Abstract
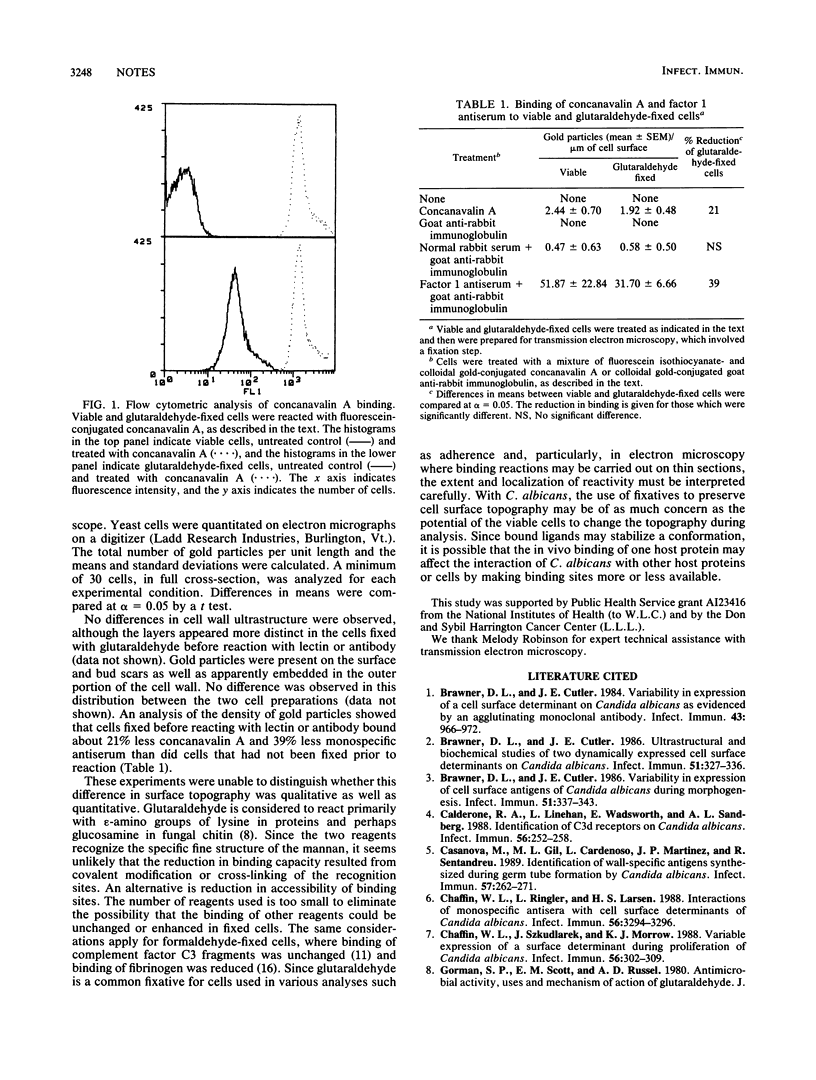
The ability of viable and glutaraldehyde-fixed, stationary-phase yeast cells of Candida albicans to bind concanavalin A and monospecific antiserum for antigenic factor 1 was examined. Both fluorescence flow cytometric analysis and transmission electron microscopy indicated that glutaraldehyde-fixed cells bound less of the two reagents than did unfixed viable cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Ultrastructural and biochemical studies of two dynamically expressed cell surface determinants on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):327–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.327-336.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Variability in expression of a cell surface determinant on Candida albicans as evidenced by an agglutinating monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):966–972. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.966-972.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Variability in expression of cell surface antigens of Candida albicans during morphogenesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):337–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.337-343.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Sandberg A. L. Identification of C3d receptors on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):252–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.252-258.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova M., Gil M. L., Cardeñoso L., Martinez J. P., Sentandreu R. Identification of wall-specific antigens synthesized during germ tube formation by Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):262–271. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.262-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Ringler L., Larsen H. S. Interactions of monospecific antisera with cell surface determinants of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3294–3296. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3294-3296.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Skudlarek J., Morrow K. J. Variable expression of a surface determinant during proliferation of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):302–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.302-309.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman S. P., Scott E. M., Russell A. D. Antimicrobial activity, uses and mechanism of action of glutaraldehyde. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;48(2):161–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb01217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen B. W., Hazen K. C. Dynamic expression of cell surface hydrophobicity during initial yeast cell growth and before germ tube formation of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2521–2525. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2521-2525.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood V., Poulain D., Fortier B., Evans G., Vernes A. A monoclonal antibody to a cell wall component of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):222–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.222-227.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Brown R. R., Pfrommer G. S. Activation and binding of C3 by Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1890–1894. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1890-1894.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell E. M., Trump B. F. Histologic fixatives suitable for diagnostic light and electron microscopy. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Aug;100(8):405–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page S., Odds F. C. Binding of plasma proteins to Candida species in vitro. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Oct;134(10):2693–2702. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-10-2693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponton J., Jones J. M. Identification of two germ-tube-specific cell wall antigens of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):864–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.864-868.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G. Experience with a three-hour electron microscopy biopsy service. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;27(6):505–510. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.6.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T. A modified method for lead staining of thin sections. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1968;17(2):158–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Kenny G. E. Enzymatic release of germ tube-specific antigens from cell walls of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):609–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.609-614.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Fukazawa Y., Kawakita S. Significance of serological studies on yeasts. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1965 Jun 15;26(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02098585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


