Abstract
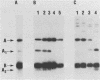
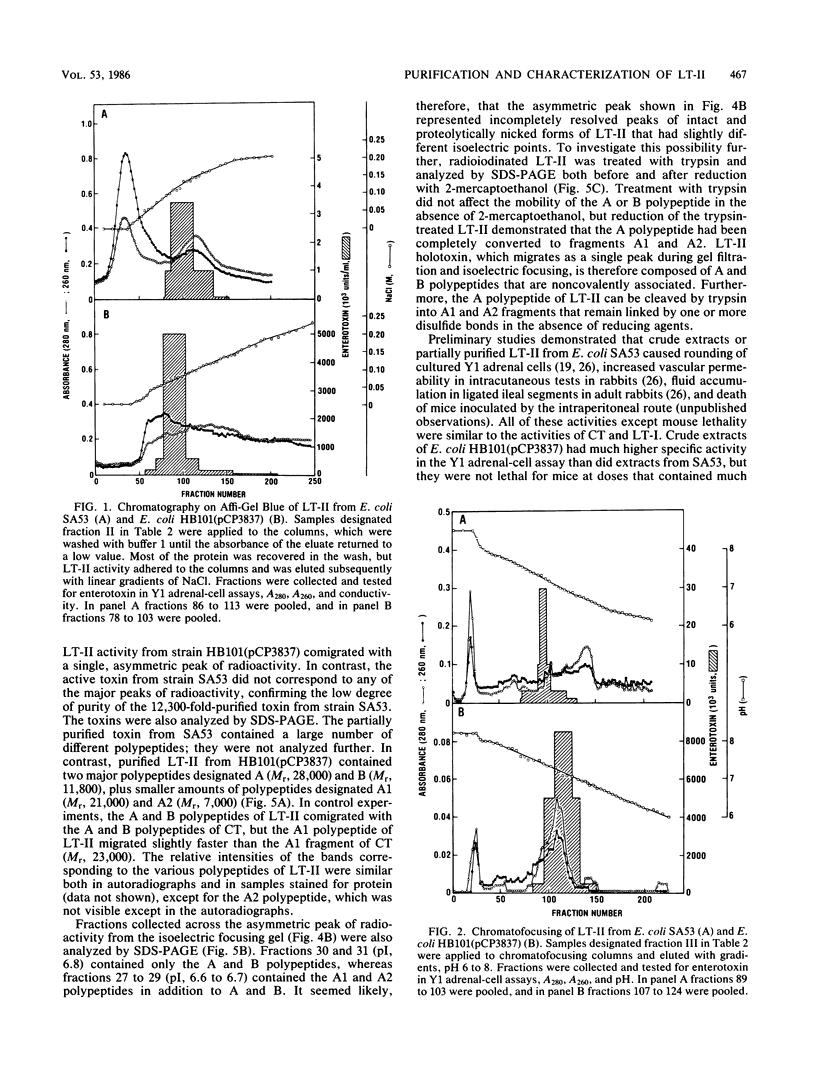
Type II heat-labile enterotoxin (LT-II) of Escherichia coli has several biologic activities similar to cholera toxin (CT) and E. coli type I heat-labile enterotoxin (LT-I), but it is not neutralized by antiserum prepared against CT or LT-I. LT-II was purified from E. coli SA53 and from E. coli HB101(pCP3837), a strain that contains the cloned LT-II genes in a hybrid plasmid and produces up to 600 times more LT-II than does SA53. Purification involved sonic disruption of bacterial cells, ammonium sulfate fractionation, chromatography on Affi-Gel Blue, chromatofocusing, and gel filtration on Sephadex G-100. The LT-II purified to apparent homogeneity from HB101(pCP3837) had an isoelectric point of 6.8, induced increased vascular permeability in rabbit intracutaneous tests, caused rounding of cultured Y1 adrenal cells accompanied by increased intracellular cyclic AMP, and was 25 to 50 times more potent than CT or LT-I in the Y1 adrenal-cell assay. In contrast, purified LT-II did not cause secretion in ligated rabbit ileal segments at doses corresponding to CT controls that gave strongly positive reactions. LT-II was composed of two different polypeptides with MrS of 28,000 (A) and 11,800 (B); treatment of LT-II with trypsin cleaved the A polypeptide to fragments A1 (Mr, 21,000) and A2 (Mr, 7,000). The activity of LT-II was not blocked by ganglioside GM1 at concentrations that inactivated LT-I or CT. Antiserum against the LT-II from E. coli HB101(pCP3837) completely neutralized purified LT-II and the LT-II in crude extracts of SA53, but it did not neutralize purified LT-I or CT.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belisle B. W., Twiddy E. M., Holmes R. K. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to heat-labile enterotoxin encoded by a plasmid from a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1027–1032. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1027-1032.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belisle B. W., Twiddy E. M., Holmes R. K. Monoclonal antibodies with an expanded repertoire of specificities and potent neutralizing activity for Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):759–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.759-764.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramucci M. G., Twiddy E. M., Baine W. B., Holmes R. K. Isolation and characterization of hypertoxinogenic (htx) mutants of Escherichia coli KL320(pCG86). Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1034–1044. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1034-1044.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Flint D. C., Klipstein F. A. Immunological and physicochemical characterization of heat-labile enterotoxins isolated from two strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):806–809. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.806-809.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S. Conformity between heat-labile toxin genes from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):647–652. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.647-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Gill D. M., Falkow S. Cistrons encoding Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):850–858. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.850-858.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Richardson S. H., Gorbach S. L. Purification of the polymyxin-released, heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):97–102. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_1.s97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Atthasampunna P., Chulasamaya M., Charunmethee P. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera: biologic ativities of purified procholeragen A. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary S. J., Marchlewicz B. A., Finkelstein R. A. Comparison of heat-labile enterotoxins from porcine and human strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.215-220.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Clements J. D., Robertson D. C., Finkelstein R. A. Subunit number and arrangement in Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):677–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.677-682.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins catalyzed by cholera toxin: basis of the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M. The arrangement of subunits in cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1242–1248. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Neill R. J., Ruyechan W. T., Holmes R. K. Evidence that a new enterotoxin of Escherichia coli which activates adenylate cyclase in eucaryotic target cells is not plasmid mediated. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):383–390. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.383-390.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Relationships among heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):277–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Perlow R. B. Quantitative assay of diphtherial toxin and of immunologically cross-reacting proteins by reversed passive hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1392–1400. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1392-1400.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Twiddy E. M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies that react with unique and cross-reacting determinants of cholera enterotoxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):914–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.914-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Fredman P., Lindblad M., Svennerholm A. M., Svennerholm L. Rabbit intestinal glycoprotein receptor for Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin lacking affinity for cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.424-433.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Tsuji T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Immunological nonidentity of heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):337–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.337-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of environmental and nontoxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.661-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockman H., Kaper J. B. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the A2 and B subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13722–13726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Purification of cholera toxin and its subunits: new methods of preparation and the use of hypertoxinogenic mutants. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):552–558. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.552-558.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill R. J., Twiddy E. M., Holmes R. K. Synthesis of plasmid-coded heat-labile enterotoxin in wild-type and hypertoxinogenic strains of Escherichia coli and in other genera of Enterobacteriaceae. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1056–1061. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1056-1061.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. L., Twiddy E. M., Belisle B. W., Holmes R. K. Cloning of genes that encode a new heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):348–352. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.348-352.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Noble J. A. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Nucleotide sequence of the A subunit gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5716–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan M., Moss J. Mechanism of action of choleragen. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(4):473–488. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nakazawa T., Miyata T., Kaji A., Yokota T. Evolution and structure of two ADP-ribosylation enterotoxins, Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin and cholera toxin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Apr 24;169(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T., Kaji A. Molecular organization of heat-labile enterotoxin genes originating in Escherichia coli of human origin and construction of heat-labile toxoid-producing strains. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):983–987. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.983-987.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoh M., Yamamoto K., Honda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Effects of lincomycin and tetracycline on production and properties of enterotoxins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):778–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.778-782.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]