification of immunogenic and antibody-binding membrane proteins of pathogenic Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):284–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.284-291.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Kasmala L., Metcalfe E., Garza G. E. Phenotypic variation and diversity among Trichomonas vaginalis isolates and correlation of phenotype with trichomonal virulence determinants. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):285–293. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.285-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Neale K. A. Relatedness of structures of a major immunogen in Trichomonas vaginalis isolates. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1849–1853. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1849-1853.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Pearlman E. Pathogenic Trichomonas vaginalis cytotoxicity to cell culture monolayers. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Apr;60(2):99–105. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.2.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Suprun-Brown L., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major surface glycoprotein immunogen differentiates isolates and subpopulations of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.70-75.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg M., Rüchel R. Expression of extracellular acid proteinase by proteolytic Candida spp. during experimental infection of oral mucosa. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):626–631. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.626-631.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti M. A., Piras M. M., Henríquez D., Piras R. The interaction of a Trypanosoma cruzi surface protein with Vero cells and its relationship with parasite adhesion. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jun;24(2):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs G. H., Hart D. T., Capaldo J. Proteinase inhibitors as antileishmanial agents. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(5):660–663. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs G. H., North M. J. An analysis of the proteinases of Trichomonas vaginalis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Parasitology. 1983 Feb;86(Pt 1):1–6. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000057103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs G. H. Proteinases of Leishmania mexicana and other flagellate protozoa. Parasitology. 1982 Feb;84(1):149–155. doi: 10.1017/s003118200005174x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND L. S. The establishment of various trichomonads of animals and man in axenic cultures. J Parasitol. 1957 Aug;43(4):488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dluzewski A. R., Rangachari K., Wilson R. J., Gratzer W. B. Plasmodium falciparum: protease inhibitors and inhibition of erythrocyte invasion. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Dec;62(3):416–422. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath J. P. Behaviour and pathogenicity of Trichomonas vaginalis in epithelial cell cultures: a study by light and scanning electron microscopy. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Apr;57(2):106–117. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.2.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Ravdin J. I., Rein M. F. Contact-dependent cytopathogenic mechanisms of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):778–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.778-786.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood B. C., North M. J., Scott K. I., Bremner A. F., Coombs G. H. The use of a highly sensitive electrophoretic method to compare the proteinases of trichomonads. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 May;24(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North M. J. Comparative biochemistry of the proteinases of eucaryotic microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Sep;46(3):308–340. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.3.308-340.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Alderete J. F. Acquisition of alpha 1-Antitrypsin by a pathogenic strain of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):640–646. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.640-646.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Alderete J. F. Host plasma proteins on the surface of pathogenic Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.755-762.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Alderete J. F. Iron uptake and increased intracellular enzyme activity follow host lactoferrin binding by Trichomonas vaginalis receptors. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):398–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Alderete J. F. Trichomonas vaginalis is dependent on uptake and degradation of human low density lipoproteins. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1261–1272. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piras M. M., Henriquez D., Piras R. The effect of proteolytic enzymes and protease inhibitors on the interaction Trypanosoma cruzi-fibroblasts. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Feb;14(2):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. L., Payne C. D. Scanning electron microscopy of epidermal adherence and cavitation in murine candidiasis: a role for Candida acid proteinase. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1942–1949. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1942-1949.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal P. J., Kim K., McKerrow J. H., Leech J. H. Identification of three stage-specific proteinases of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):816–821. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



