Abstract
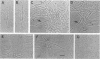
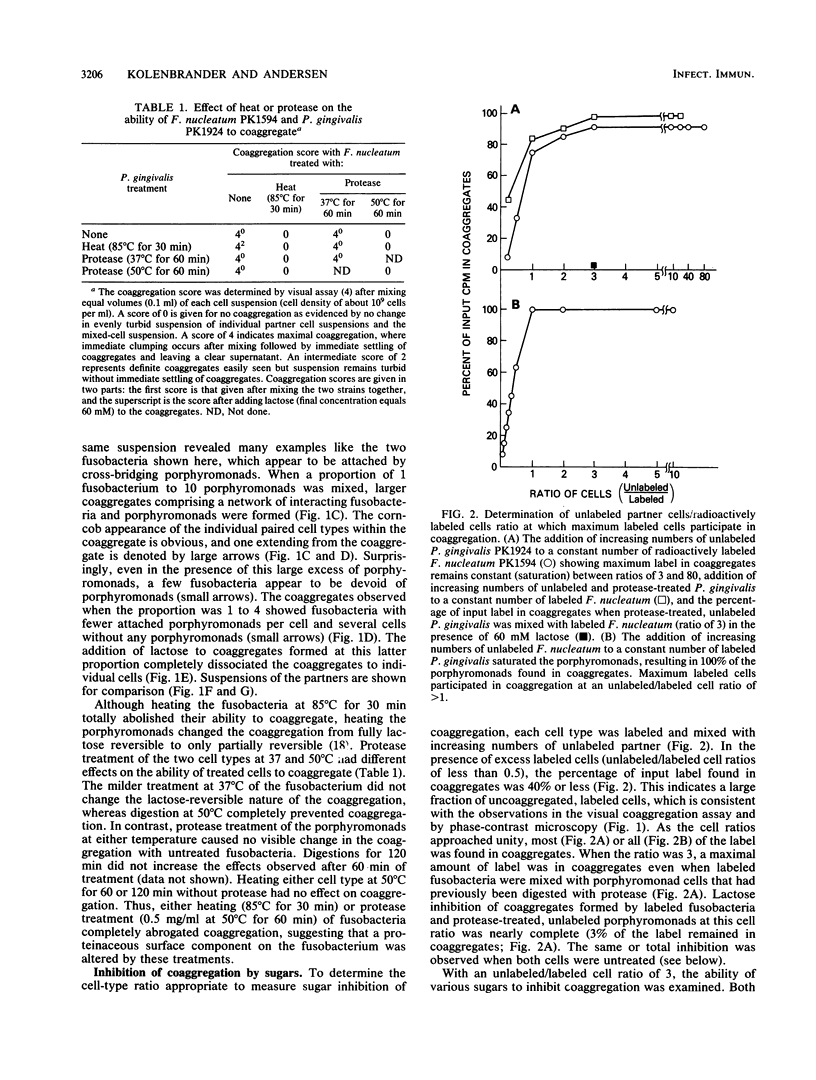
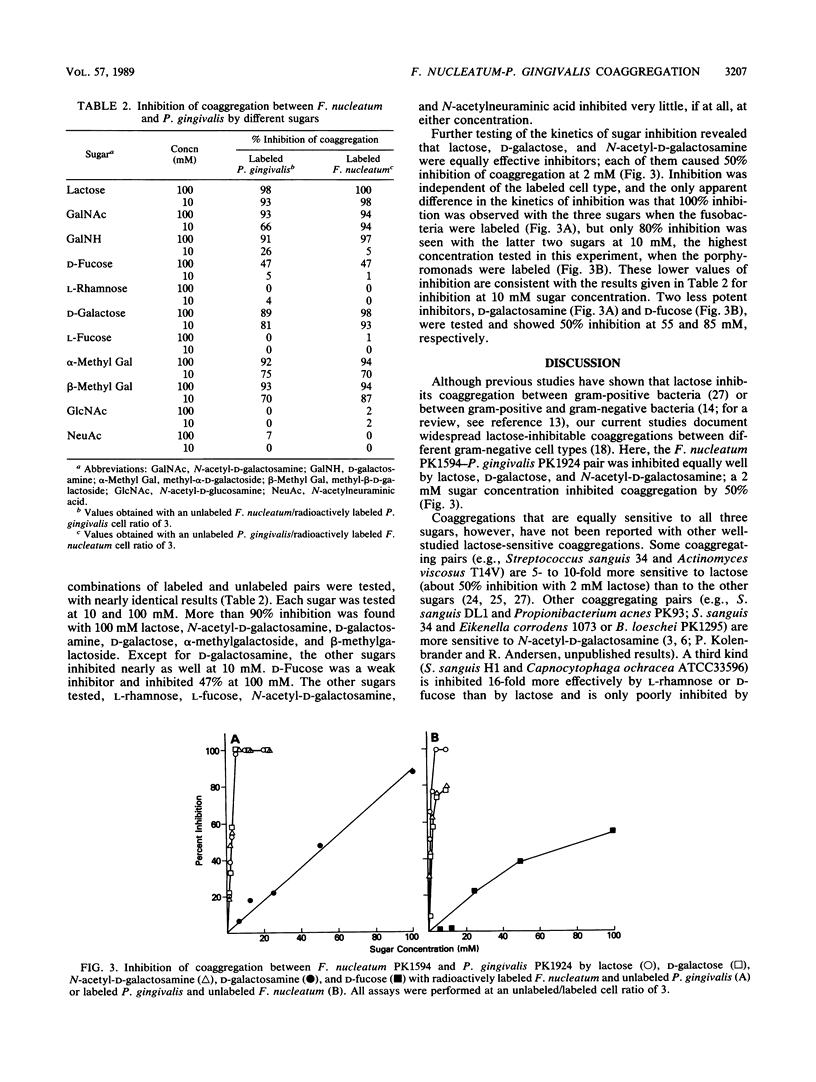
The coaggregation of Fusobacterium nucleatum PK1594 and Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis PK1924 was inhibited equally well by lactose, N-acetyl-D-galactosamine, and D-galactose, which caused 50% inhibition of coaggregation at 2 mM sugar concentration. Other sugars such as D-galactosamine, D-fucose (6-deoxy-D-galactose), and alpha-methyl- and beta-methyl-D-galactosides also inhibited coaggregation. Sugar specificity was apparent, since neither L-fucose, L-rhamnose, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, nor N-acetylneuraminic acid was an inhibitor. Protease treatment of the fusobacterium completely abolished coaggregation, whereas it had no effect on the coaggregating activity of the porphyromonad. Although numerous lactose-inhibitable coaggregating pairs are known to occur among gram-positive bacteria, this report and the accompanying survey (P. E. Kolenbrander, R. N. Andersen, and L. V. H. Moore, Infect. Immun. 57:3194-3203, 1989) are the first studies demonstrating the extensive nature of this type of interaction between gram-negative human oral bacteria. The significance of galactoside-inhibitable coaggregations between these two potential periodontal pathogens is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassels F. J., London J. Isolation of a coaggregation-inhibiting cell wall polysaccharide from Streptococcus sanguis H1. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4019–4025. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4019-4025.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesk R. A., London J. Attachment of oral Cytophaga species to hydroxyapatite-containing surfaces. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):768–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.768-777.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardi J. E., McCray G. F., Kolenbrander P. E., Lau A. Cell-to-cell interaction of Streptococcus sanguis and Propionibacterium acnes on saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1441–1446. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1441-1446.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Kolenbrander P. E., McIntire F. C. Specificity of coaggregation reactions between human oral streptococci and strains of Actinomyces viscosus or Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):742–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.742-752.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzink J. L., Socransky S. S., Haffajee A. D. The predominant cultivable microbiota of active and inactive lesions of destructive periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol. 1988 May;15(5):316–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1988.tb01590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebisu S., Nakae H., Okada H. Coaggregation of Eikenella corrodens with oral bacteria mediated by bacterial lectin-like substance. Adv Dent Res. 1988 Nov;2(2):323–327. doi: 10.1177/08959374880020022101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkler W. A., Jr, Burger B. W. Microbial surface interactions: reduction of the haemagglutination activity of the oral bacterium Fusobacterium nucleatum by absorption with Streptococcus and Bacteroides. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(12):1015–1025. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Selective bacterial adherence to oral epithelial surfaces and its role as an ecological determinant. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.567-573.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. J. A special relationship between spherical and filamentous microorganisms in mature human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Mar;17(3):613–616. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A. Animal glycolipids as attachment sites for microbes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1986 Dec 15;42(1-3):153–172. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(86)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J., DiRienzo J. M. Isolation of a corncob (coaggregation) receptor polypeptide from Fusobacterium nucleatum. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):331–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.331-337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N. Cell to cell interactions of Capnocytophaga and Bacteroides species with other oral bacteria and their potential role in development of plaque. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Nov;19(6):564–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb01315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N., Holdeman L. V. Coaggregation of oral Bacteroides species with other bacteria: central role in coaggregation bridges and competitions. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):741–746. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.741-746.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N. Intergeneric rosettes: sequestered surface recognition among human periodontal bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):1046–1050. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.1046-1050.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N., Moore L. V. Coaggregation of Fusobacterium nucleatum, Selenomonas flueggei, Selenomonas infelix, Selenomonas noxia, and Selenomonas sputigena with strains from 11 genera of oral bacteria. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3194–3203. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3194-3203.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N. Multigeneric aggregations among oral bacteria: a network of independent cell-to-cell interactions. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):851–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.851-859.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Intergeneric coaggregation among human oral bacteria and ecology of dental plaque. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:627–656. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Surface recognition among oral bacteria: multigeneric coaggregations and their mediators. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;17(2):137–159. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOE H., THEILADE E., JENSEN S. B. EXPERIMENTAL GINGIVITIS IN MAN. J Periodontol. 1965 May-Jun;36:177–187. doi: 10.1902/jop.1965.36.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancy P., Jr, Appelbaum B., Holt S. C., Rosan B. Quantitative in vitro assay for "corncob" formation. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):663–670. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.663-670.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancy P., Jr, Dirienzo J. M., Appelbaum B., Rosan B., Holt S. C. Corncob formation between Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):303–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.303-309.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listgarten M. A., Mayo H., Amsterdam M. Ultrastructure of the attachment device between coccal and filamentous microorganisms in "corn cob" formations of dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 May;18(5):651–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Bush C. A., Wu S. S., Li S. C., Li Y. T., McNeil M., Tjoa S. S., Fennessey P. V. Structure of a new hexasaccharide from the coaggregation polysaccharide of Streptococcus sanguis 34. Carbohydr Res. 1987 Aug 15;166(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(87)80050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Crosby L. K., Barlow J. J., Matta K. L. Structural preferences of beta-galactoside-reactive lectins on Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Actinomyces naeslundii WVU45. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):848–850. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.848-850.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Crosby L. K., Vatter A. E., Cisar J. O., McNeil M. R., Bush C. A., Tjoa S. S., Fennessey P. V. A polysaccharide from Streptococcus sanguis 34 that inhibits coaggregation of S. sanguis 34 with Actinomyces viscosus T14V. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2229–2235. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2229-2235.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Crosby L. K., Vatter A. E. Inhibitors of coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Streptococcus sanguis 34: beta-galactosides, related sugars, and anionic amphipathic compounds. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):371–378. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.371-378.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Vatter A. E., Baros J., Arnold J. Mechanism of coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Streptococcus sanguis 34. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):978–988. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.978-988.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongiello J. R., Falkler W. A., Jr Sugar inhibition of oral Fusobacterium nucleatum haemagglutination and cell binding. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(7):539–545. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P., Smibert R. M., Burmeister J. A., Palcanis K. G., Ranney R. R. Comparative bacteriology of juvenile periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):507–519. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.507-519.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Good I. J., Burmeister J. A., Palcanis K. G., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of experimental gingivitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):651–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.651-667.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Hash D. E., Burmeister J. A., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of severe periodontitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1137–1148. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1137-1148.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Kern D. G., Winkler J. R. Identification of a galactose-binding lectin on Fusobacterium nucleatum FN-2. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1314–1319. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1314-1319.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilade E., Wright W. H., Jensen S. B., Löe H. Experimental gingivitis in man. II. A longitudinal clinical and bacteriological investigation. J Periodontal Res. 1966;1:1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1966.tb01842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. E., Offenbacher S., Place D., Dowell V. R., Jones J. Refractory periodontitis: mixed infection with Bacteroides gingivalis and other unusual Bacteroides species. A case report. J Periodontol. 1988 Mar;59(3):184–189. doi: 10.1902/jop.1988.59.3.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. I., London J., Kolenbrander P. E., Kagermeier A. S., Andersen R. N. Characterization of lectinlike surface components on Capnocytophaga ochracea ATCC 33596 that mediate coaggregation with gram-positive oral bacteria. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1198–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1198-1202.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Reynolds H. S., Slots J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides spp. in the human oral cavity. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):198–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.198-203.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Steeg P. F., Van der Hoeven J. S., de Jong M. H., van Munster P. J., Jansen M. J. Enrichment of subgingival microflora on human serum leading to accumulation of Bacteroides species, Peptostreptococci and Fusobacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1987;53(4):261–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00393933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]