Abstract
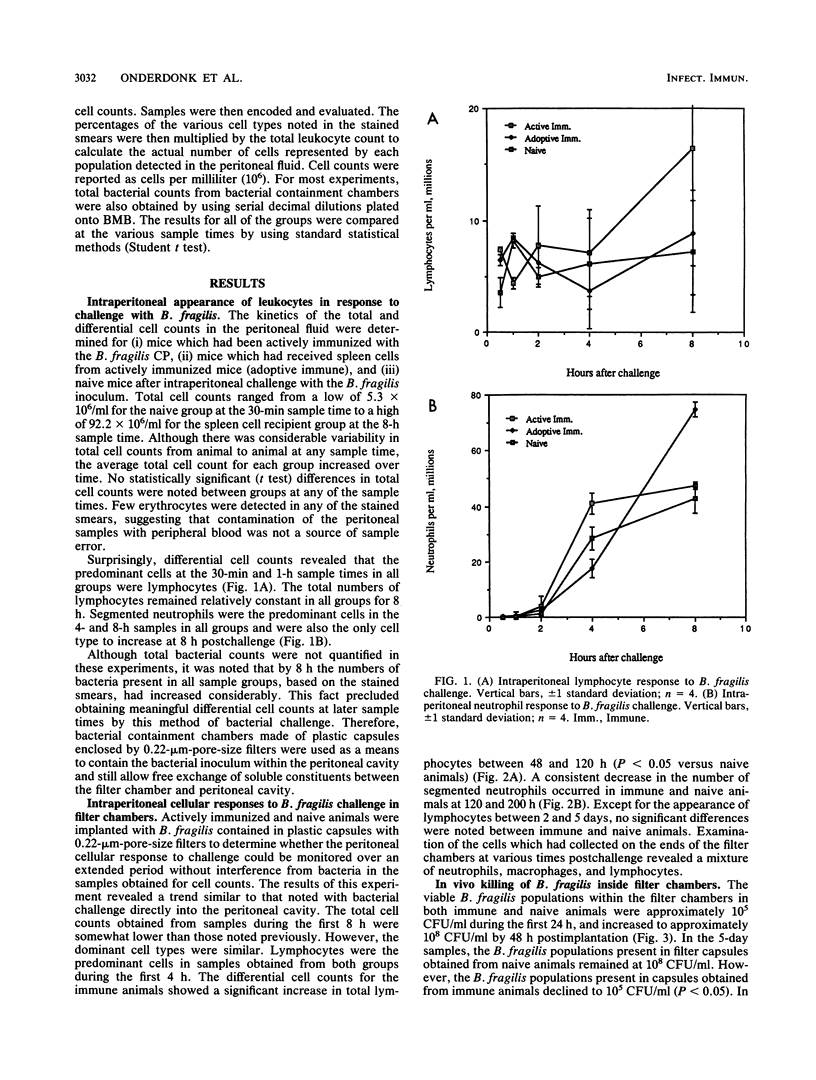
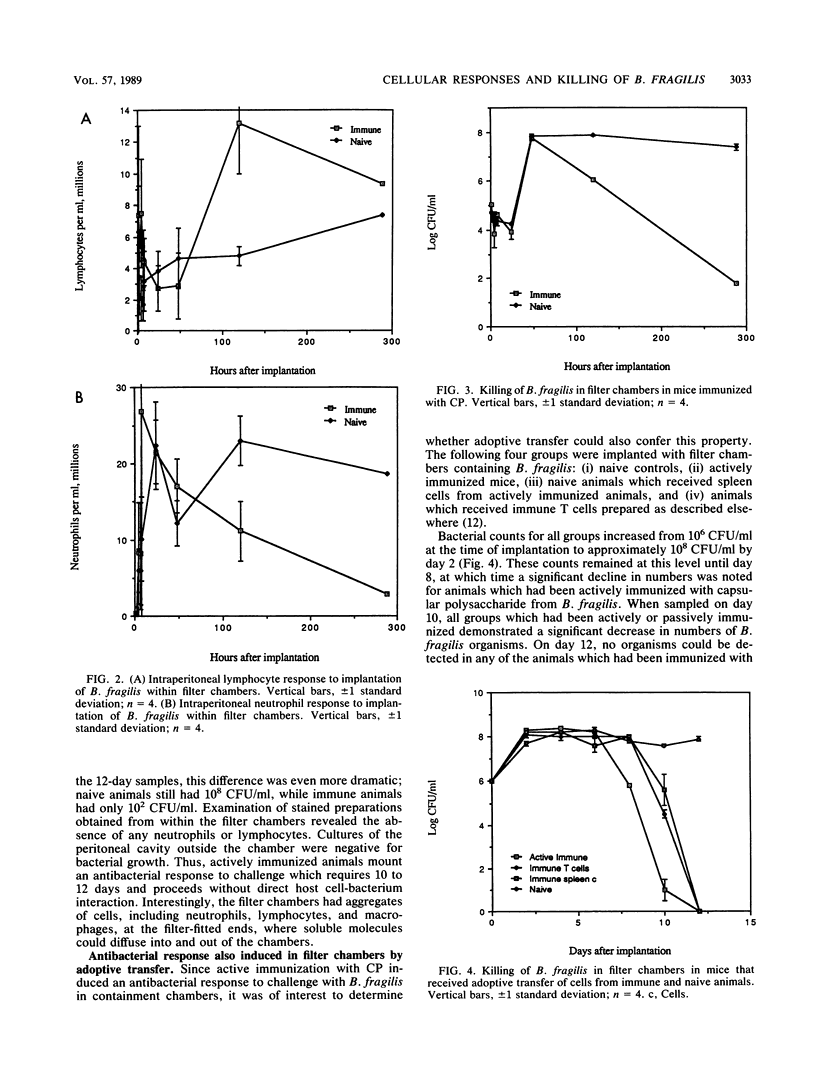
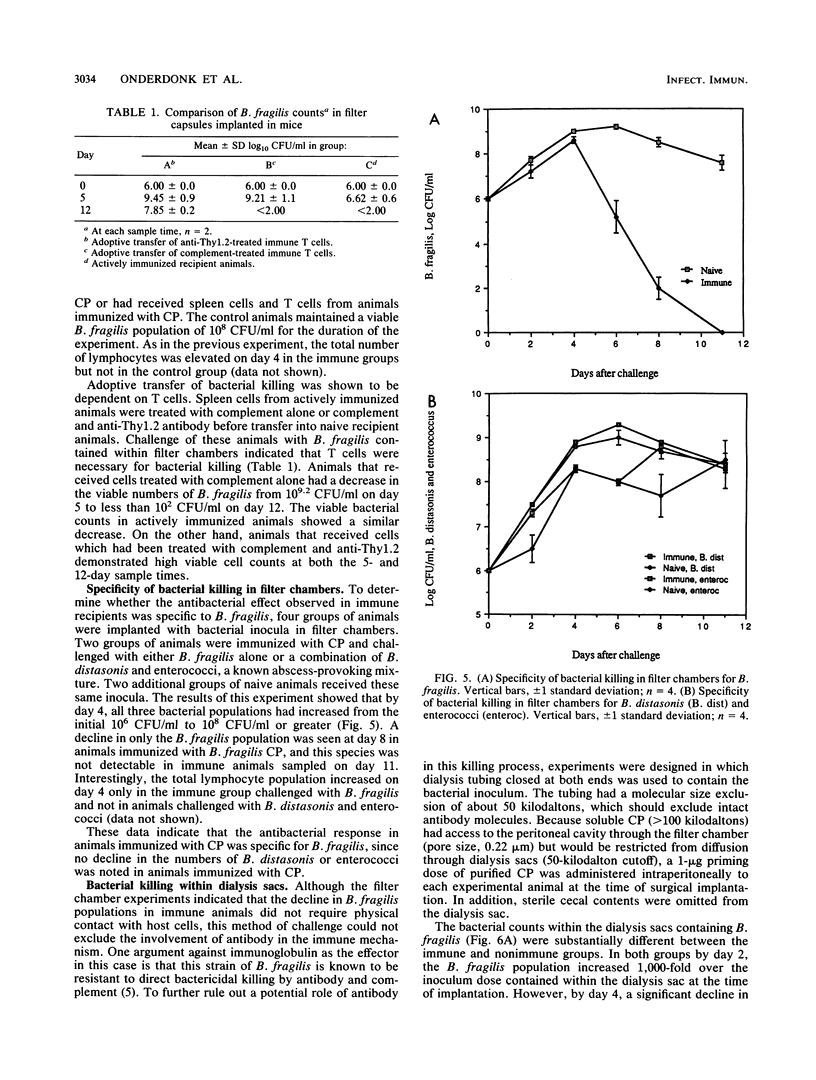
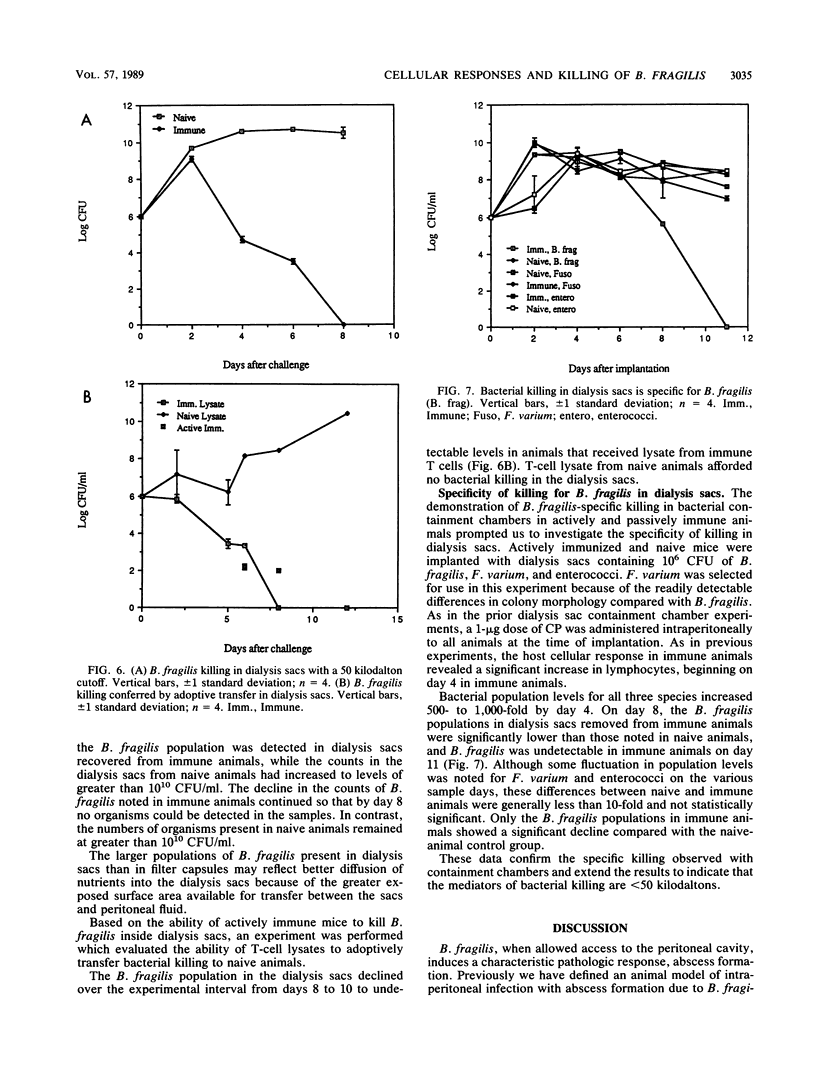
A bacterial containment chamber was used to evaluate the peritoneal cellular response to Bacteroides fragilis during intraperitoneal challenge. This containment system was also used to determine the fate of bacteria within the peritoneal cavities of animals immunized, either actively or through adoptive transfer of cells or cell lysates, with the capsular polysaccharide of B. fragilis. This system demonstrated that the dominant cell types in the peritoneal cavities within 48 h of implantation of the containment chambers containing B. fragilis were neutrophils and macrophages. However, the early cellular response in immunized animals included an increase in the lymphocyte population within 4 h of challenge which was not detected in naive animals. In immunized animals, a later dramatic increase in the lymphocyte population at approximately 4 to 6 days following implantation of the containment chambers occurred. This increase in the lymphocyte population in immunized animals coincided with a decline in the viable bacterial counts within the chambers from 10(8) to 10(9) CFU/ml to less than 10(2) CFU/ml. A similar decline was not seen in naive animals challenged in the same manner. Killing of B. fragilis within containment chambers occurred when spleen cells, T cells, or lysates of T cells from actively immunized animals were passively transferred to naive recipient animals. It was shown that the factor responsible for bacterial killing was not antibody mediated, since bacteria contained within dialysis sacs with an exclusion of 50 kilodaltons were still killed in this model. Moreover, removal of T cells from adoptively transferred cell populations before transfer abrogated the decline in viable bacterial populations. The postulated mechanisms by which this bacterial killing occurred are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coleman K. D., Wetterlow L. H. Use of implantable intraperitoneal diffusion chambers to study Bordetella pertussis pathogenesis: growth and toxin production in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):33–39. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Onderdonk A. B., Crabb J., Bartlett J. G. Protective efficacy of immunization with capsular antigen against experimental infection with Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):724–731. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Markham R. B., Zaleznik D. F., Cisneros R. L., Kasper D. L. Evidence for T cell-dependent immunity to Bacteroides fragilis in an intraabdominal abscess model. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):9–16. doi: 10.1172/JCI110445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. Wound healing. Sci Am. 1969 Jun;220(6):40–50. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0669-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. E., Onderdonk A. B., Kasper D. L., Finberg R. W. Cellular immunity to Bacteroides fragilis capsular polysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1188–1197. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thadepalli H., Gorbach S. L., Broido P. W., Norsen J., Nyhus L. Abdominal trauma, anaerobes, and antibiotics. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1973 Aug;137(2):270–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thadepalli H., Gorbach S. L., Keith L. Anaerobic infections of the female genital tract: bacteriologic and therapeutic aspects. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Dec 15;117(8):1034–1040. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(73)90750-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. Leukotactic factors in health and disease. Am J Pathol. 1971 Sep;64(3):521–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaleznik D. F., Finberg R. W., Shapiro M. E., Onderdonk A. B., Kasper D. L. A soluble suppressor T cell factor protects against experimental intraabdominal abscesses. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):1023–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI111763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


